891
Laniakea supercluster and 10 terms of astronomy, you need to know
We present to your attention a few terms with which your knowledge of astronomy will become deeper.
Apparent magnitude
Number of stars in the night sky, available to the naked eye, is not as great as it seems. If you have good visual acuity and get out of town, away from the street lighting, the monitoring will be available for about 6000 stars. At the same time half of them will always be hidden from an observer on the horizon. But even this amount is sufficient to note how stars differ in brightness. Noticed this and ancient scholars. Who lived in the II century BC Greek mathematician and astronomer Hipparchus divided all observables their stars into six magnitudes. Most striking, he took the first magnitude, the most dull - the sixth. In general, this principle is used today. But today, the possibility of astronomy possible to observe countless stars, most of which are so dim that the naked eye can not be. But the very concept of magnitude is applied not only to distant stars, but also for other objects - the Sun, the Moon, artificial satellites, planets, and so on. Therefore, it is believed that magnitude - is a dimensionless numerical characteristic of the object brightness
.
It follows from the foregoing, the apparent magnitude of the brightest objects will be negative. For comparison, the magnitude of the Sun is -26, 7, and the magnitude of our nearest star, but not visible to the naked eye star, Proxima Centauri, is 11, 1. The maximum magnitude of Mars is equal to - 2, 91 Sputnik "Mayak", which and created a plan to send into orbit a young Russian scientists, as planned should have magnitude less than -10. And if everything works out, he briefly becomes the brightest object in the night sky, unless, of course, except for the moon on a full moon (-12, 74).
The absolute magnitude
Deneb - one of the biggest stars known to science, has a magnitude of 1, 25. Its diameter is approximately equal to the diameter of Earth's orbit and more of the sun 110 times the diameter. The distance to this giant - 1640 light years. Although scientists are still debating on this issue, it is very far from it. Most of the stars at such a distance, can only be seen through a telescope. If we were to the star closer, Deneb and brightness in the sky would have been much higher. Thus, the apparent magnitude depends on the luminosity of the object and the distance to it. To be able to compare the luminosity of different stars between them, use the absolute magnitude. For stars, it is defined as the apparent magnitude of the object, if it were located at a distance of 10 parsecs from the observer. If the distance to the star is known, then calculate the absolute magnitude is easy.
The absolute star of the sun value is 4, 8 (probably recall, -26, 7). Sirius - the brightest star in the night sky - has an apparent magnitude of 1, 46, all but one absolute, 4. That, however, is not surprising, because the night sky brilliant (as they call the star) is close to us: at a distance of only 8, 6 light-years across. But the absolute magnitude of the already mentioned Deneb is -6, 95.

Parallax
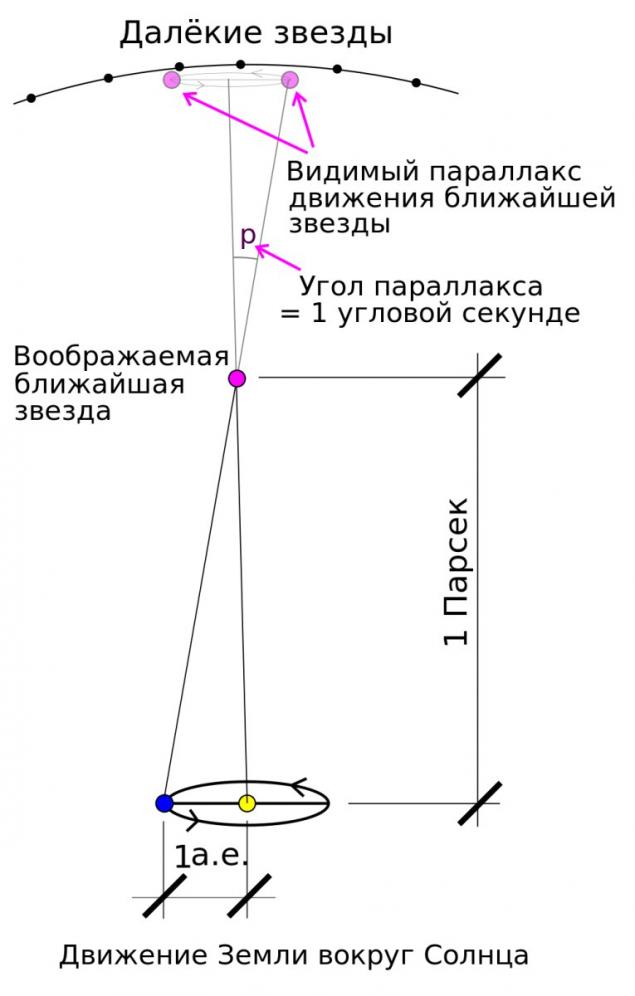
Ever wonder how scientists determine the distance to the star? After all, a laser rangefinder, this distance can not be measured. In fact, everything is simple. During the year, the position of the stars in the sky changes due to treatment of the Earth in its orbit around the sun. This change is called the annual parallax of stars. The closest star to us, the greater its bias against the stars that are further away. But even the nearest stars this shift is extremely small. Inability to detect a parallax of stars in its time was one of the arguments against the heliocentric system of the world. It was possible to do it only in the XIX century. At the present time, to measure the parallax, and hence the distances to the stars, to deduce the orbits of special space telescopes. Hipparcos Telescope of the European Space Agency (named in honor of Hipparchus, who classified the stars in brightness) allowed to measure the parallax of more than 100 thousand stars. In December 2013 launched on his successor, Gaia.
Actually, the parallax (and it is not just an astronomical term) is the change in the apparent position of the object relative to the remote background (in this case the more distant stars), depending on the observer's position. It is used in geodesy. What matters for the photos. Measure the parallax in arcseconds (seconds of arc).

Lightyear
To measure distances in space in kilometers is not convenient. For example, the distance to the nearest star, Proxima Centauri - 4, 01 × 1 013 km (40 1 trillion kilometers). It is quite difficult to imagine the distance. But if we measure the distance in light years, the unit of length equal to the distance traveled by light in one year, you get a 4, 2 light years. Light from the red dwarf that is coming to us about 4 years and 3 months. It's simple.

Parsec
But on the other unit of length used in astronomy, it is not so simple. The distance to the star Proxima Centauri, measured in parsecs is 1, 3 units. The word "parsec" is formed from the words "parallax" and "second" (referring to the angular seconds is equal to 1/3600 of a degree, remember the school protractor). The same parallax, by which we can measure the distance to the stars. Parsec (referred to as "PC") - is the distance from which a segment length of one astronomical unit (the radius of Earth's orbit), perpendicular to the line of sight, is seen at an angle of one arcsecond
. Galactic sleeve
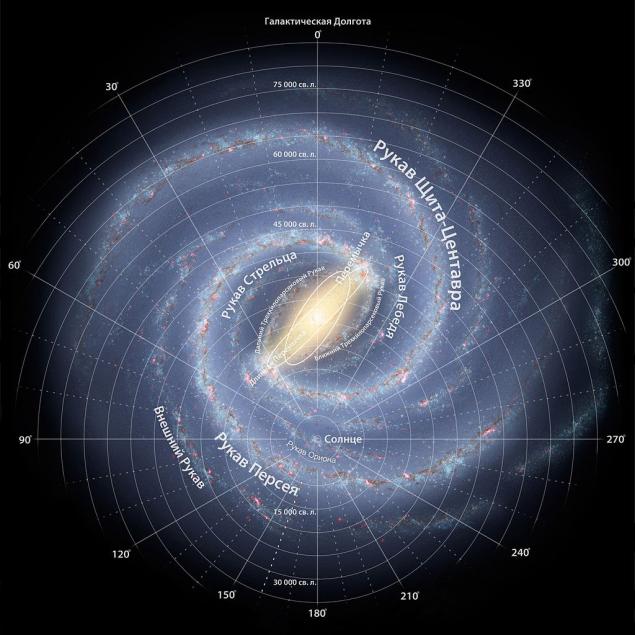
Our Milky Way has a diameter of 100,000 light years. It belongs to one of the main types of galaxies. Milky Way - is a barred spiral galaxy. All the stars we see in the sky with the naked eye are in our galaxy. Total Milky Way contains, according to various estimates, from 200 to 400 billion stars. How to navigate and to find out where the sun is among the billions of stars?
Milky Way - the spiral galaxy, and it has a spiral galactic arms, located in the plane of the disk. Galactic sleeve - it is a structural element of a spiral galaxy. Main number of stars, dust and gas is contained in the galactic arms.
Such sleeves somewhat, but it is the main arm Sagittarius, Norma Arm, the Perseus arm, sleeve and sleeve Orion Centaurus. Such names they have received on behalf of the constellations, which can be seen the bulk of the sleeves. Orion sleeve, as compared with the other small. Sometimes it is even called the Orion Spur. Its total length is about 11 000 light-years. But for us, this sleeve is remarkable that the sun and a small blue planet orbiting it, and is our home, are found in it.
Apsis
Most of the known orbits of artificial satellites and celestial bodies elliptical. And for any of the elliptical orbit is always possible to find a point that is closest to the central body and the most remote from it. The next point is called pericenter, and the most distant - apocenter
. But as a rule, instead of the word "center", after the "peri" or "apostle", substitute the name of the body, around which there is a movement. So, for the orbits of artificial satellites of the Earth (Gaia - in ancient Greek), and the Moon's orbit terms apogee and perigee is used. For the lunar (moon - Selena) orbit is sometimes used apolune and perilune. The closest to the Sun (Helios), the point of the orbit of the planet or other celestial body of the solar system - the perihelion, the future - or aphelion aphelion. For orbits around other stars (Astron - star) - periastron and apoastron
. Astronomical unit
The perihelion of the orbit of the planet (the closest point of the orbit to the Sun) is 147,098,290 km (0, 983 astronomical units), the aphelion - 152,098,232 km (1, 017 astronomical units). But if you take the average distance from the Earth to the Sun, it turns out convenient unit of measurement in space. For those distances, which measured in kilometers is already uncomfortable, but in light years and parsecs still uncomfortable. This unit is called the "astronomical unit" (denoted by "a. E.") And is used to determine the distances between the objects of the solar system, extra-solar systems, as well as between components of binary stars. After several revisions astronomical unit is recognized as equal to 149597870, 7 kilometers.
Thus, the Earth away from the Sun at a distance of 1. . E, Neptune, the farthest planet from the Sun - a distance of about 30 a. . E The distance from the Sun to the nearest to his planet - Mercury - only 0, 39 and. e. And at the time of the next great confrontation of the Earth and Mars, July 27, 2018, the distance between the planets will be reduced to 0, and 386. e.
Roche limit
In space, nothing is permanent. Just to change the usual order, we need millions of years. For example, if a supervisor in a few million years to observe Mars, he can not find him one or even two of his companions. As is known, the larger of the red planet moons - Phobos - approaches it by 1, 8 meters per century. Phobos moves at a distance of about 9000 km from Mars. For comparison, the orbit of navigation satellites are located at an altitude of 19 400-23 222 km, geostationary orbit - 35 786 km, and the Moon, the natural satellite of our planet, the Earth is at a distance of 385,000 km
. It will take another 10-11 million years, Phobos will pass its Roche limit, resulting in a collapse. Roche limit, named after Edward Roche, the first time to calculate such limits for some satellites - is the distance between the planets (stars) to her companion, whose closest satellite is destroyed by tidal forces. It was found that the force of attraction of the planet by centrifugal force is compensated only in the center of mass of the satellite. At other points of the satellite such equality no strength, and that is the reason for the formation of tidal forces. As a result of tidal forces first satellite becomes an ellipsoidal shape, and the passage of the Roche limit is broken by them. But the orbit of another satellite of the red planet - Deimos (about 23 500 km altitude orbit) - each time more and more. Sooner or later it will overcome the pull of Mars and go to an independent journey through the solar system.
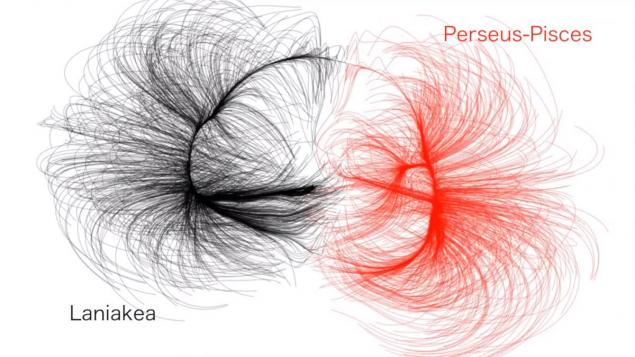
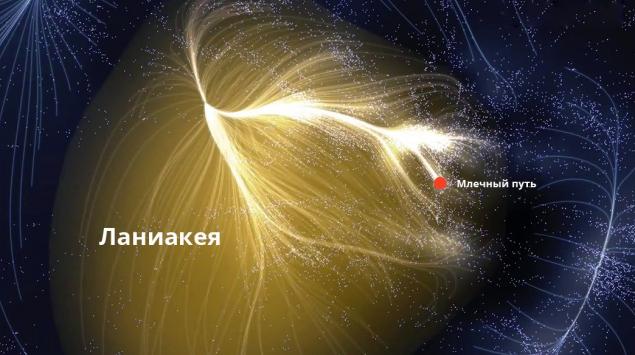
Laniakea supercluster
Can you tell me where in the universe is our planet? Of course, the planet Earth is in a solar system, which, in turn, is part of the Milky Way galaxy, which, as we know, is in the Orion Arm. Well, then? Our galaxy, the nearest to our galaxy Andromeda Galaxy and the Triangulum galaxies, more than 50 are included in the so-called Local Group of galaxies, which is part of the Virgin Supercluster.
But already supercluster Virgin, also known as the Virgo Supercluster, Hydra-Centaurus supercluster and Peacock, American Indian, and Southern supercluster supercluster of galaxies form, called laniakea supercluster. It contains approximately 100 thousands of galaxies. Diameter Laniakei - 500 million light years. For comparison, the diameter of our galaxy - only 100 thousand light-years. Translated from Hawaiian laniakea supercluster means "boundless skies." As a whole accurately reflects the fact that in the foreseeable future, to fly to the edge of the "heaven" we are unlikely.
Man lost in the woods and came across a lone car ... The story of the unexpected end
The most comprehensive guide manicure