587
Boiler room on biofuel: what you need to know
Currently, in connection with rise in prices for gas and electricity, renewed interest in equipment that allows you to use a local low-calorie fuel (wood, peat, brown coal) and combustible waste materials (agricultural, forestry & paper, solid waste) to produce heat and/or electrical energy.

Known difficulties associated with obtaining permission to use natural gas as fuel (including financial), forced consumers to seek alternative options to provide industrial and municipal facilities with thermal energy.
It is necessary to pay attention to alternative fuels – solid. And then the question arises: what to choose – charcoal or biofuels.
The most frequent types of local biofuels include:
1. wood in the form of personal logs;
2. lump wastes of lumbering and wood processing: slabs, strips, planks and boards with an unacceptable faults, non-standard cutting when cutting lumber, rejected pellets, bark, obtained after debarking machine many kinds of timber, forest residues, dried woody herbs, twigs, branches, tops, etc.;
3. non-business pieces of trunks, healthy fallen trees, undergrowth, small trees, stumps and roots, sawdust and cruzca, trees and shrubs to be removed on the designated lanes along roads, pipelines, power lines and communications;
4. herbaceous vegetation, reeds, straw, potato leaves, lignin;
5. specially manufactured fuels from wood waste and biological raw materials (briquettes, pellets);
6. milled peat.

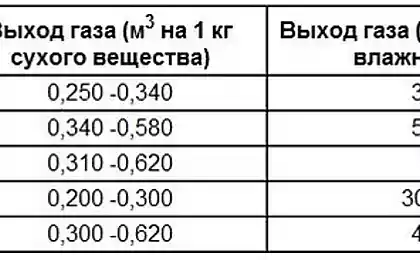
From the point of view of the process of burning any biofuel, as a rule, consists of the following components: ash, combustible material, water. Individual differences of certain types of biofuels are primarily in different percentages of moisture depending on the production method, place and duration of storage, exposure to natural or artificial drying.
For example, freshly cut wood can have a moisture content of 50-60 %, and after two or three months of storage in the open air on the cutting area in dry weather, forest residues dry up to 40-45 %; moisture content of wood waste in the shop or on the indoor storage of lumber after artificial drying is in the range of 12-20 %. Peat as a fossil, from other types of freshly mined fuel (wood, herbaceous plants) differs significantly higher content of sulphur substances and high ash content.
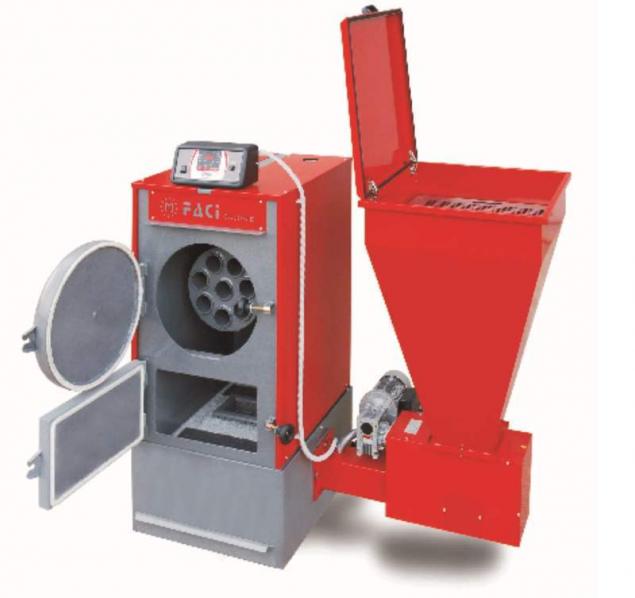

We now compare what we know about the equipment, working on diesel fuel, compared to the equipment for combustion of biofuels. There is wide selection of equipment that allows ease of operation solid fuel boiler, and diesel?
The choice is wide enough. Any interested user can easily find a sufficient number of suppliers of such products. Does the problem of storing fuel? No, there are a large number of waste storage systems and fuel delivery. Automatiseret and mechanisims process to the extent of complete lack of staff? Certainly Yes, but it is more expensive than the liquid and gaseous fuels. If the game is worth the candle, and what will be the cost of the final product – thermal energy?
Compare the option of operating costs for the two boilers with a capacity of 2 MW each, equipped with a diesel boiler and solid fuel, respectively. Assume that the boilers operate only for heating, the heating season lasts 5000 hours, the boilers are matched correctly and the average boiler load during this period will be 50 % of nominal. The main item of cost, of course, fuel. The price of diesel fuel of acceptable quality is 30 rubles/liter. The peak demand boiler with capacity of 2 MW is about 180 l/h. Thus during the heating season will be consumed:
180х0,5х5000=450000 l/season at a cost of 30 rubles/liter, 13.5 million rubles.
The power consumed by the burner, the average is 4 kW, the cost of electricity per season at a cost of 5 energy, RUB/kWh will be: 4х5000х5=100 000.
The boiler on woodchips: peak flow chips at calorie 1500 kcal/kg will be 1150 kg/hour, or a 3.85 m3/h. the Cost of wood chips is on average 400 rubles/m3. Thus, the fuel costs will be 3,85х0,5х5000х400=3 850 000 rubles per season.
Boiler for pellets or briquettes calorific value 4000 kcal/kg: peak flow 430 kg/hour, cost 6 rubles/kg, total for season: 430х0,5х5000 X6=6 450 000 RUB/season.
Energy consumption for solid fuel boiler – 15 kW, thus the energy costs during the heating season will be 15х5000х5= 375 000.
For comparison, look at the cost of gas. At the peak, the boiler consumes 240 m3/h, the cost of gas, 5 rubles/m3, the total fuel costs for the heating season:
240х0,5х5000х5=3 000 000/season.
Interesting data?
What about capital costs for the construction?
Gas: price of gas supply starts an average of 5 million rubles, the real during the project implementation this figure is doubled. On one of the objects of the Moscow region the cost of the pipeline to the boiler house with a load of 1.5 MW amounted to 82 million rubles. Of course the project hasn't been realized. The cost of boilers and burners similar diesel version but it added quite a pleasant Supplement in the form of various inspections. Diesel unlike gas is added to the fuel depot at an approximate cost of 1 million rubles.
Solid fuel boiler cost boilers of course losing both gas and diesel. The cost of the boiler approximately above the cost of the boiler and the burner in the gas and diesel version. However, the combination of capital and operating costs by far, in our opinion, allows to consider the option of a boiler room on biofuel as the most attractive.
published
Source: www.aqua-therm.ru/articles/articles_424.html

Known difficulties associated with obtaining permission to use natural gas as fuel (including financial), forced consumers to seek alternative options to provide industrial and municipal facilities with thermal energy.
It is necessary to pay attention to alternative fuels – solid. And then the question arises: what to choose – charcoal or biofuels.
The most frequent types of local biofuels include:
1. wood in the form of personal logs;
2. lump wastes of lumbering and wood processing: slabs, strips, planks and boards with an unacceptable faults, non-standard cutting when cutting lumber, rejected pellets, bark, obtained after debarking machine many kinds of timber, forest residues, dried woody herbs, twigs, branches, tops, etc.;
3. non-business pieces of trunks, healthy fallen trees, undergrowth, small trees, stumps and roots, sawdust and cruzca, trees and shrubs to be removed on the designated lanes along roads, pipelines, power lines and communications;
4. herbaceous vegetation, reeds, straw, potato leaves, lignin;
5. specially manufactured fuels from wood waste and biological raw materials (briquettes, pellets);
6. milled peat.

From the point of view of the process of burning any biofuel, as a rule, consists of the following components: ash, combustible material, water. Individual differences of certain types of biofuels are primarily in different percentages of moisture depending on the production method, place and duration of storage, exposure to natural or artificial drying.
For example, freshly cut wood can have a moisture content of 50-60 %, and after two or three months of storage in the open air on the cutting area in dry weather, forest residues dry up to 40-45 %; moisture content of wood waste in the shop or on the indoor storage of lumber after artificial drying is in the range of 12-20 %. Peat as a fossil, from other types of freshly mined fuel (wood, herbaceous plants) differs significantly higher content of sulphur substances and high ash content.

We now compare what we know about the equipment, working on diesel fuel, compared to the equipment for combustion of biofuels. There is wide selection of equipment that allows ease of operation solid fuel boiler, and diesel?
The choice is wide enough. Any interested user can easily find a sufficient number of suppliers of such products. Does the problem of storing fuel? No, there are a large number of waste storage systems and fuel delivery. Automatiseret and mechanisims process to the extent of complete lack of staff? Certainly Yes, but it is more expensive than the liquid and gaseous fuels. If the game is worth the candle, and what will be the cost of the final product – thermal energy?

Compare the option of operating costs for the two boilers with a capacity of 2 MW each, equipped with a diesel boiler and solid fuel, respectively. Assume that the boilers operate only for heating, the heating season lasts 5000 hours, the boilers are matched correctly and the average boiler load during this period will be 50 % of nominal. The main item of cost, of course, fuel. The price of diesel fuel of acceptable quality is 30 rubles/liter. The peak demand boiler with capacity of 2 MW is about 180 l/h. Thus during the heating season will be consumed:
180х0,5х5000=450000 l/season at a cost of 30 rubles/liter, 13.5 million rubles.
The power consumed by the burner, the average is 4 kW, the cost of electricity per season at a cost of 5 energy, RUB/kWh will be: 4х5000х5=100 000.
The boiler on woodchips: peak flow chips at calorie 1500 kcal/kg will be 1150 kg/hour, or a 3.85 m3/h. the Cost of wood chips is on average 400 rubles/m3. Thus, the fuel costs will be 3,85х0,5х5000х400=3 850 000 rubles per season.
Boiler for pellets or briquettes calorific value 4000 kcal/kg: peak flow 430 kg/hour, cost 6 rubles/kg, total for season: 430х0,5х5000 X6=6 450 000 RUB/season.
Energy consumption for solid fuel boiler – 15 kW, thus the energy costs during the heating season will be 15х5000х5= 375 000.
For comparison, look at the cost of gas. At the peak, the boiler consumes 240 m3/h, the cost of gas, 5 rubles/m3, the total fuel costs for the heating season:
240х0,5х5000х5=3 000 000/season.
Interesting data?
What about capital costs for the construction?
Gas: price of gas supply starts an average of 5 million rubles, the real during the project implementation this figure is doubled. On one of the objects of the Moscow region the cost of the pipeline to the boiler house with a load of 1.5 MW amounted to 82 million rubles. Of course the project hasn't been realized. The cost of boilers and burners similar diesel version but it added quite a pleasant Supplement in the form of various inspections. Diesel unlike gas is added to the fuel depot at an approximate cost of 1 million rubles.
Solid fuel boiler cost boilers of course losing both gas and diesel. The cost of the boiler approximately above the cost of the boiler and the burner in the gas and diesel version. However, the combination of capital and operating costs by far, in our opinion, allows to consider the option of a boiler room on biofuel as the most attractive.
published
Source: www.aqua-therm.ru/articles/articles_424.html