386
New Horizons — ahead region of the ice dwarfs

Region TRANS-Neptunian space (also often called "ice dwarfs") stretches from the orbit of Neptune to a distance of 55.e. from the Sun.
In contrast to the rocky-metallic objects of the asteroid belt between the orbits of Mars and Jupiter here, according to astronomers, concentrated tens of thousands of small icy celestial bodies composed mainly of volatiles such as methane, ammonia, water contained in a frozen state.
Pluto (along with its large moon Charon, and the four other satellites) is scheduled the main, although not the ultimate goal of an unprecedented space mission of NASA's "New Horizons", in the scientific program which also includes potential exploration of other celestial bodies of this region.
On the way to Pluto in mid-July 2014 was carried out the planned trajectory correction spacecraft velocity 1.08 m/s, which should ensure the arrival of the device in the specified area in the vicinity of Pluto next year,July 15, 2015. It spent about 0.25 kg of fuel.
According to the authors, may need another correction. But it could happen in six months, in February 2015, when the results of the observations of Pluto and its surroundings from a closer distance. This will allow to establish the possible presence of a small and as-yet-unseen for the observation of celestial bodies in the vicinity of Pluto (satellites, dust formations or rings near the dwarf planet).
In this case, the correction will be preventive, to avoid possible collisions on the way to the planet, goal.
I must say that the inclusion of a remote control and carrying out new adjustments will be carried out only if necessary, since the supply of available on-Board fuel 53 kg is the determining factor in carrying out the planned scientific program of the expedition. And not only in part of the study of Pluto and its satellite, but also the further implementation of the programme of studies – and span one or more dwarf celestial bodies.
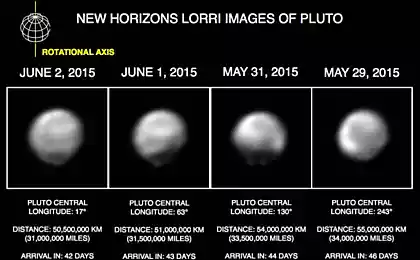
Next summer, the spacecraft will arrive in the neighborhood of Pluto, and on July 15, 2015 will be held at a minimum distance of 12.5 thousand km from its surface.
This migration, which will last about 9 days, is expected to conduct a detailed remote study of Pluto and its environs, including shooting the surface of Pluto and Charon with a resolution from 1 to 40 km, mapping the distribution of surface temperatures, the study of the atmospheres of those heavenly bodies.
During this period, should be collected and subsequently transferred from the station to the Ground more than 4.5 gigabytes of valuable scientific information.
After performing the flight phase of Pluto's station should be directed to one or two selected celestial bodies in the Kuiper belt.
In the coming days — 29 Aug 2014, the spacecraft "New horizons" will be translated in the so-called "sleep mode" to conserve energy aboard the station.
In February of 2015 to begin direct observation and filming from onboard the space station approaching, planet satellite of the Pluto system. Based on the obtained information, a decision will be made about the need to change the parameters of the flight trajectory of the spacecraft to the planet-target.
Source: nkj.ru