519
In the driest places on Earth there is life
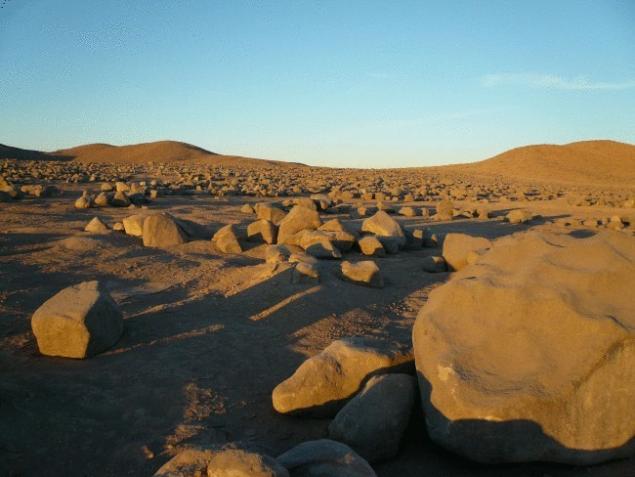

Scientists pinpointed the driest place on Earth in the Atacama desert region of Chile, which was already recognized as the most arid in the world. They also found evidence of life thriving in this place, and this discovery can mean a lot to search for life on Mars.
More than ten years, the region remains very dry Yungay region of the Atacama desert Swersey, the terms of which are approaching so-called "dry limit" for life on Earth. Published academic papers testifies to the extraordinary characteristics of this place and its resemblance to similar conditions in some places on Mars. It lures astrobiologists. However, after systematic research of the desert, a group of Chilean scientists has discovered a new place, Maria Elena South (MES), which is described as a more "drier" than Jung.
Lead author Armando Azua-Bustos, biologist and environment researcher, Space science Institute Blue Marble in Seattle reports that the team found that MES has a relative atmospheric humidity (RH) at 17.3% and RH of the soil in the permanent 14% at a depth of one meter. This value of soil moisture coincides with the lowest RH measurements made by the Mars Science Laboratory in Gale crater on Mars, and evidence that the conditions found in the dry match those found on the surface of Mars.
"Remarkably, we found a number of viable bacterial species in the slice of soil MES, using a combination of dependent and independent molecular methods, revealing the presence of life in the driest place of the Atacama desert today," says Azua-Bustos.
Микродатчики

The team used the microsensors, including atmospheric temperature, and relative humidity loggers to make detailed measurements of the conditions of microecosystem MES. Were also characterized the geochemical composition of the soil of the site, identifying the presence and types of microbial species able to survive under such conditions. The work was published in Environmental Microbiology Reports.
Azua-Bustos spent the last 12 years studying the Atacama desert and developing the field of astrobiology in Chile, earning the nickname "astrobiologist from the desert". For the first time this region and he was interested when I read "core work", published in Science in 2003, a group of scientists under the direction of Chris McKay, a planetary research center at NASA Ames.
In this work, the Yungay region of the Atacama desert was offered as a "corresponding to the same model of Mars", mostly due to the extremely dry nature of the soil characteristics, the presence of organic species at the level of detection and an extremely low kultivirovavshy bacteria.
However, based on his experiences as a native of the Region, born and raised in the desert, Azua-Bustos was convinced that the desert was a place drier than Yungay, and decided to install RH sensors in several other places.
"We found at least three places, of which the dry will describe in this work," the scientist said.
Implications for астробиологии

For Azua-Bustos, the fact that the conditions designated MES, from the point of view of dryness, are the closest to the Martian as possible, means that MES is one of the best analog models of Mars on Earth that can and need to explore. This will help to understand possible existing types of microbial life in the Martian subsurface environment.
"It also means that if you want to test the next generation of robots, tools and other discovery methods and technologies for the Mars environment, this place is the best in many ways," says Azua-Bustos.
This place can also be used to conduct experiments that could accompany the future work of the Mars Science Laboratory in Gale crater in search of extant life on Mars. From the perspective of Azua-Bustos, one of the interesting experiments will use the same tools that uses MSL in the region MES, for the purpose of comparison and "further detailing the total that can be in two places, from the point of view of habitability, suitability of places to stay and so forth."
For Azua-Bustos of the fact that we know about the existence of life in soil Maria Elena South, means that it will be interesting to see if SAM tool (a set of three tools for analysing the soil samples on the Mars Rover) and similar tools, is scheduled to be sent to Mars, to define life in similar arid place.
"Knowing the number, location, soil and type of microbial life here in Maria Elena South, it would be interesting to test the SAM tools here to check its sensitivity in the place which we know to be inhabited. In other words, if SAM or another tool will not be able to detect life in soil MES, so will not be able to detect on Mars".published
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind - together we change the world! ©
Source: hi-news.ru