493
Scientists were able to create metallic hydrogen
Researchers from Harvard University (USA) for the first time were able to obtain in the laboratory of metallic hydrogen at low temperatures. To do this they had to create a pressure higher than the center of the Earth. Although metallic hydrogen was predicted almost a century ago, exceptional difficulties in the way of obtaining this material for a long time did receive it in solid form unattainable dream.
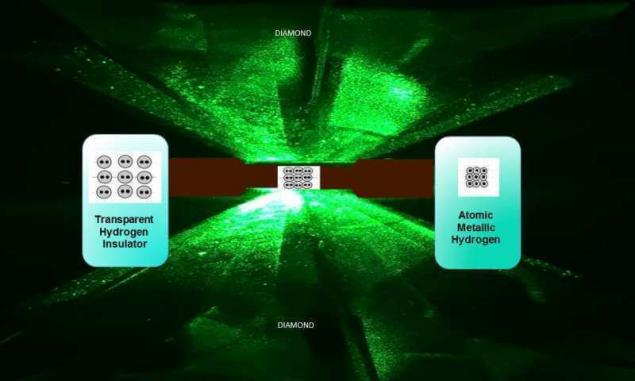
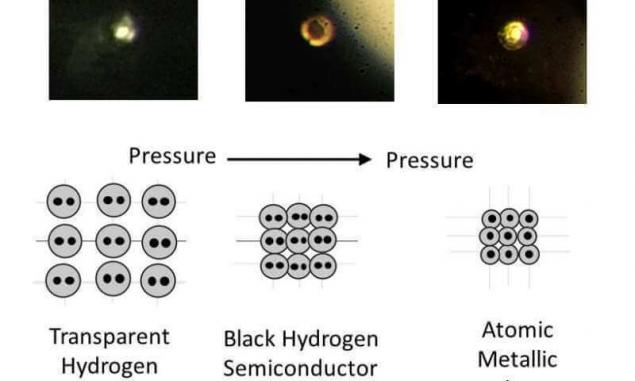
Theorists in the first half of the XX century showed that ordinary hydrogen, existing in the form of diatomic molecules, when the pressure rise will gradually lose the molecular structure. Its molecules simply fall apart, creating a much more densely Packed atomic hydrogen in the solid phase. This material is widely distributed in the bowels of Jupiter, has a number of unique properties that make it extremely promising. According to calculations, it should be a good guide, perhaps even a superconductor. And, for example, by melting a metallic hydrogen to be 21 times more energy than burning the same kilogram of hydrogen in oxygen. In theory this makes it an excellent rocket fuel, on the basis of which it is possible to build single-stage rockets and space to display a large payload on the rocket is moderate in size.But to do all this, we must first obtain this hydrogen. For a long time to create the right to obtain the pressure was possible only by using diamond anvil laser heating and compression. Temperature of such anvils were often measured in thousands of degrees — even after they metallic hydrogen, the researchers using millisecond then lost it. To measure its metallic properties at a low temperature was not significantly successful.
The scientists have optimized the diamond anvil thus to obtain metallic hydrogen that is at low temperatures. The anvil consists of two synthetic diamond conical shape. To remove the defects in diamonds (to avoid cracking under the increased pressure), their polished diamond grit. In addition, they are covered with a layer of alumina. With his help, managed to block the diffusion of hydrogen at high pressures inside diamond anvil.
Diffusible hydrogen quickly creates diamonds from defects that make them fragile, and further compression of hydrogen leads to their destruction. After modification of the cell with the diamond anvil used to produce metallic hydrogen at a temperature of 5.5 Kelvin and a pressure of 495 GPA. This is almost five million times above atmospheric. 5.5 Kelvin — record low temperatures for such pressure. Spectroscopic analysis showed that the hydrogen in the new material in the atomic state, and its density corresponds to metallic hydrogen.
While hydrogen has managed to obtain in very small quantities, which significantly clarified only the presence of metal properties and high reflectivity — reflect the order of 0.91 from falling to electromagnetic radiation. However, in the future the researchers hope to obtain large enough quantities of this material. In significant quantities it should be metastable, like a diamond. This means that although to get it required a lot of pressure, once established metallic hydrogen is stable even in normal conditions at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This is due to the fact that the energy required to break the bonds in such material is so great that in normal conditions this should not happen.

A number of works predicting in metallic hydrogen superconductivity at room temperature. At present, these superconductors to still failed.
Metallic hydrogen when you receive requires a large amount of energy, and when it goes to phase gaseous (normal) hydrogen this energy is released quickly. In the case of its use in rocket engines it can give a specific impulse of 1700 seconds. Modern better types of rocket fuel are given numbers around 400 seconds. In addition, the metal hydrogen because of its metastability does not require cryogenic tanks and will not quickly leak through the wall space (this limits the use of liquid hydrogen in rockets). With such solid fuels in theory you could create a single-stage rockets with large carrying capacity at moderate cost. In NASA consider it as a factor capable to change the balance of power in the space industry. To check whether it is or not is only possible in practice — after the improvement of existing methods of his research. published
Source: phys.org/news/2017-01-metallic-hydrogen-theory-reality.html

Theorists in the first half of the XX century showed that ordinary hydrogen, existing in the form of diatomic molecules, when the pressure rise will gradually lose the molecular structure. Its molecules simply fall apart, creating a much more densely Packed atomic hydrogen in the solid phase. This material is widely distributed in the bowels of Jupiter, has a number of unique properties that make it extremely promising. According to calculations, it should be a good guide, perhaps even a superconductor. And, for example, by melting a metallic hydrogen to be 21 times more energy than burning the same kilogram of hydrogen in oxygen. In theory this makes it an excellent rocket fuel, on the basis of which it is possible to build single-stage rockets and space to display a large payload on the rocket is moderate in size.But to do all this, we must first obtain this hydrogen. For a long time to create the right to obtain the pressure was possible only by using diamond anvil laser heating and compression. Temperature of such anvils were often measured in thousands of degrees — even after they metallic hydrogen, the researchers using millisecond then lost it. To measure its metallic properties at a low temperature was not significantly successful.

The scientists have optimized the diamond anvil thus to obtain metallic hydrogen that is at low temperatures. The anvil consists of two synthetic diamond conical shape. To remove the defects in diamonds (to avoid cracking under the increased pressure), their polished diamond grit. In addition, they are covered with a layer of alumina. With his help, managed to block the diffusion of hydrogen at high pressures inside diamond anvil.
Diffusible hydrogen quickly creates diamonds from defects that make them fragile, and further compression of hydrogen leads to their destruction. After modification of the cell with the diamond anvil used to produce metallic hydrogen at a temperature of 5.5 Kelvin and a pressure of 495 GPA. This is almost five million times above atmospheric. 5.5 Kelvin — record low temperatures for such pressure. Spectroscopic analysis showed that the hydrogen in the new material in the atomic state, and its density corresponds to metallic hydrogen.
While hydrogen has managed to obtain in very small quantities, which significantly clarified only the presence of metal properties and high reflectivity — reflect the order of 0.91 from falling to electromagnetic radiation. However, in the future the researchers hope to obtain large enough quantities of this material. In significant quantities it should be metastable, like a diamond. This means that although to get it required a lot of pressure, once established metallic hydrogen is stable even in normal conditions at room temperature and atmospheric pressure. This is due to the fact that the energy required to break the bonds in such material is so great that in normal conditions this should not happen.

A number of works predicting in metallic hydrogen superconductivity at room temperature. At present, these superconductors to still failed.
Metallic hydrogen when you receive requires a large amount of energy, and when it goes to phase gaseous (normal) hydrogen this energy is released quickly. In the case of its use in rocket engines it can give a specific impulse of 1700 seconds. Modern better types of rocket fuel are given numbers around 400 seconds. In addition, the metal hydrogen because of its metastability does not require cryogenic tanks and will not quickly leak through the wall space (this limits the use of liquid hydrogen in rockets). With such solid fuels in theory you could create a single-stage rockets with large carrying capacity at moderate cost. In NASA consider it as a factor capable to change the balance of power in the space industry. To check whether it is or not is only possible in practice — after the improvement of existing methods of his research. published
Source: phys.org/news/2017-01-metallic-hydrogen-theory-reality.html
Make a well in the country: tips and advice
The use of EDLC supercapacitors in renewable energy. World practice