1956
German rocket artillery during the war
Today, I write a post "British and American rocket artillery, during the Second World War", and commenting examining the request, decided to make a correction to its story about the German rocket artillery.
In the first part of the German artillery can be found by reading the post «Nebelwerfer», it was written in aprele.Segodnya will continue to tell you about the arming of Germany during the Second World War and the Great Patriotic War.
In February 1943, adopted the German armed forces was adopted by 300-mm rocket blast mine 30 cm Wurfkorper Wurfgranate Spreng (30 cm WK.Spr.42), created by taking into account the experience of combat use of 280/320-mm rockets. This projectile weighing 127 kg and a length of 1248 mm had range 4550 m, ie twice as large as in previous rounds.
16 pictures, via Sergei Linnik.

Firing projectiles 300 mm projectiles intended to carry on with a newly developed six-launcher Nebelwerfer 42 30 cm (30 cm WK Spr. 42). Since February 1943 the division of these units passed combat tests in July of the same year adopted a unit. Unit weight - 1100 kg, the highest elevation angle - 45 degrees, the angle of the horizontal fire - 22, 5 degrees.
Launchers 30 cm WK Spr. 42 operated by the heavy battalions of the Wehrmacht of rocket artillery brigades. They were used in the fighting on the Eastern and Western fronts until the end of hostilities.
For the production of bursts of installation 30 cm Nebelwerfer 42 took only 10 seconds, and after two and a half minutes of installation could give another volley. As retaliation for the enemy was required, as a rule, much more time divisions such installations are usually given two volleys and then left their firing positions. Availability of progress sprung carriages allowed to tow a unit with a speed of 30 km / h.
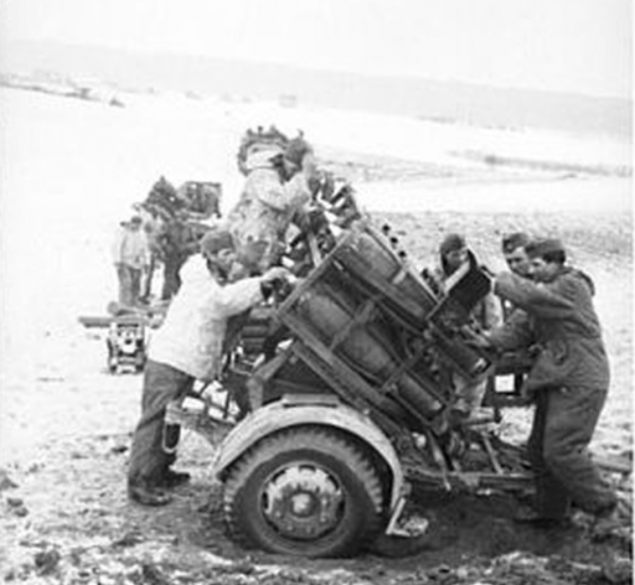
Preparation of 30 cm to 42 Nebelwerfer shooting

In the future, this setting has changed in the production of a more advanced missile launcher 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56. Total for the production of 380 units were released 30 cm Nebe Svyerfer 42. Since the beginning of the production of 300-mm rockets in 1943, it lasted almost until the end of the war, only produced more than 200,000 units.
Launcher 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56 mounted on a converted carriage of 50-mm anti-tank cannon 5 cm PaK 38. The angle pointing vertically from -3 to +45 degrees horizontally - 22 degrees. By means of special inserts of 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56 can be firing 150-mm shells 15cm Wurfgranate 41, which significantly increases the flexibility of the MLRS. Also, there was a possibility of firing 300-mm shells from the ground. Ammunition were charged in the closing 280/320-mm rocket min. Obturation is achieved by using special inserts. Weight, charged rockets, reached 738 kg.
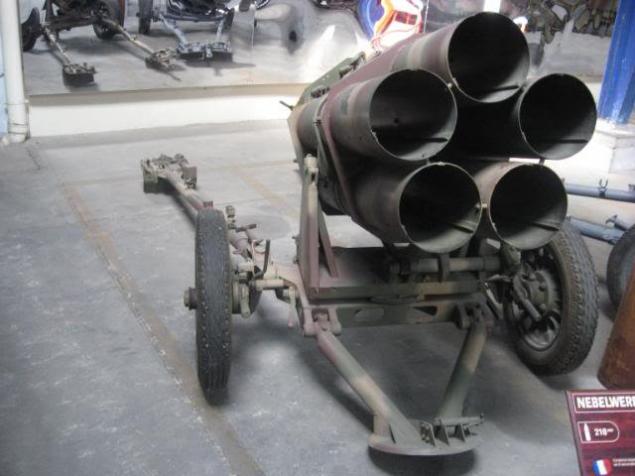
Installation 30 56 cm Raketenwerfer

Of produced a total of 1,300 units of 30 cm Nebe Svyerfer 42 and 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56 who actively used on all fronts until the end of hostilities, the battles were lost not more than a third of the original amount.
The most successful of all German towed MRL became pyatistvolnaya 210 mm 21cm Nebelwerfer 42 wheeled carriage guns Pak 35/36. To fire missiles used 21 cm Wurfgranate. Other characteristics 21cm Nebelwerfer 42 were identical PU applied to run the 150-mm rockets. Combat weight 1100 kg mass in the stowed position - up to 605 kg. The shells were produced alternately with the smallest interval of 1, 5 seconds, a volley was made for 8 seconds, cooldown mortar takes about 1, 5 minutes. During operation of a jet engine (1, 8 seconds) RS accelerated to speed of 320 m / s, which provides range in 7850metrov.
21 cm Nebelwerfer 42

High-explosive rocket 21cm Wurfgranate 42 Spreng was first used on the front in 1943. She was very reliable and efficient, and had a successful ballistic shape. The stamped combustion chamber was placed 18 kg of jet fuel (7 tubular sticks of powder). The neck is screwed camera perforated bottom 22 inclined nozzles (angle of inclination of 16 degrees) and a small central hole, which invest in the electric fuse.
The body of the warhead was made by hot stamping of 5 mm sheet steel. It equips cast trinitrotoluene or amatol mass 28, 6 kg, and then screwed onto the thread in front of the combustion chamber. To the front of the warhead fuze is screwed shock. The required form of ballistic missile was provided housing, put on the front of the warhead.
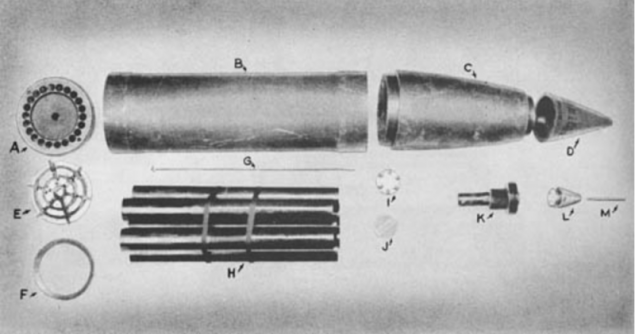
Rocket 21cm Wurfgranate 42 Spreng unassembled
From installation 21 cm Nebelwerfer 42 had the opportunity to fire single rounds, which facilitated the sighting. Also, by using special inserts could fire 150-mm shells from six-15 cm Nebelwerfer 41.
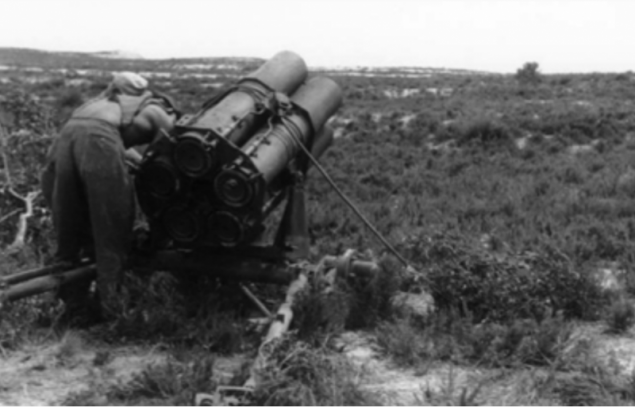

If necessary, 21 cm Nebelwerfer 42 can be transported over short distances by the calculation. These units are actively used by the Germans to the last days of the war. Total produced nearly 1,600 towed MLRS type.
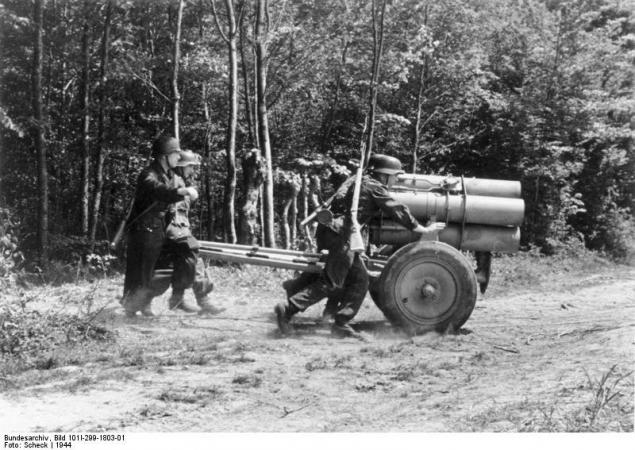

In 1942, the Germans managed to capture the Soviet machine rocket artillery BM-13 rockets to it. Contrary to popular myth, the Soviet, the machines themselves rocket artillery with guide rail type and missiles M-13 presents no particular secret. They were very simple device, manufacturable, and inexpensive to manufacture.
Secret has been the technology of production of powder sticks jet shells of M-8 and M-13. It was necessary to make drafts of smokeless gunpowder nitroglycerin, which would provide a uniform traction, and have no cracks and cavities, the presence of which could lead to uncontrolled processes of burning jet fuel. The diameter of the powder sticks to the Soviet missile is 24 mm. Their size and determined two main caliber rockets - 82 and 132 mm. German experts have failed to reproduce the technology of powder sticks for engines of Soviet missiles, and they had to develop its own propellant formulations.
Captured by the Germans install BM-13

In late 1943, the Czech plant engineers «Ceska Zbrojovka» Brno created their own version of the Soviet 82-mm missile M-8.
80-mm rocket was similar to its prototype characteristics, but accuracy due to the rotation to be reported stabilizers (set at an angle to the body shell) was higher than that of the Soviet model. The electric fuse was put to one of the leading belts, making the rocket more reliable. Missile, designated 8 cm Wurfgranate Spreng was more successful than its Soviet prototype.
It was copied and charging 48 launcher, unusual for a German rail type, dubbed 8 cm Raketen-Vielfachwerfer. Launchers 48 rockets mounted on the chassis of captured French tanks SOMUA S35. Guides mounted turret removed instead.
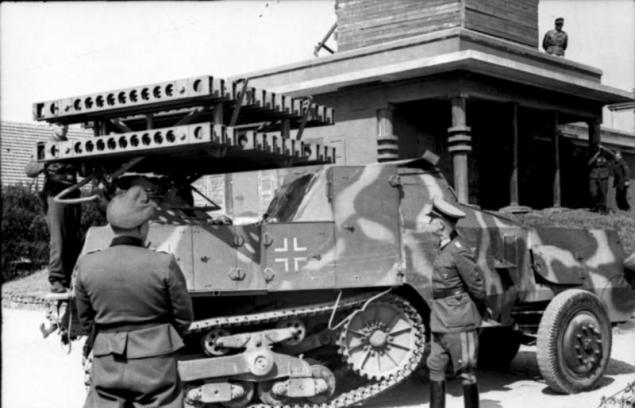

Lite version of the system - 24 guides arranged in two tiers, established on the basis of various half-track armored vehicles and a specially designed sample, which was used for the base of the trophy of the French semi-tracked tractor SOMUA MCG / MCL. Installation was designated 8 cm R-Vielfachwerfer auf m.ger.Zgkw S303 (f).
80-mm rocket launchers were mainly used rocket artillery divisions chetyrehbatareynogo composition, which gave the tank and motorized units SS
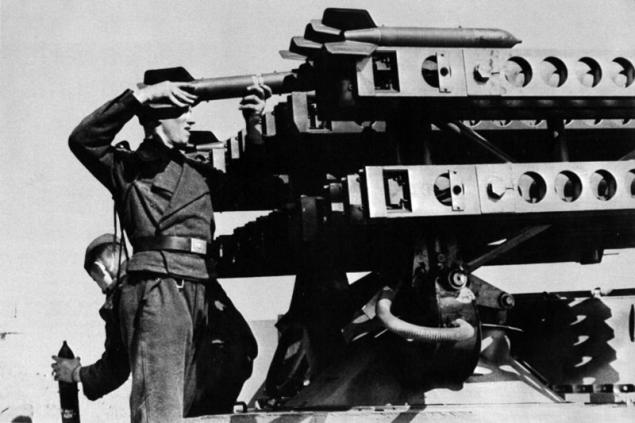

Unlike the missile M-8, a copy of the German M-13 has undergone great changes. To increase the fragmentation warhead, the German version of the caliber was increased to 150 mm. Manufacturing process has been simplified, rather than bolted connections used welding. Instead of powder sticks used grainy jet fuel. Due to this, we managed to stabilize the pressure in the engine and reduce thrust eccentricity.
However, to combat the use of these missiles, it never came, although the decision on their mass production was made.
At the front were used occasionally other types of missiles (lighting and propaganda), as well as missiles, originally developed for the Air Force and Air Defense.
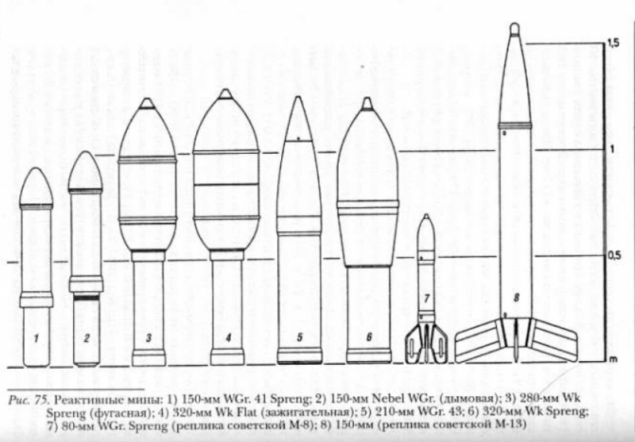
Besides missiles in Germany for large-caliber long-range guns were set up active-reactive with increased firing range. Jet engine, placed in the body of the projectile, began work on the path some time after the projectile left the barrel of the weapon. Because of the placement in the body shell of the jet engine active-missiles have a reduced bursting charge. Work on the trajectory of the jet engine adversely affects the dispersion of shells
In October 1944, a Wehrmacht adopted a heavy assault ACS - 38 cm RW61 auf Sturmmörser Tiger, known as "Shturmtigr." "Shturmtigr" converted from heavy tank "Tiger", with the conversion subject only to the fighting compartment of the tank and partly frontal reservation housing, other components also remained virtually unchanged.
SAU "Shturmtigr»
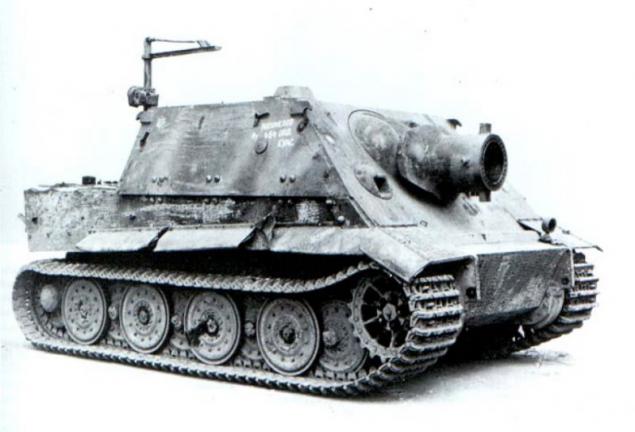

This heavy ACS was armed with 380-mm jet bombomёtom Raketenwerfer ship 61 with a barrel length of 5, 4 caliber.
Bombomёt led fire missiles with solid engine, stable in flight due to rotation, is achieved due to the inclined position of its engine nozzles, as well as the occurrence of protrusions on the body of the rocket into channels cut the gun barrel. The initial velocity of the rocket downstream of the barrel was 300 m / s. Rocket Blast Raketen Sprenggranate weighing 351 kg contained 125 kilograms of TNT.
380 mm high-explosive rocket "Shturmtigr»
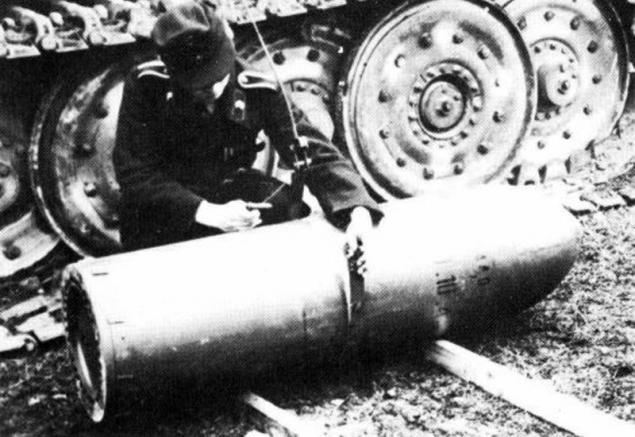

Firing range this "jet monster" was in the range of 5000 m, but in practice more than 1000 meters, did not shoot.
"Shturmtigr" were issued in the amount of only 18 copies, and influence on the course of hostilities did not have.
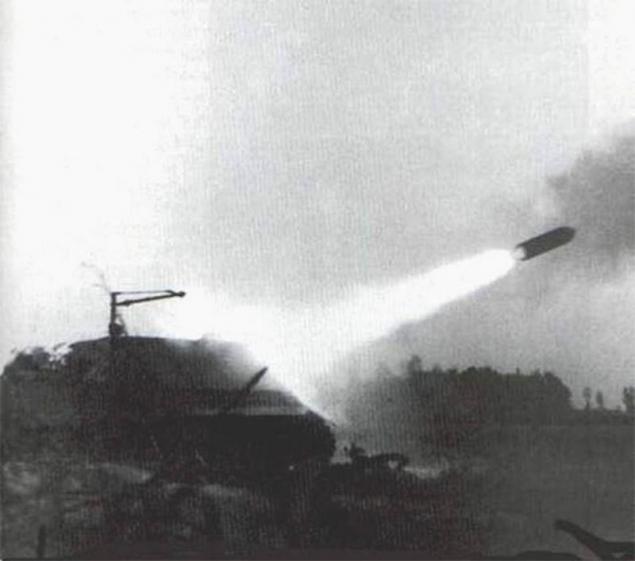

"Shturmtigr" were issued in the amount of only 18 copies, and influence on the course of hostilities did not have.
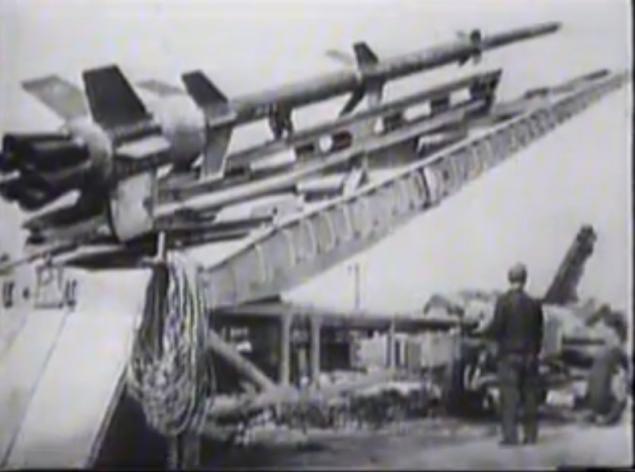
There were several versions of the rocket, which differed range and warhead weight. For service modification was adopted - RhZ6l / 9 with a warhead filled with 40 kg of high explosives. The explosion in the soil medium density formed crater depth of about 1, 5 m and a diameter of 4 meters. An important advantage of the rocket was considered its simplicity and relatively low cost. For manufacturing a rocket only required 132 man-hours.
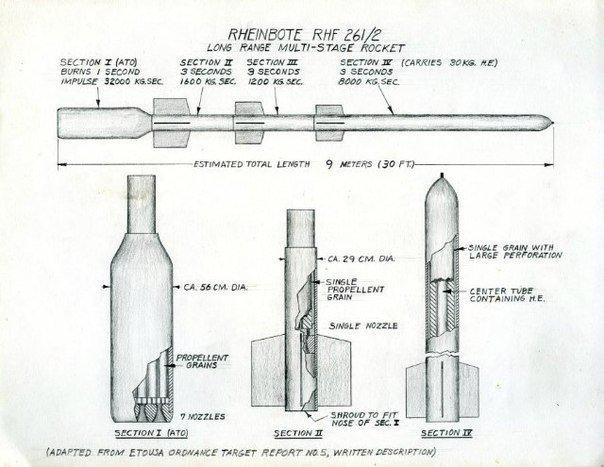
The final version of the missile had a length of 11,400 mm and weighing 1715 kg.
The diameter of the first stage was 535 mm, followed by followed by two steps 268 mm in diameter and carrying warhead fourth had a diameter of 190 mm. Solid rocket motors of all four stages contained 585 kg of gunpowder and rocket broke up to 1600 m / s.

The launch was carried out from a mobile launcher at a distance of 200 km. The accuracy was low; dispersion relative to the point of aiming higher than 5 km.
Rockets' Reinboth "was armed with specially formed 709 th Independent Artillery Battalion with a personnel strength of 460 officers and men.
From December 1944 until mid-January 1945 Division I led bombardment of the port facilities in Antwerp, through which passed the supply of Anglo-American troops. It was launched about 70 rockets. However, a significant influence on the course of fighting the shelling did not have.
Analyzing the actions of the German rocket artillery during the war, it is possible to note the differences in the tactics of the Soviet rocket artillery pieces. German self-propelled system much more involved for the destruction of individual targets and provide direct fire support. This can be explained by the fact that the accuracy of fire in the German system by stabilizing the rotation of the shells was very high: the coefficient of circular error probable no more than 0, 025-0, 0285 the value of the maximum firing range.
At the same time the Soviet MLRS, being more long-range, used a much larger scale for the destruction of surface targets.
Many technical solutions, first used in the German rocket launchers, were implemented in the post-war MLRS taken into service in different countries.
On this I have everything, thank you!

In the first part of the German artillery can be found by reading the post «Nebelwerfer», it was written in aprele.Segodnya will continue to tell you about the arming of Germany during the Second World War and the Great Patriotic War.
In February 1943, adopted the German armed forces was adopted by 300-mm rocket blast mine 30 cm Wurfkorper Wurfgranate Spreng (30 cm WK.Spr.42), created by taking into account the experience of combat use of 280/320-mm rockets. This projectile weighing 127 kg and a length of 1248 mm had range 4550 m, ie twice as large as in previous rounds.
16 pictures, via Sergei Linnik.

Firing projectiles 300 mm projectiles intended to carry on with a newly developed six-launcher Nebelwerfer 42 30 cm (30 cm WK Spr. 42). Since February 1943 the division of these units passed combat tests in July of the same year adopted a unit. Unit weight - 1100 kg, the highest elevation angle - 45 degrees, the angle of the horizontal fire - 22, 5 degrees.
Launchers 30 cm WK Spr. 42 operated by the heavy battalions of the Wehrmacht of rocket artillery brigades. They were used in the fighting on the Eastern and Western fronts until the end of hostilities.
For the production of bursts of installation 30 cm Nebelwerfer 42 took only 10 seconds, and after two and a half minutes of installation could give another volley. As retaliation for the enemy was required, as a rule, much more time divisions such installations are usually given two volleys and then left their firing positions. Availability of progress sprung carriages allowed to tow a unit with a speed of 30 km / h.
Preparation of 30 cm to 42 Nebelwerfer shooting

In the future, this setting has changed in the production of a more advanced missile launcher 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56. Total for the production of 380 units were released 30 cm Nebe Svyerfer 42. Since the beginning of the production of 300-mm rockets in 1943, it lasted almost until the end of the war, only produced more than 200,000 units.
Launcher 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56 mounted on a converted carriage of 50-mm anti-tank cannon 5 cm PaK 38. The angle pointing vertically from -3 to +45 degrees horizontally - 22 degrees. By means of special inserts of 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56 can be firing 150-mm shells 15cm Wurfgranate 41, which significantly increases the flexibility of the MLRS. Also, there was a possibility of firing 300-mm shells from the ground. Ammunition were charged in the closing 280/320-mm rocket min. Obturation is achieved by using special inserts. Weight, charged rockets, reached 738 kg.
Installation 30 56 cm Raketenwerfer

Of produced a total of 1,300 units of 30 cm Nebe Svyerfer 42 and 30 cm Raketenwerfer 56 who actively used on all fronts until the end of hostilities, the battles were lost not more than a third of the original amount.
The most successful of all German towed MRL became pyatistvolnaya 210 mm 21cm Nebelwerfer 42 wheeled carriage guns Pak 35/36. To fire missiles used 21 cm Wurfgranate. Other characteristics 21cm Nebelwerfer 42 were identical PU applied to run the 150-mm rockets. Combat weight 1100 kg mass in the stowed position - up to 605 kg. The shells were produced alternately with the smallest interval of 1, 5 seconds, a volley was made for 8 seconds, cooldown mortar takes about 1, 5 minutes. During operation of a jet engine (1, 8 seconds) RS accelerated to speed of 320 m / s, which provides range in 7850metrov.
21 cm Nebelwerfer 42

High-explosive rocket 21cm Wurfgranate 42 Spreng was first used on the front in 1943. She was very reliable and efficient, and had a successful ballistic shape. The stamped combustion chamber was placed 18 kg of jet fuel (7 tubular sticks of powder). The neck is screwed camera perforated bottom 22 inclined nozzles (angle of inclination of 16 degrees) and a small central hole, which invest in the electric fuse.
The body of the warhead was made by hot stamping of 5 mm sheet steel. It equips cast trinitrotoluene or amatol mass 28, 6 kg, and then screwed onto the thread in front of the combustion chamber. To the front of the warhead fuze is screwed shock. The required form of ballistic missile was provided housing, put on the front of the warhead.
Rocket 21cm Wurfgranate 42 Spreng unassembled

From installation 21 cm Nebelwerfer 42 had the opportunity to fire single rounds, which facilitated the sighting. Also, by using special inserts could fire 150-mm shells from six-15 cm Nebelwerfer 41.

If necessary, 21 cm Nebelwerfer 42 can be transported over short distances by the calculation. These units are actively used by the Germans to the last days of the war. Total produced nearly 1,600 towed MLRS type.

In 1942, the Germans managed to capture the Soviet machine rocket artillery BM-13 rockets to it. Contrary to popular myth, the Soviet, the machines themselves rocket artillery with guide rail type and missiles M-13 presents no particular secret. They were very simple device, manufacturable, and inexpensive to manufacture.
Secret has been the technology of production of powder sticks jet shells of M-8 and M-13. It was necessary to make drafts of smokeless gunpowder nitroglycerin, which would provide a uniform traction, and have no cracks and cavities, the presence of which could lead to uncontrolled processes of burning jet fuel. The diameter of the powder sticks to the Soviet missile is 24 mm. Their size and determined two main caliber rockets - 82 and 132 mm. German experts have failed to reproduce the technology of powder sticks for engines of Soviet missiles, and they had to develop its own propellant formulations.
Captured by the Germans install BM-13

In late 1943, the Czech plant engineers «Ceska Zbrojovka» Brno created their own version of the Soviet 82-mm missile M-8.
80-mm rocket was similar to its prototype characteristics, but accuracy due to the rotation to be reported stabilizers (set at an angle to the body shell) was higher than that of the Soviet model. The electric fuse was put to one of the leading belts, making the rocket more reliable. Missile, designated 8 cm Wurfgranate Spreng was more successful than its Soviet prototype.
It was copied and charging 48 launcher, unusual for a German rail type, dubbed 8 cm Raketen-Vielfachwerfer. Launchers 48 rockets mounted on the chassis of captured French tanks SOMUA S35. Guides mounted turret removed instead.

Lite version of the system - 24 guides arranged in two tiers, established on the basis of various half-track armored vehicles and a specially designed sample, which was used for the base of the trophy of the French semi-tracked tractor SOMUA MCG / MCL. Installation was designated 8 cm R-Vielfachwerfer auf m.ger.Zgkw S303 (f).
80-mm rocket launchers were mainly used rocket artillery divisions chetyrehbatareynogo composition, which gave the tank and motorized units SS

Unlike the missile M-8, a copy of the German M-13 has undergone great changes. To increase the fragmentation warhead, the German version of the caliber was increased to 150 mm. Manufacturing process has been simplified, rather than bolted connections used welding. Instead of powder sticks used grainy jet fuel. Due to this, we managed to stabilize the pressure in the engine and reduce thrust eccentricity.
However, to combat the use of these missiles, it never came, although the decision on their mass production was made.
At the front were used occasionally other types of missiles (lighting and propaganda), as well as missiles, originally developed for the Air Force and Air Defense.
Besides missiles in Germany for large-caliber long-range guns were set up active-reactive with increased firing range. Jet engine, placed in the body of the projectile, began work on the path some time after the projectile left the barrel of the weapon. Because of the placement in the body shell of the jet engine active-missiles have a reduced bursting charge. Work on the trajectory of the jet engine adversely affects the dispersion of shells

In October 1944, a Wehrmacht adopted a heavy assault ACS - 38 cm RW61 auf Sturmmörser Tiger, known as "Shturmtigr." "Shturmtigr" converted from heavy tank "Tiger", with the conversion subject only to the fighting compartment of the tank and partly frontal reservation housing, other components also remained virtually unchanged.
SAU "Shturmtigr»

This heavy ACS was armed with 380-mm jet bombomёtom Raketenwerfer ship 61 with a barrel length of 5, 4 caliber.
Bombomёt led fire missiles with solid engine, stable in flight due to rotation, is achieved due to the inclined position of its engine nozzles, as well as the occurrence of protrusions on the body of the rocket into channels cut the gun barrel. The initial velocity of the rocket downstream of the barrel was 300 m / s. Rocket Blast Raketen Sprenggranate weighing 351 kg contained 125 kilograms of TNT.
380 mm high-explosive rocket "Shturmtigr»

Firing range this "jet monster" was in the range of 5000 m, but in practice more than 1000 meters, did not shoot.
"Shturmtigr" were issued in the amount of only 18 copies, and influence on the course of hostilities did not have.

"Shturmtigr" were issued in the amount of only 18 copies, and influence on the course of hostilities did not have.
There were several versions of the rocket, which differed range and warhead weight. For service modification was adopted - RhZ6l / 9 with a warhead filled with 40 kg of high explosives. The explosion in the soil medium density formed crater depth of about 1, 5 m and a diameter of 4 meters. An important advantage of the rocket was considered its simplicity and relatively low cost. For manufacturing a rocket only required 132 man-hours.

The final version of the missile had a length of 11,400 mm and weighing 1715 kg.
The diameter of the first stage was 535 mm, followed by followed by two steps 268 mm in diameter and carrying warhead fourth had a diameter of 190 mm. Solid rocket motors of all four stages contained 585 kg of gunpowder and rocket broke up to 1600 m / s.

The launch was carried out from a mobile launcher at a distance of 200 km. The accuracy was low; dispersion relative to the point of aiming higher than 5 km.
Rockets' Reinboth "was armed with specially formed 709 th Independent Artillery Battalion with a personnel strength of 460 officers and men.
From December 1944 until mid-January 1945 Division I led bombardment of the port facilities in Antwerp, through which passed the supply of Anglo-American troops. It was launched about 70 rockets. However, a significant influence on the course of fighting the shelling did not have.
Analyzing the actions of the German rocket artillery during the war, it is possible to note the differences in the tactics of the Soviet rocket artillery pieces. German self-propelled system much more involved for the destruction of individual targets and provide direct fire support. This can be explained by the fact that the accuracy of fire in the German system by stabilizing the rotation of the shells was very high: the coefficient of circular error probable no more than 0, 025-0, 0285 the value of the maximum firing range.
At the same time the Soviet MLRS, being more long-range, used a much larger scale for the destruction of surface targets.
Many technical solutions, first used in the German rocket launchers, were implemented in the post-war MLRS taken into service in different countries.
On this I have everything, thank you!