638
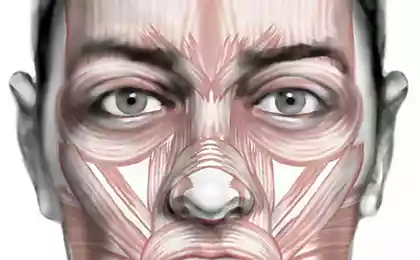
Fascia of the face
Represent the fascia sheets of connective tissue of varying density, composed predominantly of collagen fibers with few cells (fibroblasts).
They surround groups or individual muscles and organs and form of the vagina around the neurovascular bundles. Its spurs fascia attached to the bones forming the bony and fascial sheaths.
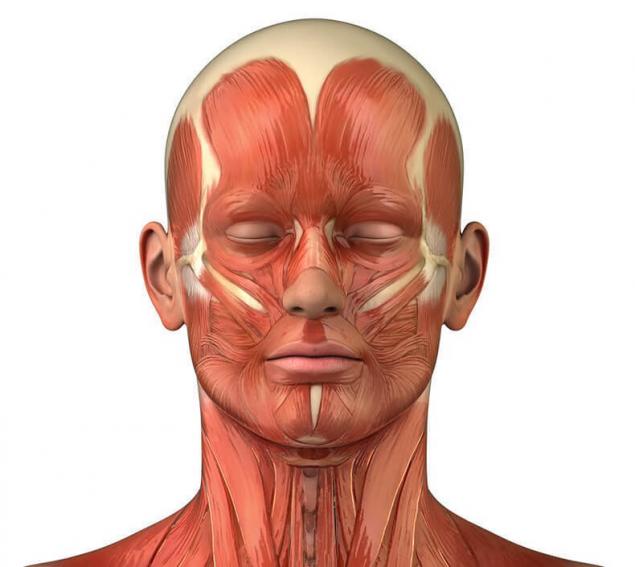
Functionally they are soft core, hard muscles, vessels, nerves, and internal organs. The space between the fascia, fascia and organs filled with loose fatty tissue (cellular spaces spaces and crevices), which is easily spread of the phlegmon, and hematoma.
There are three types of fascia: superficial, private and visceral.
Superficial fascia of the face.
Superficial fascia of the face has the appearance of a delicate, loose plate. It is located in the subcutaneous tissue, forming cases for the facial muscles and superficial vessels and nerves. At the bottom it passes in the superficial fascia of the neck covering the subcutaneous muscle of the neck.
In the arch of the skull, it forms a cases for the frontal and occipital muscles, fused with aponeurotic helmet in the form of a thin plate descends into the subcutaneous tissue of the temporal region, forming sunken cunt of the subcutaneous vessels and nerves.
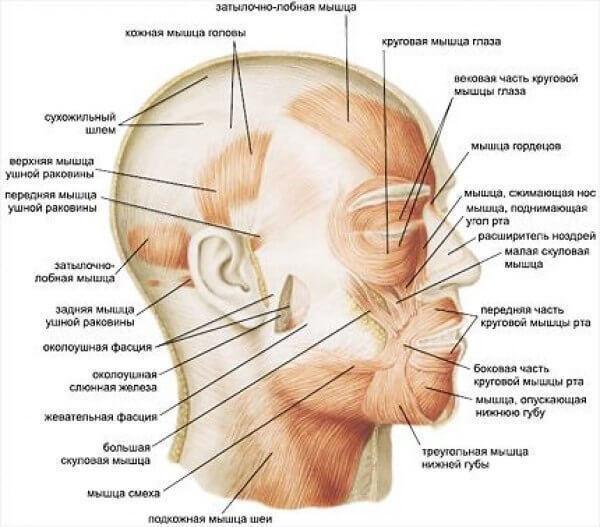
Own fascia of the face.
Own fascia of the face as well as in other areas, presents a more dense plate. It attaches to bones and forms the bony and fascial receptacle for the muscles, vessels and nerves. Departments own fascia are called respectively areas or muscles which they cover. On the face there are the following private functions.
1. Temporal fascia is a very dense plate, which covers the outside of the temporal muscle. It is attached at the top to the upper temporal line, and below to the zygomatic arch. 2-4 cm above the zygomatic arch temporal fascia splits into two pieces, one of which is attached to the outer, the other to the internal surface of the zygomatic arch.
2.The parotid-masticatory fascia covers the outside of the chewing muscle, laminating, forms the capsule of the parotid gland. At the top of the fascia attaches to the zygomatic arch and the bottom outer surface of the angle and body of mandible. At the rear edge of the mandibular Ramus, it is firmly fused with the periosteum. From the front edge of the masseter muscle parotid-masticatory fascia passes in a fascial sheath buccal fat lump (Bruce Laguna).
3. Makryashina fascia covers the inside and outside lateral medial pterygoid muscles. At the top is attached to the outer base of the skull on the line from the corner spine to the base of the pterygoid process and the outer plate, and the bottom — to the inner surface of the angle of the mandible and the periosteum of the posterior edge of its branches. Makryashina front fascia, below the pterygoid process, fused with the buccal-pharyngeal (visceral) fascia, which itself is attached to the rear edge of the internal oblique line of the mandible.
4. Predpolagaetsya fascia
covers the front of the long muscles of the head and neck. It starts at the base of the skull, attaches to the side of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, at the bottom reaches the IV thoracic vertebra, forms together with spine bone-fascial case for predposlednij muscles.
Visceral fascia of the face.
The visceral fascia in the face surrounds the back and sides with the throat it is called peripharyngeal at the Top it is attached with the pharynx to the skull base. In okoloplodna enters the bottom of the fascia. Anteriorly it passes into the Bucco-pharyngeal fascia covering the cheek muscle.
From posterolateral departments of peripharyngeal fascia to predposlednii depart right and left on the spur of the pharyngeal-vertebral spurs separating the tissue behind the pharynx, from fiber located on the side of the pharynx.
What scared varices: an effective treatment
The channel of the spleen: the first signs of imbalance
These spurs come from the base of the skull down, further locking the throat. From the styloid process and three muscles extending from it (awl-pharyngeal, awl-lingual and awl-hyoid) and their fascial sheaths to the peripharyngeal fascia, there is a spur, called the pharyngeal-subulate or awl-diaphragm.
This spur is located from the base of the skull to the level of the styloid process and separates tissue surrounding the neurovascular bundle from the lateral peripharyngeal cellular spaces, division of space.published
Author: Alexander Black
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.facebook.com/metavitonica/posts/1776479432563642:0
They surround groups or individual muscles and organs and form of the vagina around the neurovascular bundles. Its spurs fascia attached to the bones forming the bony and fascial sheaths.

Functionally they are soft core, hard muscles, vessels, nerves, and internal organs. The space between the fascia, fascia and organs filled with loose fatty tissue (cellular spaces spaces and crevices), which is easily spread of the phlegmon, and hematoma.
There are three types of fascia: superficial, private and visceral.
Superficial fascia of the face.
Superficial fascia of the face has the appearance of a delicate, loose plate. It is located in the subcutaneous tissue, forming cases for the facial muscles and superficial vessels and nerves. At the bottom it passes in the superficial fascia of the neck covering the subcutaneous muscle of the neck.
In the arch of the skull, it forms a cases for the frontal and occipital muscles, fused with aponeurotic helmet in the form of a thin plate descends into the subcutaneous tissue of the temporal region, forming sunken cunt of the subcutaneous vessels and nerves.

Own fascia of the face.
Own fascia of the face as well as in other areas, presents a more dense plate. It attaches to bones and forms the bony and fascial receptacle for the muscles, vessels and nerves. Departments own fascia are called respectively areas or muscles which they cover. On the face there are the following private functions.
1. Temporal fascia is a very dense plate, which covers the outside of the temporal muscle. It is attached at the top to the upper temporal line, and below to the zygomatic arch. 2-4 cm above the zygomatic arch temporal fascia splits into two pieces, one of which is attached to the outer, the other to the internal surface of the zygomatic arch.
2.The parotid-masticatory fascia covers the outside of the chewing muscle, laminating, forms the capsule of the parotid gland. At the top of the fascia attaches to the zygomatic arch and the bottom outer surface of the angle and body of mandible. At the rear edge of the mandibular Ramus, it is firmly fused with the periosteum. From the front edge of the masseter muscle parotid-masticatory fascia passes in a fascial sheath buccal fat lump (Bruce Laguna).
3. Makryashina fascia covers the inside and outside lateral medial pterygoid muscles. At the top is attached to the outer base of the skull on the line from the corner spine to the base of the pterygoid process and the outer plate, and the bottom — to the inner surface of the angle of the mandible and the periosteum of the posterior edge of its branches. Makryashina front fascia, below the pterygoid process, fused with the buccal-pharyngeal (visceral) fascia, which itself is attached to the rear edge of the internal oblique line of the mandible.
4. Predpolagaetsya fascia
covers the front of the long muscles of the head and neck. It starts at the base of the skull, attaches to the side of the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, at the bottom reaches the IV thoracic vertebra, forms together with spine bone-fascial case for predposlednij muscles.
Visceral fascia of the face.
The visceral fascia in the face surrounds the back and sides with the throat it is called peripharyngeal at the Top it is attached with the pharynx to the skull base. In okoloplodna enters the bottom of the fascia. Anteriorly it passes into the Bucco-pharyngeal fascia covering the cheek muscle.
From posterolateral departments of peripharyngeal fascia to predposlednii depart right and left on the spur of the pharyngeal-vertebral spurs separating the tissue behind the pharynx, from fiber located on the side of the pharynx.
What scared varices: an effective treatment
The channel of the spleen: the first signs of imbalance
These spurs come from the base of the skull down, further locking the throat. From the styloid process and three muscles extending from it (awl-pharyngeal, awl-lingual and awl-hyoid) and their fascial sheaths to the peripharyngeal fascia, there is a spur, called the pharyngeal-subulate or awl-diaphragm.
This spur is located from the base of the skull to the level of the styloid process and separates tissue surrounding the neurovascular bundle from the lateral peripharyngeal cellular spaces, division of space.published
Author: Alexander Black
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: www.facebook.com/metavitonica/posts/1776479432563642:0
The plants change places, and you will not need to fertilize the soil
Air cooling with "ice batteries"