746
A look at Mars from Mars Express

In a Mars orbit thirteenth year continues its work the European Mars Express satellite. This product was launched in cooperation with the Russian Space Agency - gave our rocket and put some scientific instruments and satellite built the European Space Agency. Mars Express flying on an elongated orbit that allows it not only to map the surface, but rather shoot spectacular views from a great distance. Several shots look today.
Mars Express has a large number of scientific instruments that allow him to study the atmosphere and geology of Mars, but the most impressive images creates a High Resolution Stereo Camera (HRSC), developed in Germany.
All the results of the Mars Express are laid out in the open access , so they may be used not only by professionals, but and enthusiasts. For example the gorgeous panorama created enthusiast space research Justin Cowart.
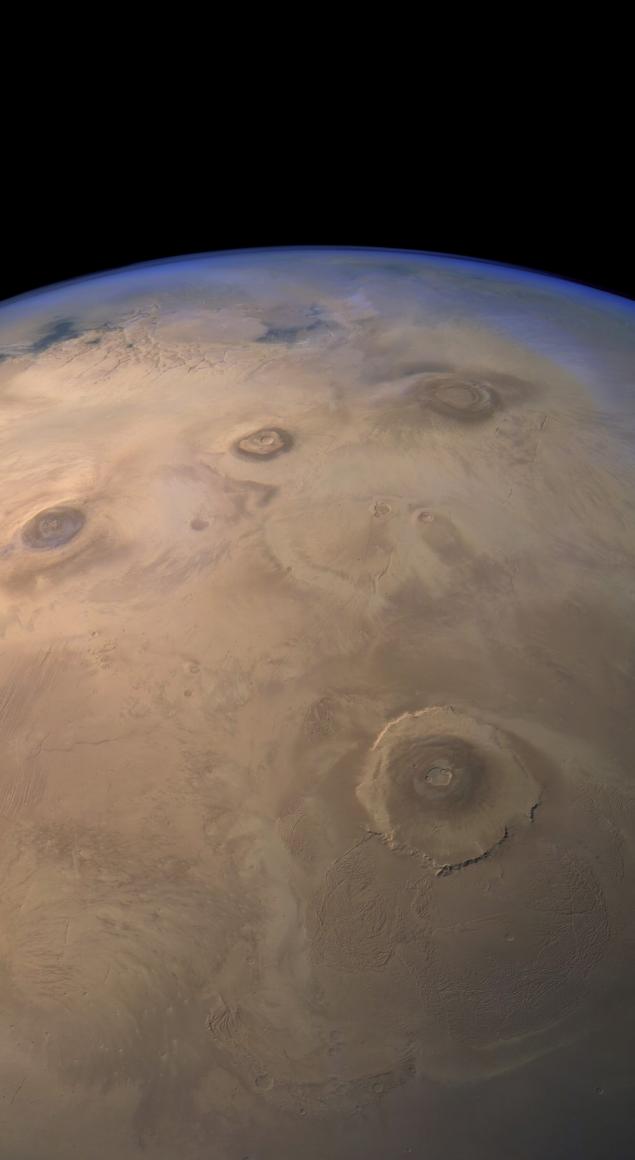

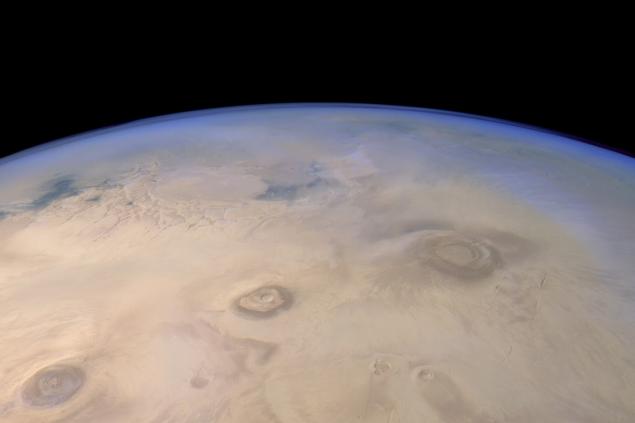
At the bottom of the frame you can see the cake is the largest volcano in the solar system - Olympus. A little further - three volcanoes: Arsiya mountain Askariyskaya and Pavonis Mons. At the horizon - Labyrinth of Night and Western branches of Valles Marineris
.
Survey conducted during windless weather, when the atmosphere is clean from dust. This can be seen scattering of sunlight, which is painted in blue shades of the atmosphere near the horizon.
HRSC camera uses technology multispectral (multichannel) shooting , ie its sensors include not only visible light, but also near-infrared. And creating a color image can be alternated different channels to obtain not only the natural color and a "false", which allows you to better understand the geological structure.
For example, it is a color photo of the South Pole collected from staff in the three spectral bands: blue, green and near-infrared, so the color does not correspond to what our eyes would see. In the visible range rust Mars is closer to orange or pink rather than claret. The reddish color of Mars due to the admixture of iron oxides in its dust, covering almost the entire surface.
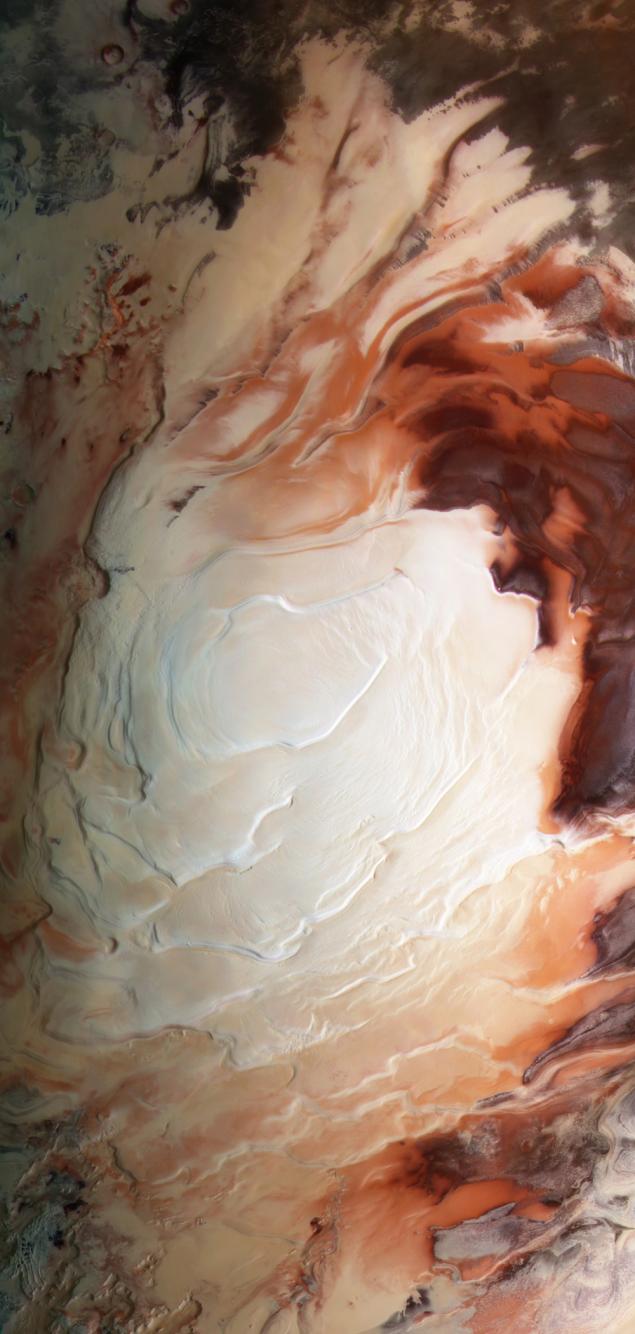

The basic structure of the polar caps of Mars - water ice . At the South Pole, its thickness reaches 3, 5 km, in the North - 1, 7 km. Carbon dioxide ice poles are covered only in the winter, and the thickness of the dry ice is 1-2 meters, rarely more. In this photo we see mainly water ice.
Pay attention to the geometrically correct structures in the lower left corner of the pan. This site is officially called Inca Sity - «City of the Incas". However, the formation of this structure is not associated with the Incas, nor the Martians, and came under the influence of a large meteorite on the ice cap of Mars.
And this view is already in natural colors - a winter view of the north pole of Mars
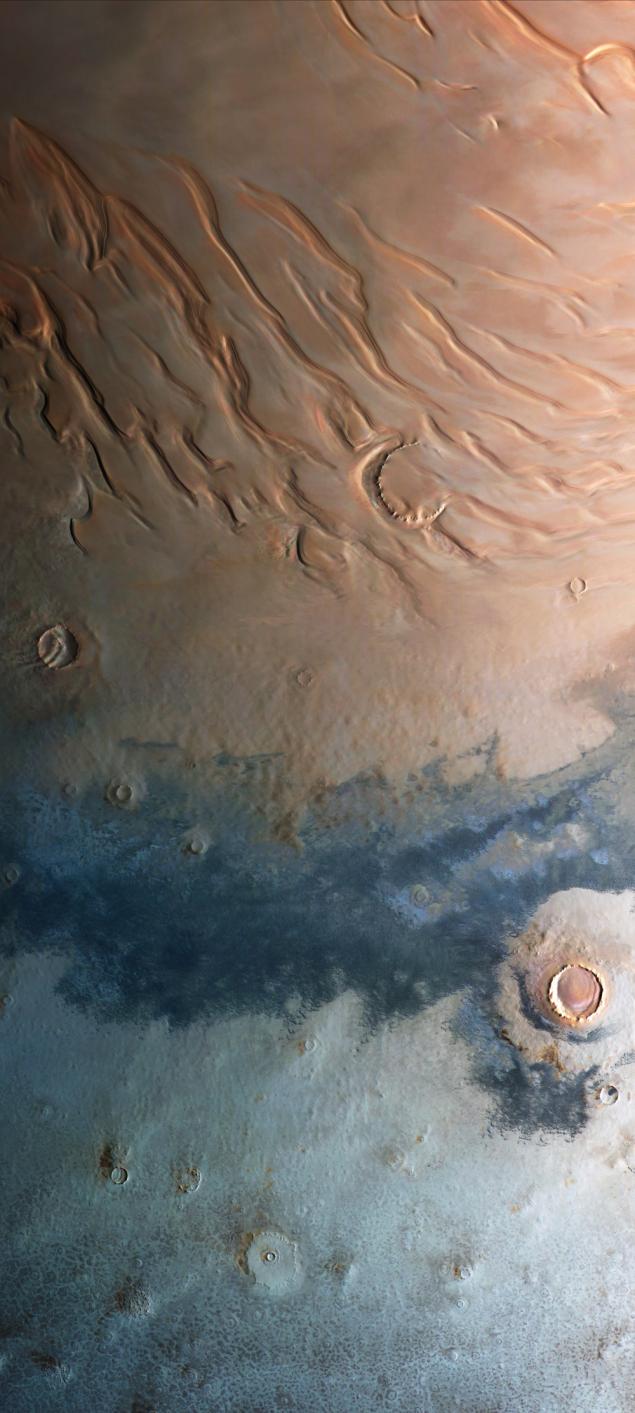

At the top of the panorama we see long-term polar cap composed of water ice. In the central part - the field of black sand dunes, which are considered, used to be the bottom of the Arctic Ocean Mars. Below the surface of Mars, covered with a thin layer of seasonal carbon dioxide ice.
Note the steep cliffs of the polar caps, which reveal its layered structure. Look for thin ice glaze covering the circumpolar regions. Consider halos round craters that arose when the meteor strikes melted the frozen ground water, spreading the dirt around the boat, but quickly froze.
In March of 2016 to Mars have to go one more joint research unit ExoMars. I hope it will please us no less impressive scenery, and expand our knowledge of the structure and evolution of Mars. I still talk about it more.
The post is based on materials planetary.org and community " Best Mars ». i>
Source: geektimes.ru/post/270882/