1191
Seven of tiny dust particles may clarify the origin of the solar system
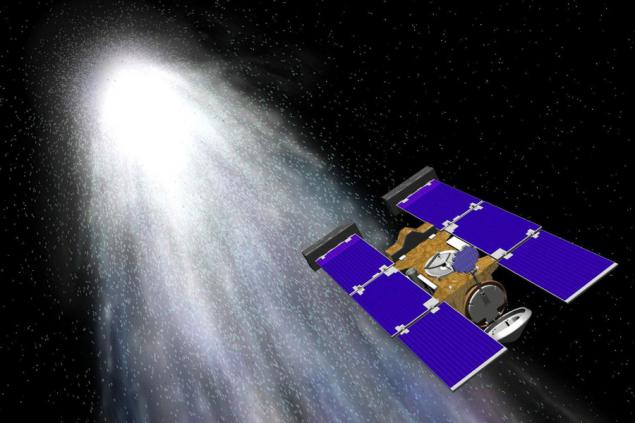

Project Stardust - one of the most extensive and complex in the world of science. Back in 1999, was sent into space a small spacecraft Stardust. Its name reflects the main purpose for which the probe was launched: to collect samples of interstellar dust, and deliver collected on Earth. The first mission of the unit was in the rapprochement with the comet Wild 2 and collect samples of the substance in its tail.
After the comet probe continued its mission, and successfully collected samples of cosmic dust. It is clear that no dust is collected in a paper bag: for the assembly of the samples substances used Aerogel collector, which when ingested mikrochastichki remained intact. According to scientists, these mikrochastichki - The oldest traces the evolution of our solar system and the galaxy as a whole. The study samples of interstellar dust can be clarified and the way in which the formation of the solar system went on, the birth of stars and many other issues.

Stardust collected dust until 2006, the unit was a journey of 3 billion kilometers. Then Stardust passed close to Earth, dropping capsule trapped dust (capsule fell in Utah). In the fall of the collector itself was not damaged, but airgel inside - was, so scientists had to solve even the problem with the damaged surface of the airgel. This problem was solved successfully.
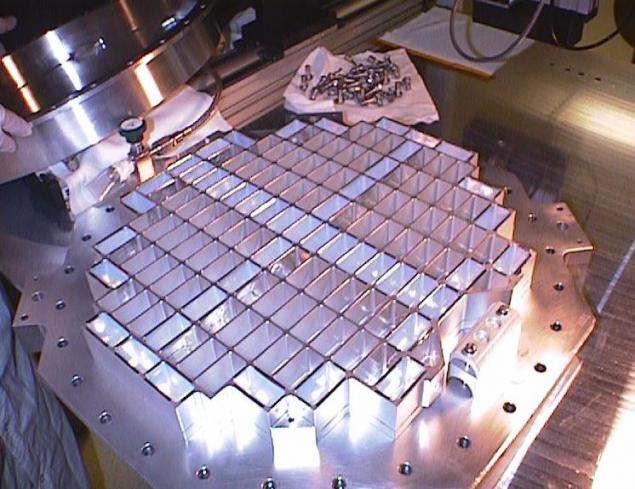
Here is the collector (diameter - about 30 centimeters)
They then began to scan specific areas of the airgel, and scanning was carried out in layers, starting from the surface of the gel, and ending with "bottom" of the cell. After scanning, it turned out that in the hands of scientists - more than 700 thousand sets of images kazhogo area (the number of individual images exceeds several million). Work on the study of interstellar matter was complicated, because the photographs recorded not only the "dust", but also damage to the airgel.
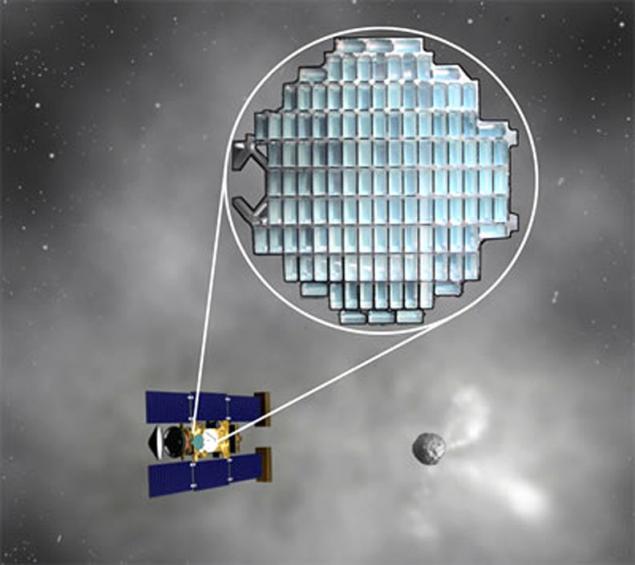
In general, researchers faced a lot of work, which for the foreseeable future, they could not cope. Therefore it was decided to involve the public. To this end, the project was organized by «Stardust @ home», where after initial training to any interested person could start work on the detection of samples of interstellar matter.
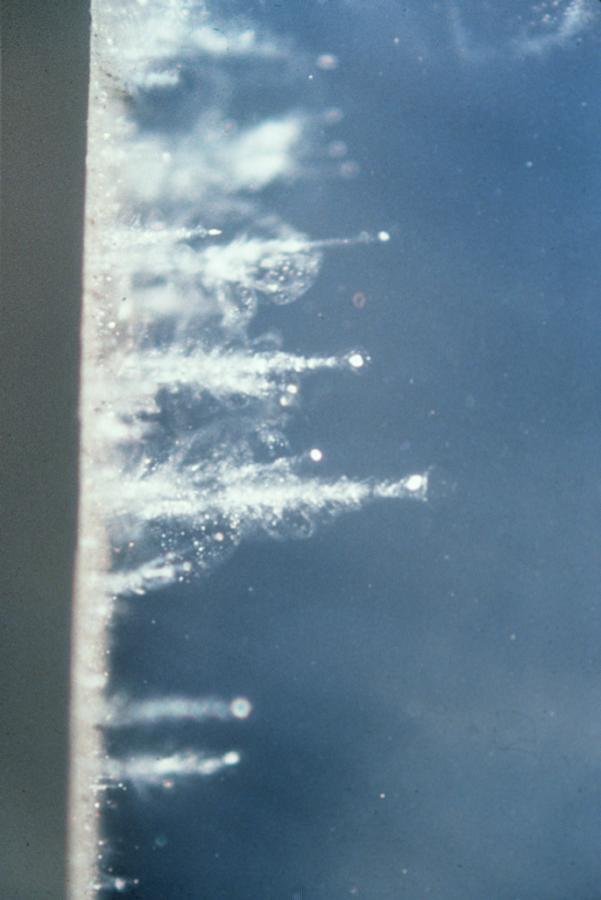
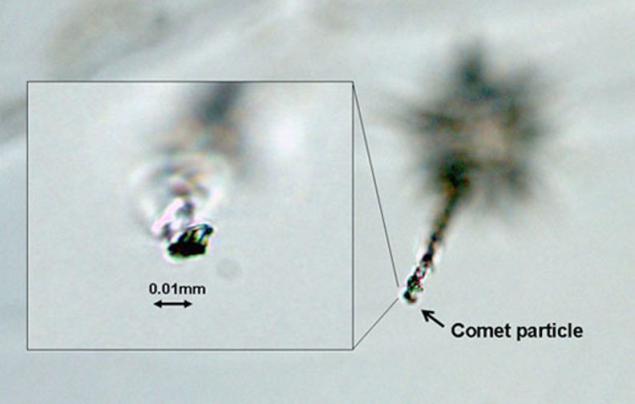
Traces of penetration of particles in airgel
Only now, in 2014, were published preliminary results all this gigantic work (work in progress, it is checked only 77 airgel plates, left 55). The project involved more than 30,000 volunteers, in addition to scientists from NASA . When it detects something, what volunteer suspected desired sample photo tagged. After this picture closely studied by scientists, followed by the study sample, which was photographed. For the study sample used a scanning X-ray microscope, to obtain information about the chemical composition of the sample. Volunteers, by the way, each other called «Dusters». Of the 30 thousand 714 voluntary participants in the project have already been mentioned in scientific publications related to the project «Stardust».

After careful consideration of all the materials it turned out that most of the samples - microscopic particles of the device, broken shell of micrometeorites (if these objects can be called that, of course, very much they are small), faced with the device within the solar system. These particles are easily detected because they have a lot of aluminum is made from the metal shell «Stardust». Found in particles of traces of gas produced in the collision of particles from the solar panels of the probe.
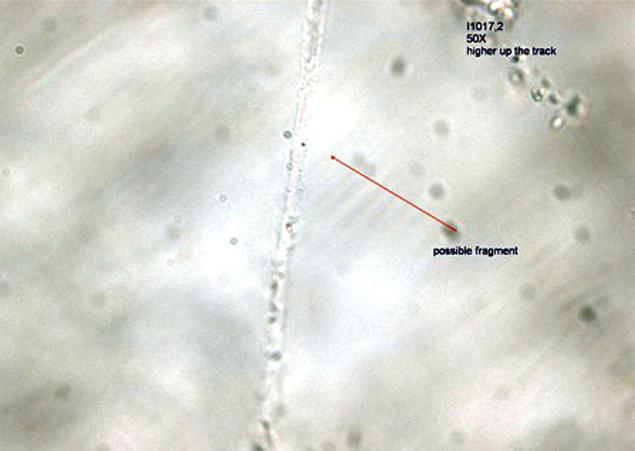
At the moment, found only 7 samples that scientists are more likely to believe thus interstellar matter. The size of particles - a maximum of 2 microns (0, 002mm), is 2% of the thickness of a human hair. Nevertheless, the scientists hope that these samples will clarify our stages of the solar system. Furthermore, in the future, researchers hope remaining samples give additional material for testing. Now study has found samples.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/235071/