151
Thrombosis: Simple rules of disease prevention
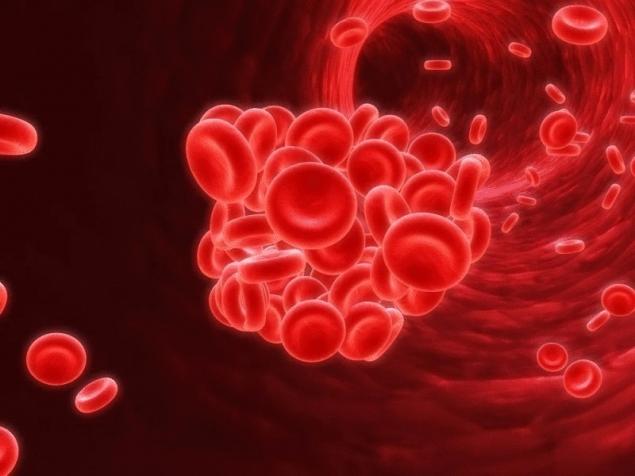
Thrombosis is a disease that affects many people around the world. Causes can be a sedentary lifestyle, smoking, unhealthy diet. From this article you will learn what thrombosis is and how to prevent it.
With thrombosis, blood clots form in the vessels, which create a partial or complete "congestion" and, thus, interfere with the normal process of blood flow. Increased blood clotting (caused by a genetic predisposition, external or any unknown factors), damage to the endothelial cells of the vascular wall (it can also be exacerbated by infection or damage) and the flow of stagnant blood can cause blood clots.
Complete or partial separation of the blood clot from the vascular wall can cause the blood clot to block access to vital organs such as the brain, heart, lungs or arteries of the legs. Blood clots circulating freely inside the circulatory system disrupt blood flow. This can lead to serious and even deadly health consequences; among them are myocardial infarction, stroke, pulmonary embolism and gangrene.
Venous thromboembolism is a disease consisting of venous thrombosis and pulmonary artery embolism. Venous thromboembolism can be caused by many different factors, and here are some of them:
- Inactivity
- Hypercoagulation, or increased blood clotting
- Damage to the venous wall
- Age.
- Transferred operations (especially when it comes to knee surgery and knee replacement)
- Cancer
- Genetic predisposition
- Pregnancy
- Increased levels of estrogen in the blood (due to taking oral contraceptives or hormonal treatment)
- Overweight
- Smoking
- Crohn's disease
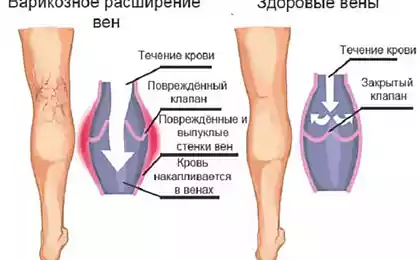
Deep venous thrombosis is the most common subtype of this disease. Some of the main symptoms of deep venous thrombosis are painful and unpleasant sensations, heaviness, throbbing pain, burning sensation and itching in the legs, any changes in the skin (paleness, seals, sores), swelling of the legs, ankles or feet.
Post-thrombosis symptoms develop in at least half of patients suffering from deep thrombosis. It can manifest itself in the form of chronic swelling of the legs, pain in the calves, a feeling of heaviness, fatigue, pale skin and / or sores on the veins of the affected limb. This symptom significantly reduces the quality of life of patients.
Pulmonary embolism can be one of the complications caused by deep venous thrombosis. It can be recognized by the following symptoms:
- A sharp shortage of air
- Chest pain
- Coughing up blood
- Acceleration or disruption of heart rate
- Dizziness
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle and exercise regularly. Walking, swimming, cycling are great ways to prevent deep venous thrombosis.
- Control your weight: both through sports and through healthy eating.
- If you smoke, we strongly recommend quitting. Special therapy and support groups will help ease the process.
- Measure your blood pressure regularly. Take the necessary measures if it needs to be reduced.
- Be sure to tell your doctor if your family history has problems with blood clotting.
- Discuss with your doctor possible alternatives to hormonal contraceptives, as well as hormone replacement therapy.
- If you have a flight that will last more than 4 hours, during the flight walk around the cabin, stretch and stretch your legs while sitting, and drink plenty of liquids (but avoid alcoholic beverages!)
- Consult your doctor about how to prevent thrombosis during pregnancy.
- Wear spacious clothes
- Exercise periodically, such as trying to raise your legs above heart level.
- Use special tights (compression tights) if prescribed by a doctor
- Do the exercises prescribed by your doctor.
- Change your position often, especially if you have to be on the road for a long time.
- Do not stand or sit still for more than 1 hour in a row
- Try to eat less salt.
- Take care not to beat your feet or cross them.
- Don't put a pillow under your knees.
- Lift the lower part of the bed a few centimeters.
- Take all the medications prescribed by your doctor.
- Lead an active lifestyle, move more.Published
Source: steptohealth.ru/
Top 5 "drugs", which can be found at his dacha
Portable heater that will warm a room or a Cup of coffee without electricity