535
Wooden battery for renewable energy
It may seem that the main problem preventing widespread adoption of alternative renewable energy technologies cost of equipment. However, it is not so, in recent years, solar panels and wind generators are getting cheaper, and in the foreground the problem of low stability of energy supply. In a Sunny and windy day alternative energy sets records in performance, but at night and in calm, the situation is quite different.
Before the energy industry faces the challenge of reliable and cheap storage technology developed at peak performance energy to provide it to consumers in peak hours, and at a time when generating capacity sits idle.
Chemical batteries are suitable for this purpose better than other ways, but they have a serious drawback – high price. To reduce the price will allow the use of cheap materials on which you are working Milczarek Grzegorz (Grzegorz Milczarek) from Poznan University of technology in Poland and Olle Inganas (Olle Inganäs) at the University of linköping in Sweden. Scientists propose to use in the manufacture of batteries (in particular for one of its components, cathode), waste paper industry.

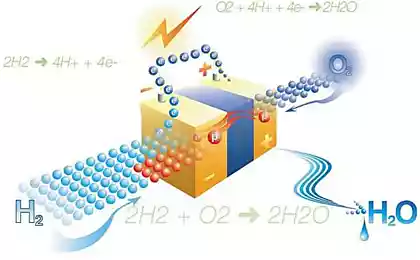
Any chemical battery consists of three main elements: the cathode, anode and electrolyte. Positive ions move through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode. Their current is compensated by the movement of negatively charged electrons through the load. Before returning "home", the electrons perform useful work. During battery charging, the electrons make the return journey under the action of the energy source, e.g. solar.
For the electrolyte typically used is cheap, simple and common chemicals. However, the electrodes require metals (e.g., lead or Nickel), which cost quite high. Replacement of metals by cheaper materials will significantly reduce the cost of production of batteries and make them available that would allow wide use of them to compensate for disadvantages of alternative energy sources.
The cathode material should "be able to" accept and hold a charge in the form of positive ions and electrons. Such properties may have lignin, if it is appropriately modified.
Lignin is one of the two main components of wood. Product of wood processing paper contains mostly cellulose, another major component. Thus, the liquid waste is paper production, called black or brown with a solution mostly composed of lignin and water.
Milczarek and Inganas suggested that the molecules of lignin can be used for cathodes of rechargeable batteries because rich in chemical groups called phenols. Phenols, in turn, are easily converted to quinones, which are required by the cathode due to the fact that in a pair of polypyrroles (organic conductive polymers) are able to effectively separate electrons and positively charged particles. Polypyrroles are not as cheap as lignin, but much cheaper metals.
Results of research confirmed the theory of scientists. The combination of modified lignin and polypyrrole is able to effectively hold a charge, and thus can serve as a basis for cathodes chemical batteries. Obviously, these are the first steps to the creation of cheap batteries on the basis of wood waste.
Source: /users/104
Before the energy industry faces the challenge of reliable and cheap storage technology developed at peak performance energy to provide it to consumers in peak hours, and at a time when generating capacity sits idle.
Chemical batteries are suitable for this purpose better than other ways, but they have a serious drawback – high price. To reduce the price will allow the use of cheap materials on which you are working Milczarek Grzegorz (Grzegorz Milczarek) from Poznan University of technology in Poland and Olle Inganas (Olle Inganäs) at the University of linköping in Sweden. Scientists propose to use in the manufacture of batteries (in particular for one of its components, cathode), waste paper industry.

Any chemical battery consists of three main elements: the cathode, anode and electrolyte. Positive ions move through the electrolyte from the anode to the cathode. Their current is compensated by the movement of negatively charged electrons through the load. Before returning "home", the electrons perform useful work. During battery charging, the electrons make the return journey under the action of the energy source, e.g. solar.
For the electrolyte typically used is cheap, simple and common chemicals. However, the electrodes require metals (e.g., lead or Nickel), which cost quite high. Replacement of metals by cheaper materials will significantly reduce the cost of production of batteries and make them available that would allow wide use of them to compensate for disadvantages of alternative energy sources.
The cathode material should "be able to" accept and hold a charge in the form of positive ions and electrons. Such properties may have lignin, if it is appropriately modified.
Lignin is one of the two main components of wood. Product of wood processing paper contains mostly cellulose, another major component. Thus, the liquid waste is paper production, called black or brown with a solution mostly composed of lignin and water.
Milczarek and Inganas suggested that the molecules of lignin can be used for cathodes of rechargeable batteries because rich in chemical groups called phenols. Phenols, in turn, are easily converted to quinones, which are required by the cathode due to the fact that in a pair of polypyrroles (organic conductive polymers) are able to effectively separate electrons and positively charged particles. Polypyrroles are not as cheap as lignin, but much cheaper metals.
Results of research confirmed the theory of scientists. The combination of modified lignin and polypyrrole is able to effectively hold a charge, and thus can serve as a basis for cathodes chemical batteries. Obviously, these are the first steps to the creation of cheap batteries on the basis of wood waste.
Source: /users/104