640
10 mistakes of the space program NASA

Anyway, and NASA has the best professionals. But they could be wrong. When you are constantly trying new things, meeting with the unknown and move progress, mistakes are inevitable. Of course, they happen quite rarely, but given the risk of NASA, they can be quite significant. We're not talking about outright failures — remember the ten serious mistakes in the performance of NASA.
Record the moon landing
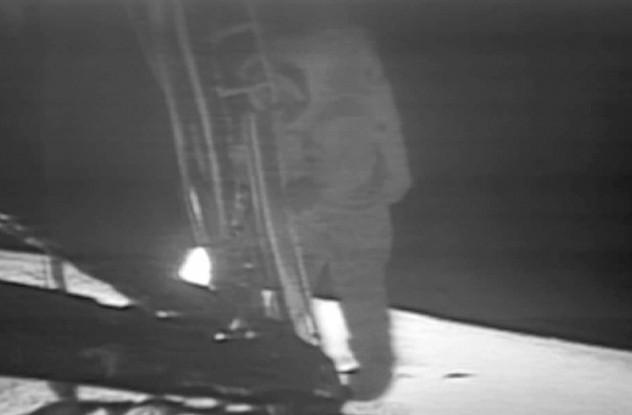

I think you could find a time when video cassettes were recording something important, then to reconsider. Yes, perhaps nothing more significant than your favorite football match or school concert of your child, you are not recorded. And certainly not recorded footage of the first landing of mankind on the moon.
The fact that the original videotapes of the iconic landing of Neil Armstrong during the mission "Apollo-11" was lost.
NASA took 35 years just to realize that these tapes were missing. They then began a search operation and found that the original tape was re-recorded in 1980-ies. Then there was a shortage of the tapes and it was standard procedure.
Arsenic life form
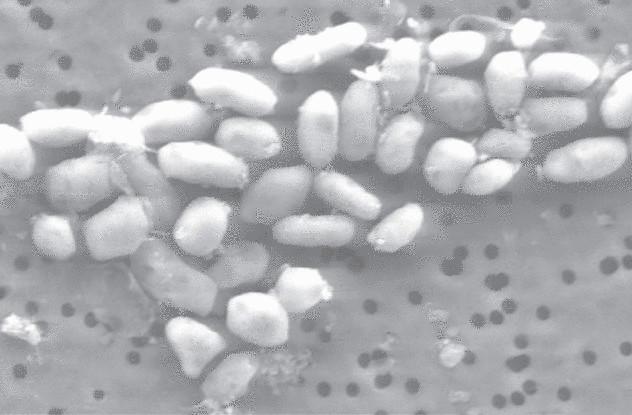
In 2010, the project, funded by NASA and led by the then astrobiology NASA Felisa Wolfe-Simon, made a shocking statement. Scientists have found bacteria with the new DNA structure in which arsenic replaces phosphorus. Supposedly an alien life form (GFAJ-1) became the center of attention of biologists around the world.
Biologists counted six elements, vital for all known forms of life: hydrogen, oxygen, carbon, nitrogen, sulfur and phosphorus. A life form that is supposedly used arsenic in the chain instead of phosphorus. Two elements have similar structure, but the arsenic is toxic to most isreport. Of course, skepticism was off the charts.
Soon published two new studies in the journal Science, refuting the initial findings. The habitat of the bacteria was poor in phosphorus and marked by high levels of arsenic, but the DNA of the bacteria is still used phosphorus. Although the bacterium was extremophiles that can survive in arsenic-rich environment, it was not an alien life form.
NOAA-19
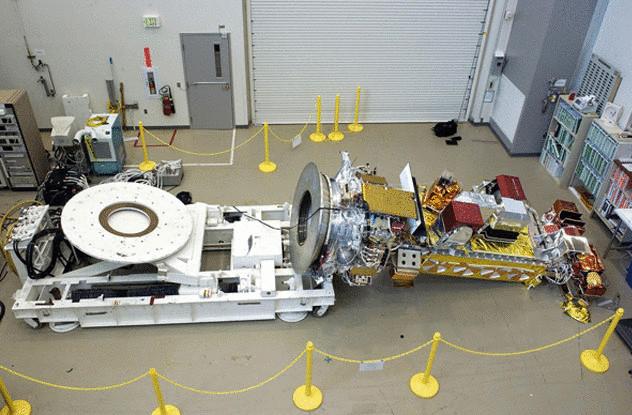
NOAA-19 was the last in a series of meteorological satellites of the National oceanic and atmospheric administration for the project POES. The aim of the project is the creation of a system of satellites that would provide scientists with more information about the climate.
Manufacturer Lockheed Martin, one of the main subcontractors of NASA, has extensive experience in the construction of large, complex and expensive devices. However, the satellite was severely damaged before launch. NASA officially described the cause as "lack of procedural discipline," which in ordinary language means "we seriously ran the sides". The satellite fell on the floor, because it simply forgot to fix.
Equipment used special cards to turn the satellite on its side. Usually it is attached to the seat 24 by the bolts, but some techniques before that they removed. And not documented it. The rest had to test fixed satellite or not — and again failure. The satellite simply crashed on the floor, and scientists have learned a valuable lesson about how gravity works. The repairs took about 135 million dollars.
OCO
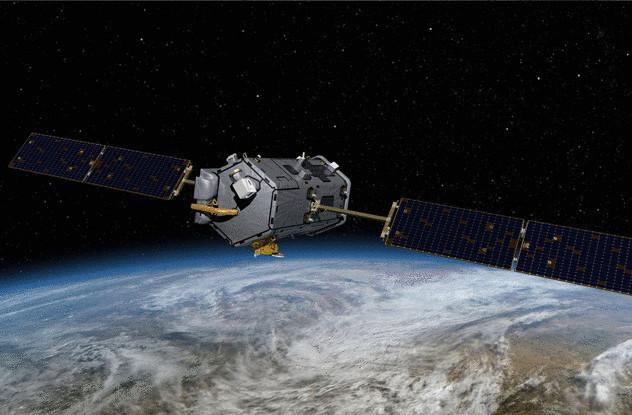

The orbital carbon Observatory (OCO) was to measure the level of carbon dioxide in the Earth's atmosphere. She was launched on 24 February 2009, but never reached the atmosphere. Instead, she fell to the Ground, landing in the Indian ocean off the coast of Antarctica. Ten years of development and more than $ 270 million has been spent on this satellite. In the fall of the satellite was damaged beyond repair.
The problem was minor, but had serious consequences. When the rocket takes off, the conical casing, the "fairing" that protects the payload. Then, as the rocket ejects the item. In this case it did not happen. The extra mass meant that the rocket did not have enough power to exit the atmosphere.
Five years later, in July 2014, was successfully launched OCO-2.
NASA Helios
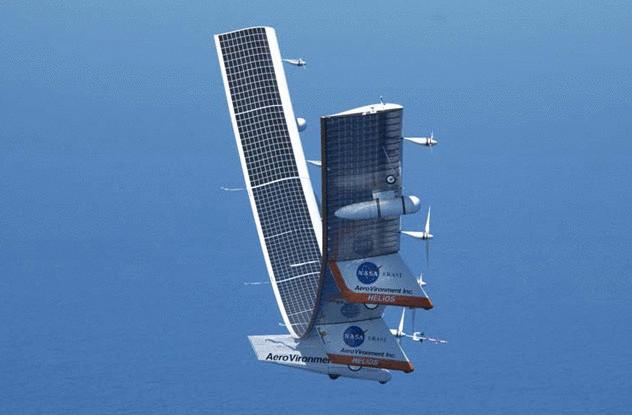

In the 90 years, NASA has developed a program ERAST, which was supposed to be created long-term atmospheric satellites in the form of drones with a remote control. First came the NASA Pathfinder. Then came the Pathfinder Plus. Both models proved to be good, so on their basis was created and a model of the NASA Centurion. All three of the aircraft exceeded all expectations. Was planned for the fourth version, the NASA Helios, as the top of the ERAST program.
But Helios has fallen into the Pacific ocean. It crashed in 2001 during a test flight, during which was tested the remote piloting system. From the outset there were fears that the weather was not the best, but Helios had carefully prepared launch, which, by the way, was put the machine on maximum power. This was a mistake.
Instead of his 10 successful flight of a drone just fell down, after 30 minutes after takeoff, off the coast of the Hawaiian island of Kauai. The reason — bad weather conditions. But before the fall the unit set a record: he reached the greatest height among aircraft with rocket engines.
DART
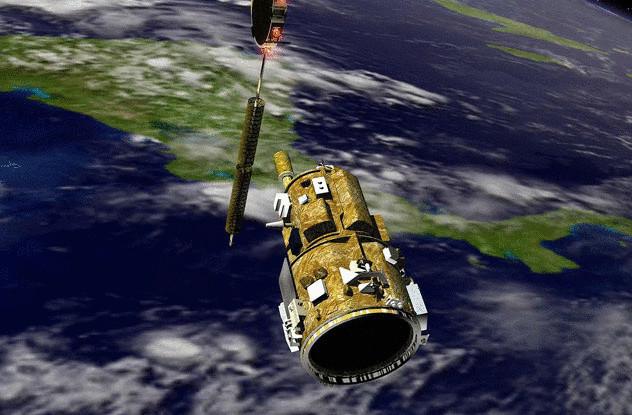

DART was another satellite, which saw the untimely death because of a simple error. The project has engaged Orbital Sciences Corporation, but the financial problems were solved by NASA. The goal was to develop a robotic satellite that will be able to service and repair other satellites. It would be cheaper and safer, than each time to send astronauts into orbit.
The first mission of DART was held on 15 April 2005. His goal was MUBLCOM, satellite communications repeater. DART was gently to dock and begin maintenance. Unfortunately, the satellite is a little not so understood the word "gently" and just drove into the side of his colleague.
Even if this had not happened, the mission would have failed. Another error led to the fact that DART has spent more rocket fuel than needed, so it ended in the middle of the mission. After 11 hours of a 24-hour mission, the satellite detected that the tank is empty, so began an automatic evacuation, not to be left floating in space.
Skylab
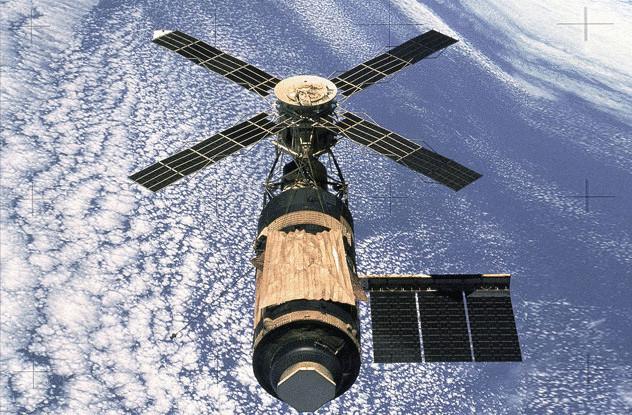

Skylab was the first American space station launched in 1973 and worked until 1979. It gave Americans a lot of useful information, but the only thing her remembered was her downfall. In the end, watched all over the world. And it could be much worse.
The lack of foresight was uncharacteristic of NASA. The Agency did not worry too much about how Skylab return to Earth, but knew that one day it will happen. At best the station has worked for nine years. The navigation system did not exist. Technology was not as such, but if there was, it was very expensive. Therefore, it was necessary to come up with something optional.
Before the crash, NASA assumed that the chance that the fall of the station will lead to human victims was 1 to 152. It would be best to use a rocket to transport the station into the Indian ocean. It happened — for the most part. The largest part of the station fell into the ocean, but a lot of the debris landed in Australia. Fortunately, no one was hurt.
Even more — one Australian teenager has won $ 10,000 from the San Francisco Examiner, because he was the first person who brought the chip station. In fact, NASA was lucky that they were only fined $ 400 for littering.
Mars Polar Lander
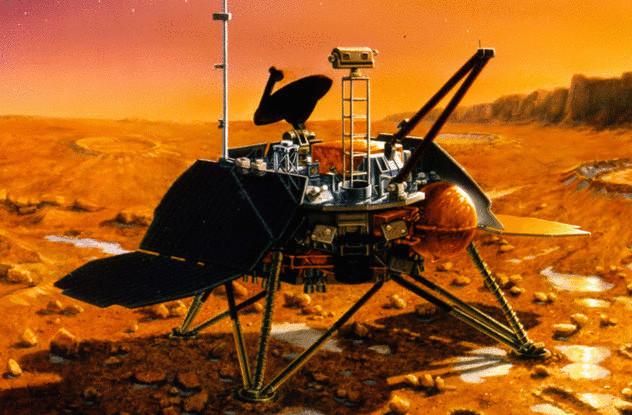

Mars Polar Lander (MPL) was one of the most ambitious projects of NASA. This robotic lander was the first to land on Mars and explore its polar environment. NASA was really hoping MPL will provide valuable information about the possible existence of water on Mars and about the possibility of the red planet to support life.
It was launched in January 1999. Destination reached in December. Then MPL began its soft descent to Mars — and that was the last thing we know about him.
Relationship with MPL stopped suddenly and never recovered. No one knows exactly what happened. NASA a whole month tried in vain to contact the lander before they announced the complete failure of the mission.
One theory is that the error in the onboard computer of the apparatus led to the fact that he prematurely thought to have landed. Thinking that he was already on solid ground, MPL turned off the engines, fell down and crashed.
Mars Climate Orbiter
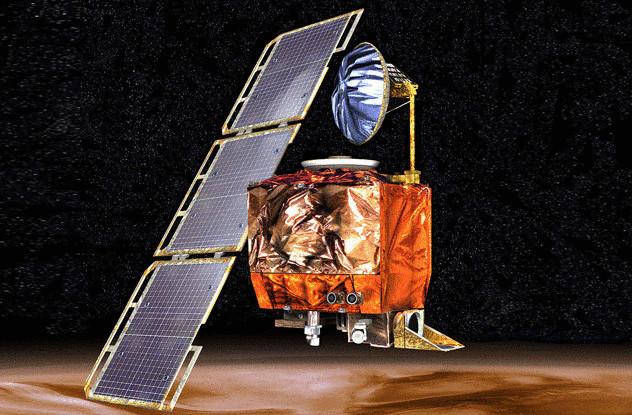

Mars Climate Orbiter (MCO) was launched in December 1998, shortly before the MPL. His mission was to enter orbit Mars and record the atmospheric conditions, temperature, weather conditions, contents of water vapor and surface change. Like MPL, MCO reached Mars, and then disappeared into the atmosphere.
The failure was due to the incredibly simple and small mistake, which cost NASA $ 125 million. Manufacturer Lockheed Martin was counting the pulse produced by the engines using the metric system (Newton-seconds). In their own calculations, NASA decided that using standard units (pound-seconds). In the result, the Orbiter entered the Martian atmosphere on a trajectory lower than necessary, and the engines are not lost by overheating.
What is most awkward in this mission is the fact that the failure could have been prevented. The majority of errors occurs when a spacecraft already in space and it's too late to correct the error. In this case, the error happened 10 months when the unit was still on the Ground. Despite the countless number of people who have tested the performance of the spacecraft, no one noticed the error.
"Apollo 13"
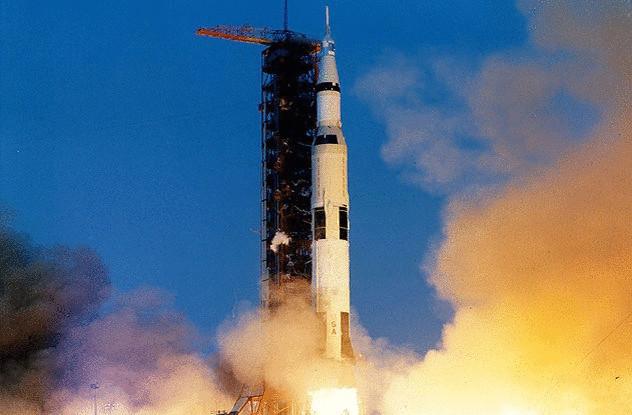

"Apollo 13" could be a disaster comparable to the collapse of Shuttle "Challenger" and "Columbia". Launched on 11 April 1970, "Apollo 13" had to perform the third manned mission with the objective of landing on the moon. The crew, led by captain Jim Lovell had to land in the highlands of fra Mauro and explore the 80-kilometer crater located there.
The mission went wrong. One of the astronauts, Ken Mattingly, was replaced by the inexperienced Jack Swigert due to infection with rubella. Things got even worse when one of the cryogenic oxygen tank exploded and damaged the other. The spacecraft lost the ability to generate electricity, to maintain the level of oxygen or clean water. Swigert responded to the famous "Houston, we've had a problem" (which in the movie was changed to "Houston, we have a problem" and attributed to Jim Lovell).
The ship immediately turned around and objectives were revised. Just had to rescue the astronauts. Although it was not very good, "Apollo 13" was a workable backup compartment. The astronauts were able to survive in it on the way home, and then moved to the main ship during re-entry.
Materials listverse.com
Source: hi-news.ru