955
Deep Space (8 photos)
The best space pictures in November. Excellent.
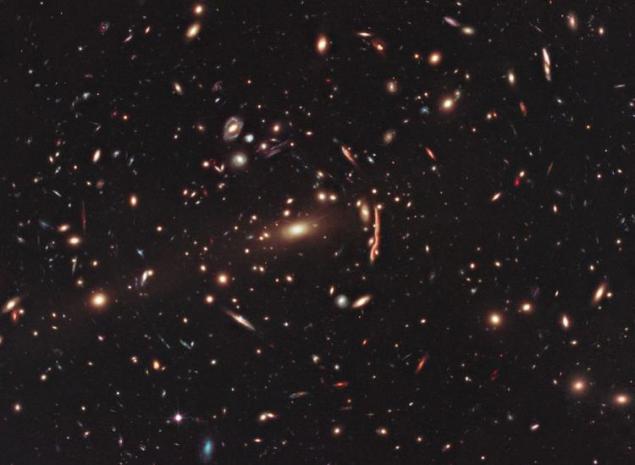
Galaxy cluster MACS J1206. MACS J1206 mass is so large that its gravity arches light coming to us from the more distant galaxies, as an ordinary magnifying glass. Such phenomena in the universe are called gravitational lensing. Huge cluster MACS J1206 is very far away, in the 4 billion light-years from Earth. In order to see a clear picture of these distant galaxies, took the penetrating power of the "Hubble».

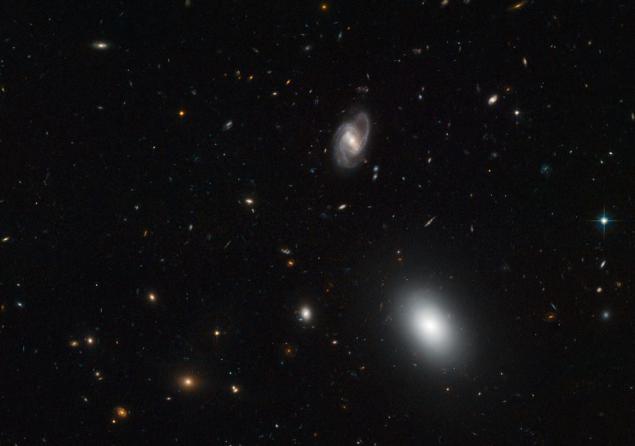
galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. Before us is a wide variety of hundreds of galaxies, both in shape and size; Some are relatively close to us, others can be seen almost on the "edge" of the universe. This is just one of the many pictures taken wide-angle camera "Hubble" to remove the patch of sky called the Extended Groth Strip. This plot covers a relatively small area of about the thickness of a finger at arm's length. But it includes more than 50,000 galaxies. Massive study of galaxies will help astronomers to trace the evolution of the universe in the last 8 billion years.

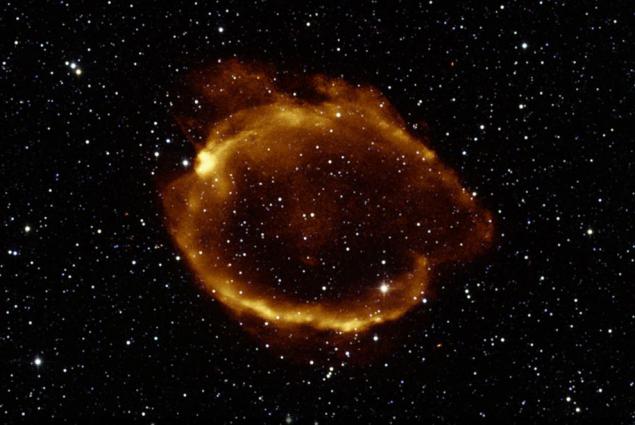
G299.2-2.9 - supernova remnant "average" age. This cloud of expanding gas is 16,000 light-years from Earth. Its progenitor - a star whose mass is at least 8 times that of the sun. At the end of the evolutionary path of the star lost stability and therefore broke out as SNe Ia. By studying distant galaxies in the outbreak of this type of supernovae, astronomers discovered the accelerated expansion of the Universe. For what, in fact, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2011.

By studying the light coming to us from the most distant galaxies, astronomers of the European Southern Observatory examine the conditions that have been in space for nearly 14 billion years ago. Then the universe was still so young that it is filled with a primary hydrogen fog that absorbs ultraviolet light. In this image, the artist presented at the end of the first galaxies recombination era, when it took less than a billion years after the Big Bang.
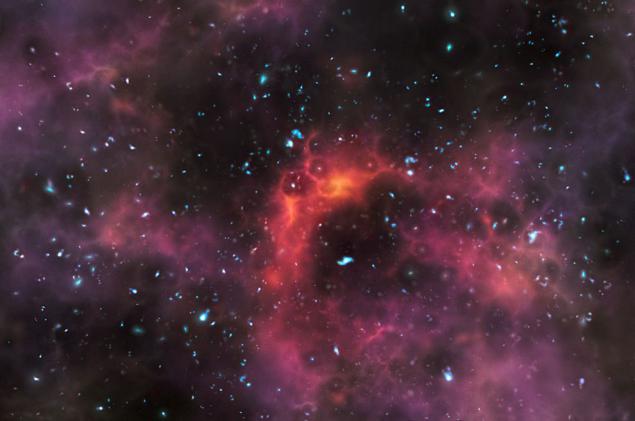

Nebula "Pacman» (NGC 281) is located in the constellation Cassiopeia. In the photos in the optical nebula really resembles devouring loaf, hero of computer games 80s. But this image was acquired in the thermal rays Space Infrared Telescope WISE. As we can see, with the good "Pacman" suddenly erupted predatory teeth, which are actually giant columns of gas and dust. Perhaps right at this moment, in these new stars are born
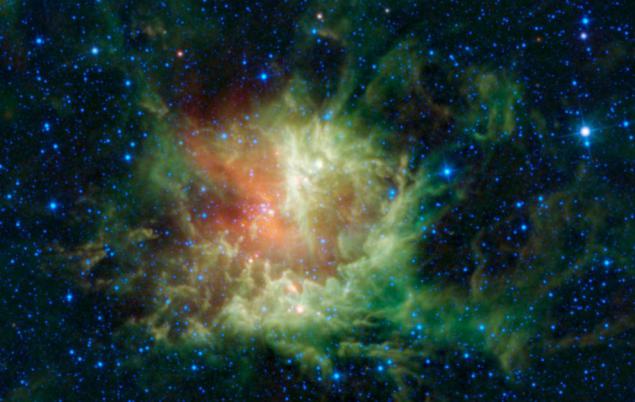

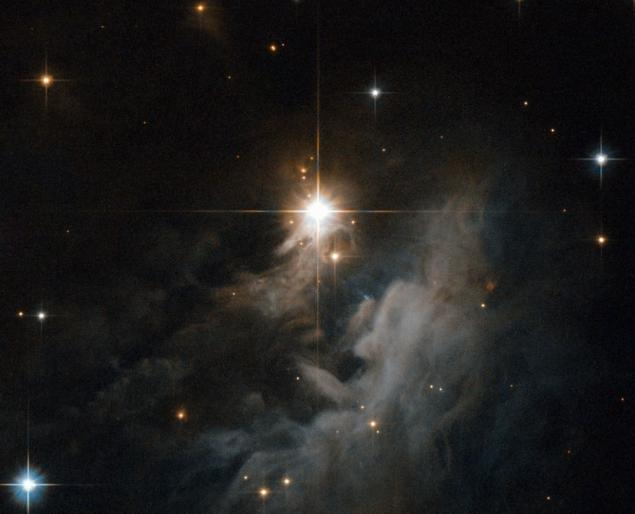
Reflection nebula around the star IRAS 10082-5647. Soft pearly glow of this cloud of gas and dust appears only in photos with great exposure. Interestingly, the illuminating star belongs to the rare class of young stars Herbig Ae / Be. Star IRAS 10082-5647 has not "sat" on the main sequence. This means that the "whole life ahead of her," because on the main sequence stars spend up to 99% of the time of its existence (except for "life after death" - white dwarfs, neutron stars and other exotic objects)

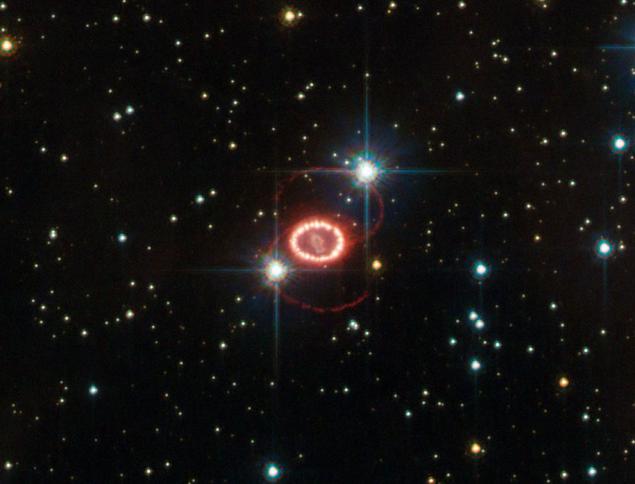
Supernova remnant SN 1987A. The closest and brightest supernova that erupted since the invention of the telescope, SN 1987A was visible to the naked eye as a star 3 star. values in the satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, the Large Magellanic Cloud. Since the outbreak has been almost a quarter-century. All this time the fluttering remains of stars are the subject of intense research. In this picture, produced by space telescope "Hubble", we see two faint rings surrounding residue. Although their origin is still not clear at the present time, astronomers are inclined to think that the rings formed by the merger of two gravitationally bound stars, one of which gave rise to the flash SN 1987A.

The project Via Lactea VISTA telescope of the European Southern Observatory discovered in our galaxy, two new globular clusters. One of them (VVV CL001) can be seen in this photo just above and left of center. Right - another globular cluster, UKS 1.

Galaxy cluster MACS J1206. MACS J1206 mass is so large that its gravity arches light coming to us from the more distant galaxies, as an ordinary magnifying glass. Such phenomena in the universe are called gravitational lensing. Huge cluster MACS J1206 is very far away, in the 4 billion light-years from Earth. In order to see a clear picture of these distant galaxies, took the penetrating power of the "Hubble».

galaxy in the constellation Ursa Major. Before us is a wide variety of hundreds of galaxies, both in shape and size; Some are relatively close to us, others can be seen almost on the "edge" of the universe. This is just one of the many pictures taken wide-angle camera "Hubble" to remove the patch of sky called the Extended Groth Strip. This plot covers a relatively small area of about the thickness of a finger at arm's length. But it includes more than 50,000 galaxies. Massive study of galaxies will help astronomers to trace the evolution of the universe in the last 8 billion years.

G299.2-2.9 - supernova remnant "average" age. This cloud of expanding gas is 16,000 light-years from Earth. Its progenitor - a star whose mass is at least 8 times that of the sun. At the end of the evolutionary path of the star lost stability and therefore broke out as SNe Ia. By studying distant galaxies in the outbreak of this type of supernovae, astronomers discovered the accelerated expansion of the Universe. For what, in fact, received the Nobel Prize in Physics in 2011.

By studying the light coming to us from the most distant galaxies, astronomers of the European Southern Observatory examine the conditions that have been in space for nearly 14 billion years ago. Then the universe was still so young that it is filled with a primary hydrogen fog that absorbs ultraviolet light. In this image, the artist presented at the end of the first galaxies recombination era, when it took less than a billion years after the Big Bang.

Nebula "Pacman» (NGC 281) is located in the constellation Cassiopeia. In the photos in the optical nebula really resembles devouring loaf, hero of computer games 80s. But this image was acquired in the thermal rays Space Infrared Telescope WISE. As we can see, with the good "Pacman" suddenly erupted predatory teeth, which are actually giant columns of gas and dust. Perhaps right at this moment, in these new stars are born

Reflection nebula around the star IRAS 10082-5647. Soft pearly glow of this cloud of gas and dust appears only in photos with great exposure. Interestingly, the illuminating star belongs to the rare class of young stars Herbig Ae / Be. Star IRAS 10082-5647 has not "sat" on the main sequence. This means that the "whole life ahead of her," because on the main sequence stars spend up to 99% of the time of its existence (except for "life after death" - white dwarfs, neutron stars and other exotic objects)

Supernova remnant SN 1987A. The closest and brightest supernova that erupted since the invention of the telescope, SN 1987A was visible to the naked eye as a star 3 star. values in the satellite galaxy of the Milky Way, the Large Magellanic Cloud. Since the outbreak has been almost a quarter-century. All this time the fluttering remains of stars are the subject of intense research. In this picture, produced by space telescope "Hubble", we see two faint rings surrounding residue. Although their origin is still not clear at the present time, astronomers are inclined to think that the rings formed by the merger of two gravitationally bound stars, one of which gave rise to the flash SN 1987A.

The project Via Lactea VISTA telescope of the European Southern Observatory discovered in our galaxy, two new globular clusters. One of them (VVV CL001) can be seen in this photo just above and left of center. Right - another globular cluster, UKS 1.