6793
Atavism and rudiments
This article will talk about the phenomenon of the human body, about the unnecessary organs are not functioning properly in the general human anatomy.

2.Appendiks
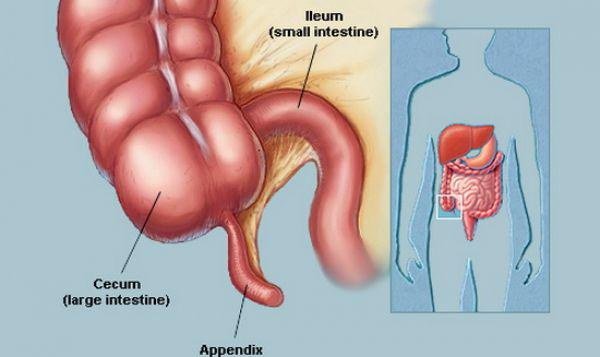
The appendix is a blind appendage intestine, which averages 10 cm in length. It is located near the connection of the small intestine and colon. Evolutionists claim that the appendix is part of a larger digestive system that existed in the early stages of mankind. This digestive system is needed when a person's diet consisted mainly of plant foods, and there was no bowel functions, which he has now. However, studies now indicate that the appendix has helper functions that may be useful in the large intestine.
4. Sinus
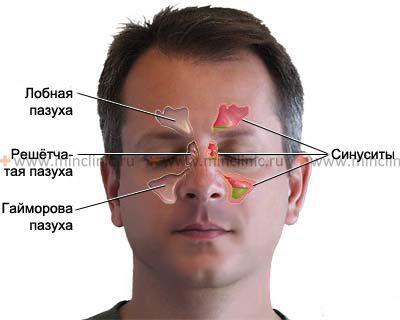
Humans have four pairs of cavities which are located in the head and facial bones. These air-filled space are lined with moist, thin layer of tissue known as mucosa. The mucosa secrete mucus that traps dust and germs that are found in the inspired air contact. Doctors do not know a lot about the sinuses, but some researchers believe that sinus intended to head was not too heavy. Sinuses also provide us the height and the tone of our voice.
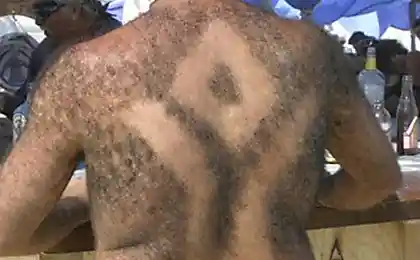
3. Body hair
Three million years ago, the hair on the human body was so much more. The temperature at the earth's surface at the time was much colder than today, so that our body was covered with hair for better insulation from cold climates. But there was Homo erectus, and formed together with the ability to sweat meant that we could lose our furry sheath. Today, the presence of hair on the body is so annoying that people who have this "deficiency", seek help from a dermatologist. Due to popular today method of hair removal wax, excess body hair can be easily removed. Thus, the question is: "Do we really need body hair?».
Body hair
Three million years ago, the hair on the human body was so much more. The temperature at the earth's surface at the time was much colder than today, so that our body was covered with hair for better insulation from cold climates. But there was Homo erectus, and formed together with the ability to sweat meant that we could lose our furry sheath. Today, the presence of hair on the body is so annoying that people who have this "deficiency", seek help from a dermatologist. Due to popular today method of hair removal wax, excess body hair can be easily removed. Thus, the question is: "Do we really need body hair?».
5. Adenoids
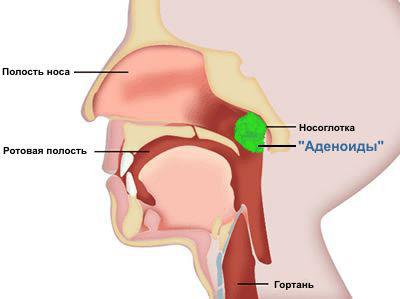
Adenoids are masses of lymphoid tissue formed to help protect children from diseases. They are located in the rearmost part of the nose and the upper jaw. Adenoids most people do not even used after the third year of life. In fact, the size of the adenoids is usually reduced by about the fifth year of life, and in adolescence they virtually disappear. Adenoids provide an important function, such as a barrier to infection in infants and young children. But they become less important as the child gets older and the body develops other ways to fight pathogens. In addition, the adenoids are prone to swelling and infection.
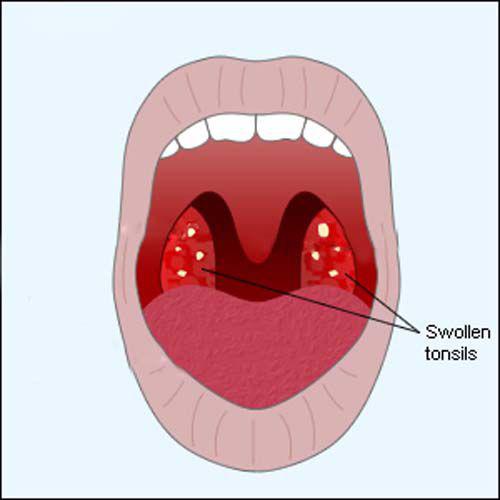
6. glands
The tonsils are accumulations of lymphoid tissue on each side of the throat. They act as part of the immune system to protect against infection. But they are really very important. Studies lead us to believe that the glands are involved in the fight against certain types of infections, such as worms or other parasites. It is clear that in many cases the glands become "dysfunctional" and provide more problems than advantages, since they are prone to infection and edema.
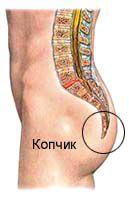
7. The coccyx
Coccyx or hvostets is the last segment of the human spine. It consists of three to five separate or fused vertebrae, held in place by ligaments and joints. In humans and other primates tailless Nakalipithecus (Miocene hominoid), coccyx - this is all that remains of a rudimentary tail, but he is not entirely useless. The coccyx is part of the carrier support structure, which acts as a support for a seated person. In addition, the coccyx serves as a place for attachment of certain muscles of the pelvic floor.

8. Rectifying follicular muscles
Rectifying follicular muscles - are tiny microscopic muscle fibers that connect the hair follicles in the dermis. With stimulation of these tissues contract and cause the effect of "hair-raising". This feature has been helpful in the days when reared by a hair we had to look bigger and scarier, causing goosebumps. Rectifying follicular muscles exist in most mammals, including humans, but some animals these muscles play an important role by acting as insulation from the external environment, keeping the body warm. Other animals, such as porcupines, use them as a defense mechanism when there is any danger.
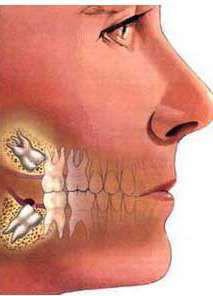
9. Wisdom teeth
Third molars, also known as wisdom teeth, are the last teeth that appear in your mouth. Typically, this occurs between the ages of 17 to 25 years. Back in the days when people ate coarse food, but do not bother to care for your teeth, the result was excessive wear on his teeth. Therefore, when the "wisdom teeth" grew, they were welcome and necessary. At the present time, when the modern diet has become much softer, and the popularity of fluorine and orthodontic procedures have rendered "bad" service wisdom teeth, their need for us to become questionable. That's why we feel terrible pain when they start to grow.

10. semilunar fold
Yes, you have a third eyelid, and it is called the semilunar fold. This is a small fold of bulbar conjunctiva is in the inner corner of the eye. Subsidiary Body eyes semilunar fold left over from what is known as a "nictitating membrane." For most mammals is vestigial organ that is still present in chickens, lizards and sharks. But people semilunar fold plays an important role: it produces a special substance (mucus), which collects foreign bodies such as dirt and dust entering the eye and cause damage to the cornea. These foreign bodies are then moved into the tear duct, and in the morning ready for removal from the eye.
--img11--
Source:

2.Appendiks
The appendix is a blind appendage intestine, which averages 10 cm in length. It is located near the connection of the small intestine and colon. Evolutionists claim that the appendix is part of a larger digestive system that existed in the early stages of mankind. This digestive system is needed when a person's diet consisted mainly of plant foods, and there was no bowel functions, which he has now. However, studies now indicate that the appendix has helper functions that may be useful in the large intestine.

4. Sinus
Humans have four pairs of cavities which are located in the head and facial bones. These air-filled space are lined with moist, thin layer of tissue known as mucosa. The mucosa secrete mucus that traps dust and germs that are found in the inspired air contact. Doctors do not know a lot about the sinuses, but some researchers believe that sinus intended to head was not too heavy. Sinuses also provide us the height and the tone of our voice.

3. Body hair
Three million years ago, the hair on the human body was so much more. The temperature at the earth's surface at the time was much colder than today, so that our body was covered with hair for better insulation from cold climates. But there was Homo erectus, and formed together with the ability to sweat meant that we could lose our furry sheath. Today, the presence of hair on the body is so annoying that people who have this "deficiency", seek help from a dermatologist. Due to popular today method of hair removal wax, excess body hair can be easily removed. Thus, the question is: "Do we really need body hair?».

Body hair
Three million years ago, the hair on the human body was so much more. The temperature at the earth's surface at the time was much colder than today, so that our body was covered with hair for better insulation from cold climates. But there was Homo erectus, and formed together with the ability to sweat meant that we could lose our furry sheath. Today, the presence of hair on the body is so annoying that people who have this "deficiency", seek help from a dermatologist. Due to popular today method of hair removal wax, excess body hair can be easily removed. Thus, the question is: "Do we really need body hair?».

5. Adenoids
Adenoids are masses of lymphoid tissue formed to help protect children from diseases. They are located in the rearmost part of the nose and the upper jaw. Adenoids most people do not even used after the third year of life. In fact, the size of the adenoids is usually reduced by about the fifth year of life, and in adolescence they virtually disappear. Adenoids provide an important function, such as a barrier to infection in infants and young children. But they become less important as the child gets older and the body develops other ways to fight pathogens. In addition, the adenoids are prone to swelling and infection.

6. glands
The tonsils are accumulations of lymphoid tissue on each side of the throat. They act as part of the immune system to protect against infection. But they are really very important. Studies lead us to believe that the glands are involved in the fight against certain types of infections, such as worms or other parasites. It is clear that in many cases the glands become "dysfunctional" and provide more problems than advantages, since they are prone to infection and edema.

7. The coccyx
Coccyx or hvostets is the last segment of the human spine. It consists of three to five separate or fused vertebrae, held in place by ligaments and joints. In humans and other primates tailless Nakalipithecus (Miocene hominoid), coccyx - this is all that remains of a rudimentary tail, but he is not entirely useless. The coccyx is part of the carrier support structure, which acts as a support for a seated person. In addition, the coccyx serves as a place for attachment of certain muscles of the pelvic floor.

8. Rectifying follicular muscles
Rectifying follicular muscles - are tiny microscopic muscle fibers that connect the hair follicles in the dermis. With stimulation of these tissues contract and cause the effect of "hair-raising". This feature has been helpful in the days when reared by a hair we had to look bigger and scarier, causing goosebumps. Rectifying follicular muscles exist in most mammals, including humans, but some animals these muscles play an important role by acting as insulation from the external environment, keeping the body warm. Other animals, such as porcupines, use them as a defense mechanism when there is any danger.

9. Wisdom teeth
Third molars, also known as wisdom teeth, are the last teeth that appear in your mouth. Typically, this occurs between the ages of 17 to 25 years. Back in the days when people ate coarse food, but do not bother to care for your teeth, the result was excessive wear on his teeth. Therefore, when the "wisdom teeth" grew, they were welcome and necessary. At the present time, when the modern diet has become much softer, and the popularity of fluorine and orthodontic procedures have rendered "bad" service wisdom teeth, their need for us to become questionable. That's why we feel terrible pain when they start to grow.

10. semilunar fold
Yes, you have a third eyelid, and it is called the semilunar fold. This is a small fold of bulbar conjunctiva is in the inner corner of the eye. Subsidiary Body eyes semilunar fold left over from what is known as a "nictitating membrane." For most mammals is vestigial organ that is still present in chickens, lizards and sharks. But people semilunar fold plays an important role: it produces a special substance (mucus), which collects foreign bodies such as dirt and dust entering the eye and cause damage to the cornea. These foreign bodies are then moved into the tear duct, and in the morning ready for removal from the eye.
--img11--
Source: