982
Printed on a 3D printer missile was tested injector temperature of 3000 degrees Celsius
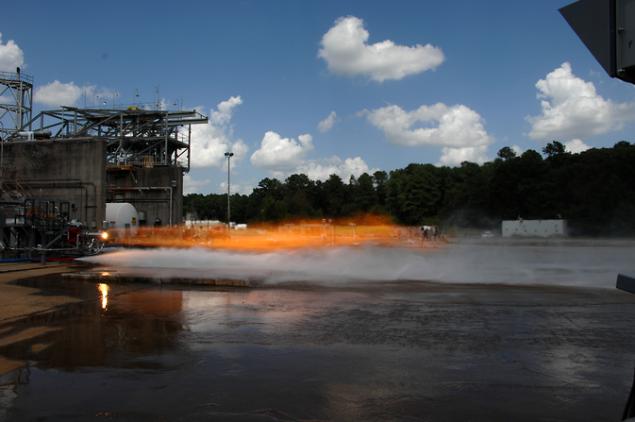

Not so long ago, NASA is already talked about their success in making important engine parts spacecraft c using the method of laser-sintering. Technology is gradually improving, and engineers are becoming more reliable and sophisticated engine components.
Thus, recently were tested rocket injectors who were tested very high temperature: about 3300 degrees Celsius. In the injector mixed liquid oxygen and hydrogen gas, whereby thrust developed at 9 tonnes.
Rocket Injector - one of the most difficult parts in the production of rocket motor, so that the production of that item using the laser sintering process is much cheaper. By the way, tested element size is obyno injector small rockets, and Disa new injector is similar to the design of injectors large engines (for example, for the largest motor RS-25).
The traditional process of manufacturing of such injectors require the creation of the entire system of 163 parts. A 3D technology reduces the number of elements to two, which, of course, reduces the cost of time and money for the production of injectors and engine as a whole.
Tests were carried out for the two injectors, each of which is made by a private company commissioned by NASA. One of the injectors manufactured by Solid Concepts, another - Directed Manufacturing. According to the developers, the new technology can accelerate the process of creating a reliable engine for the new type of missile, without the need for tens and hundreds of parts for one injector.
Via NASA
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/235195/