3445
Russian diamonds
Surprisingly, diamonds are now mined from kimberlite pipe - only underground volcano eruption that occurred millions of years ago. Take a look as extract the most expensive and aesthetic gems in the continuation of this post.
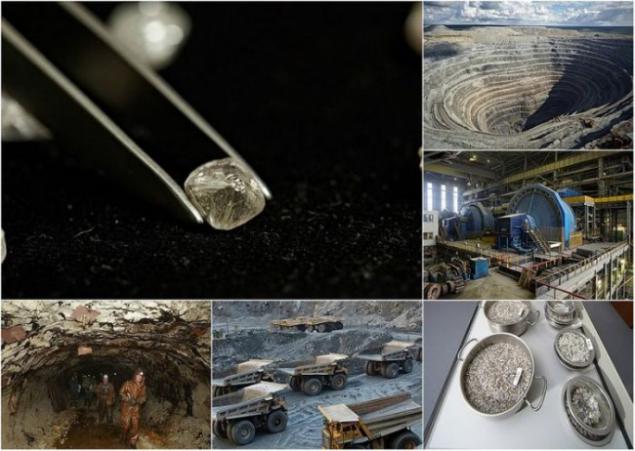

In the photo - view of the main career Udachninsky ore processing plant - "Lucky." Mining operations on the same field were started in 1971 and over the past 25 years Plant is a leading diamond mining company in Russia and one of the largest open-pit mines in the world. In 2010, the share of Udachninsky GOK had 33, 8% of diamond production in terms of value and 12, 5% of mining operations from the total in the group "Alrosa».

The first large-scale commercial production of diamonds began in southern Africa about a hundred years ago. In Russia, the kimberlite pipes were discovered only in the middle of the last century - in Yakutia. This discovery marked the beginning of "ALROSA" - today a world leader in diamond mining. So, probable reserves of the company amount to about a third of the world's, and explored enough to maintain current production levels for 25 years without reducing the quality of raw materials. If the figures, the reserves of diamonds belonging to the "ALROSA" fields is (according to data released in May 2011) 1, 23 billion carat under Russian classification (1, 014 billion - proven and 0 211 000 000 000 - possible).

The past five years, the company annually sends Exploration 2, 5 and 3, 5 billion rubles. In 2011, exploration costs amounted to about 4 billion rubles., In 2012 - more than 5, 36 billion rubles.
In their fields "Alrosa" produces about 35 million carats of diamonds per year, being the world's largest producer of this raw material in physical terms: it accounts for about 97% of Russian oil production and 25% of the world. The content of the diamond grade kimberlite pipes are traditionally small - usually a few carats per tonne. Yakut deposits are advantageous in this respect, and is considered one of the richest in content.

In 2010, the volume of sales of diamonds and diamond raw materials "ALROSA" was $ 3, 48 billion, and in 2011, according to preliminary data, the company sold products worth $ 5 billion - a record number in its history. The company's revenue in the first half of 2011 under IFRS was 66, 15 billion rubles. (+ 3% the previous year), and net profit increased fivefold to 26, 27 billion.
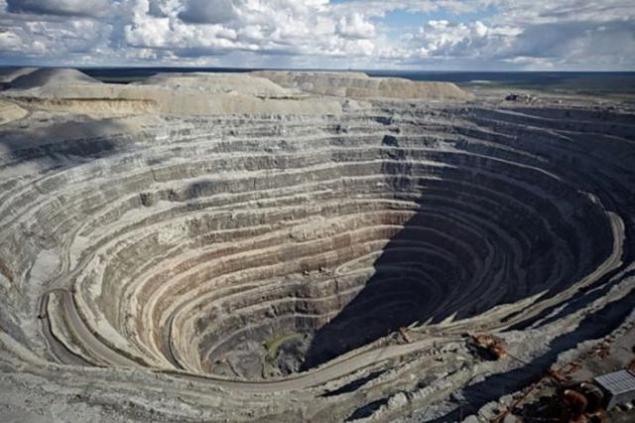
Kimberlite pipes are cone-shaped, extending up, so they usually start practicing with quarrying. The project depth of the quarry "Lucky" depicted in these photographs - 600 m. In order to rise from the bottom of the quarry to the surface, dump on the "serpentine" overcomes the path length of about 10 km.

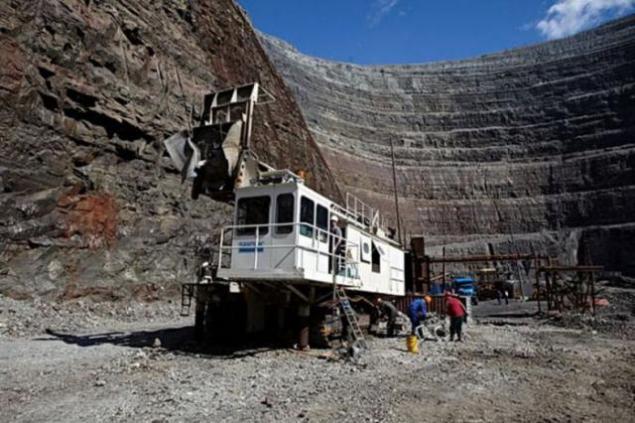
But so are mined in quarries. The rig is doing well, which laid the explosive (pictured - the process of laying). By the way, even though the diamond is the hardest mineral, it is quite fragile. Therefore, when blasting uses soft technologies, allowing to preserve the integrity of the crystals. After the explosion of rock fragments are loaded into dump trucks and transported to the processing plant.
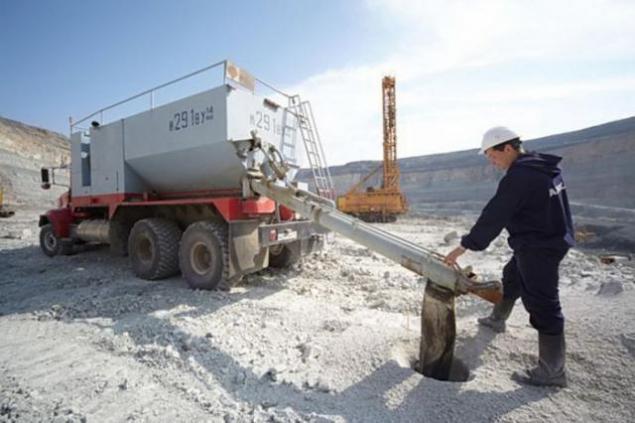

Major companies are located in Western Yakutia, in four districts of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) - Mirny, Lena, Anabarskiy, Nurbinskogo - in one of the harshest regions of the planet, with a sharply continental climate, with large temperature differences in the permafrost zone. In a good winter lasts up to 8 months, winter temperatures sometimes drop to -60 C.
Therefore, most of the equipment is made to order - a machine adapted for use in low temperature conditions. As a result of work carried out in the fields all year round in all weather conditions. In quarrying simultaneously involves a large amount of equipment - wheel loaders, dump trucks, excavators. Heavy trucks in the park "ALROSA" only about 300, with capacity from 40 to 136 m. - Basically, "BelAZ", there is also a Cat and Komatsu.
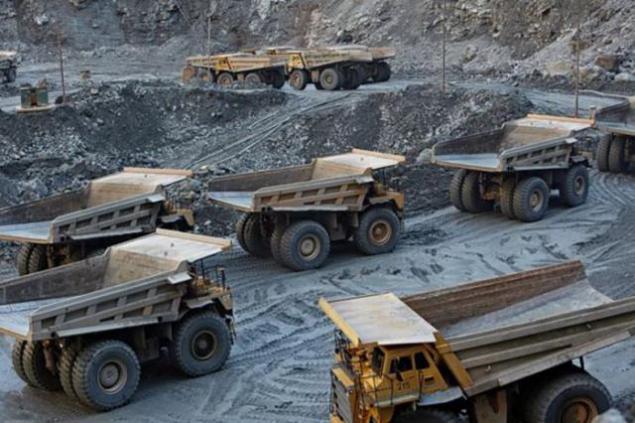

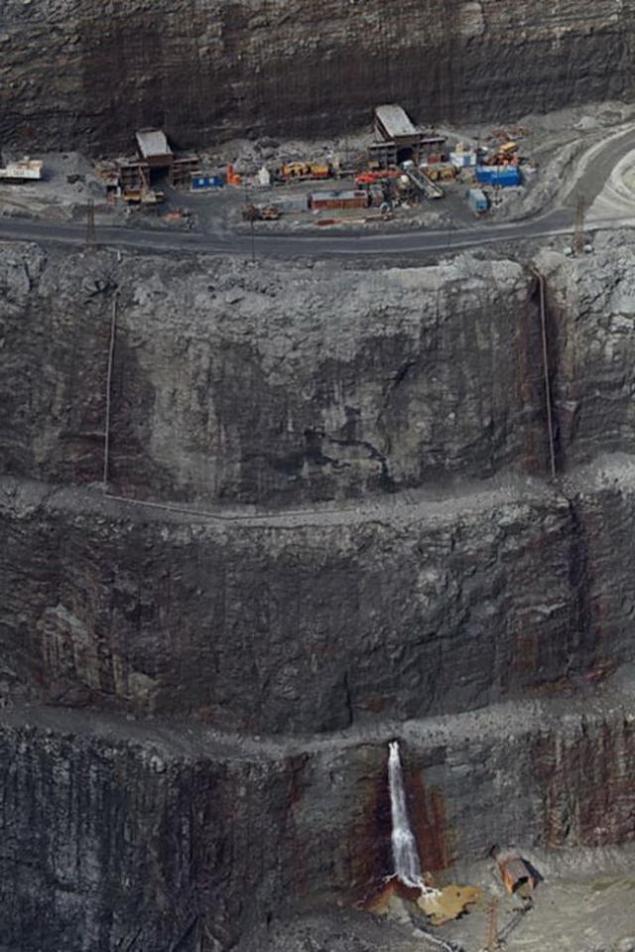
After reaching a certain depth within the open pit reserves are exhausted, the development of open pit becomes unprofitable. The average career developed to a depth of about 600 m. However, kimberlite pipes lie under the ground to a depth of 1, 5 km. For further mining built mine. Underground mining is more costly compared to the quarry, but it is the only cost-effective way to reach deeply buried reserves. In the future, "Alrosa" is going to significantly increase the share of underground mining of diamonds. Now the company completes the open quarrying "Lucky" and is building a parallel underground mine. He is expected to be launched in 2014
The cost of the transition to underground mining of diamonds valued at $ 4.3 billion, but in the future it should lead to a reduction in costs. Largely due to the construction of underground mines duty "ALROSA" to the acute phase of the crisis in 2008 grew by 64% to 134, 4 billion rubles. But the state company in trouble will not leave: she got into the list of strategic enterprises, non-core gas assets VTB bought for $ 620 million, and when the demand for diamonds fell, production of "ALROSA" began to buy Gokhran.
Controlling stake "ALROSA" (51%) is federally owned (from 2006 to 2008, 10% of the package belonged VTB), 32% of the shares owned by the government of Yakutia, 8% of the ulus control of the Federation. In April 2011, the company was transformed from JSC JSC to be able to raise funds on the market. From the middle of last year, the campaign "ALROSA" are traded on the Russian stock exchanges, but the volume of transactions on them is small due to low liquidity (the stock market were only the shares of minority shareholders). In the autumn of 2011, the number of shareholders "ALROSA" entered "Nafta-Moscow" Suleiman Kerimov, skimp on the market for about 1% of the company.
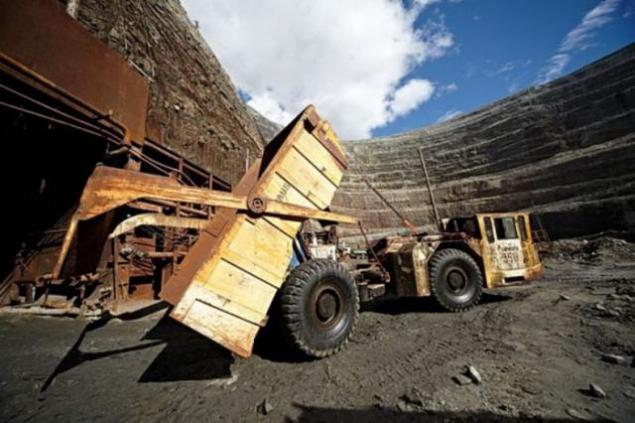

At the word "diamond mines" involuntarily imagine a beautiful picture: cave walls which gems are iridescent. In fact, diamond mine - not the most romantic place on earth. The walls are not sparkle with diamond glitter, and looking for ore, generally hard to imagine that it hid the future "girl's best friend." In the photo - working in one of the vent horizontal workings of the future underground mine, depth - 380 meters.
Mine development takes place in the unique geological conditions. In addition to the permafrost, it is complicated by aggressive groundwater, which due to the high salinity are not only able to wash out the walls of mine workings, but also eat away (!) Wheel tire dump. In addition, the fields "ALROSA" present bitumo- and oil shows that also complicate the extraction of diamonds.
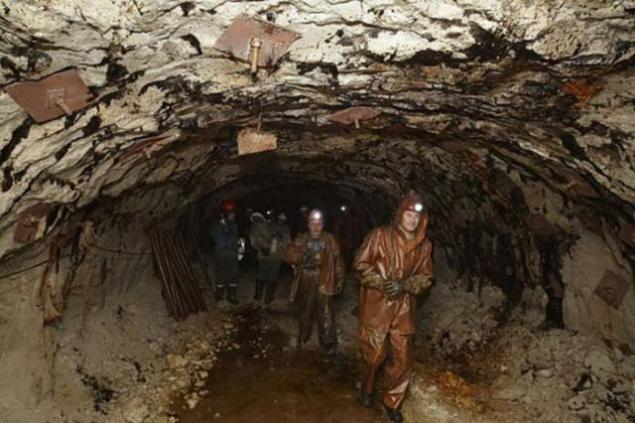

Parallel is building the future of the mine surface facilities - such as ventilation and air heater installations. Underground mine "Lucky" will become one of the largest in the world - its performance is expected to reach 4 million tonnes of ore per year. This is not the first underground mine company: 1999 "Alrosa" works at the mine "International". In addition, in August 2009, the company has commissioned an underground mine "Mir».
It is expected that when all mines are at full capacity, the share of underground mining in total operations "ALROSA" will rise to 40%. Total in Russia, the company has been producing diamonds on indigenous 9 and 10 placer deposits located in Yakutia and Arkhangelsk region. In addition, the company owns a diamond mining company "Catoca" in Angola - together with the local state-owned company "ENDIAMA».
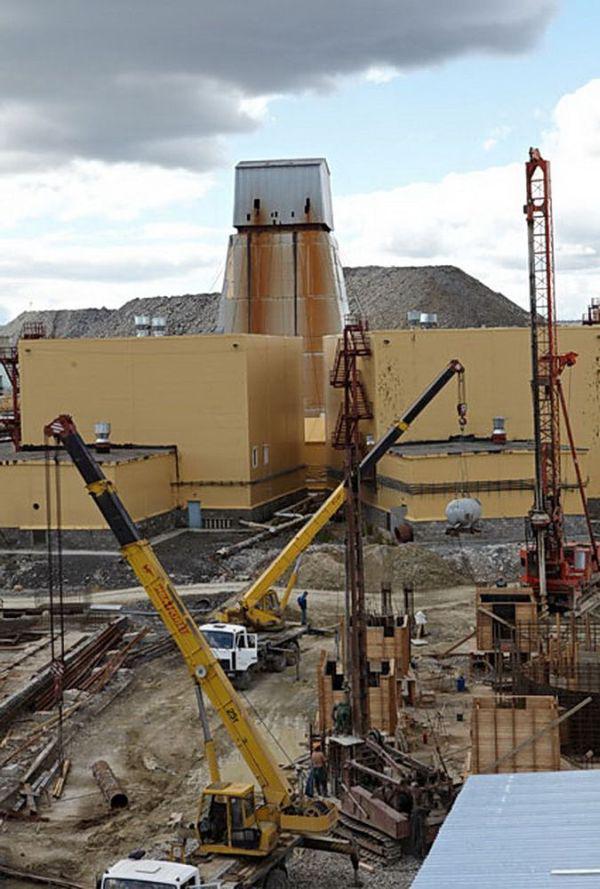

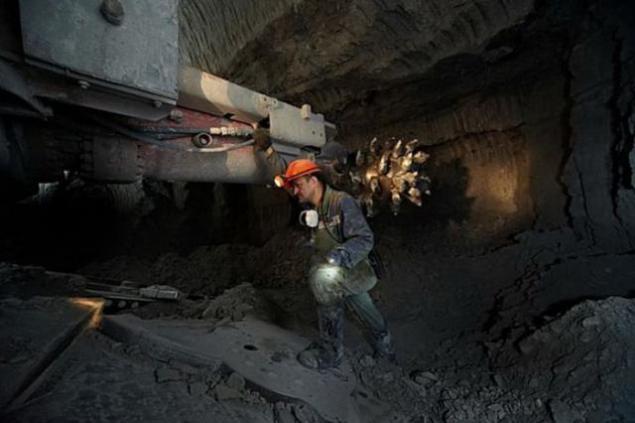
How will the underground mining on the "good" in 2-3 years? For example - the picture is already working mine "Mir". Diamond mining ore under the ground is conducted mainly shearer penetration (see photo). The company's staff are studying the possibility of using traditional mining shpurovyh breaking - when the rock is broken explosives planted in drilled wells. Next scheme is the same: take the ore loaders and transported to the surface where it gets to the processing plant. Now it will go and we will.

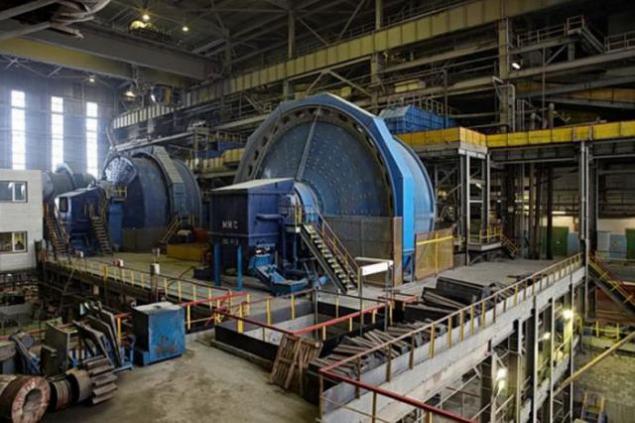
The initial stage of the diamond ore enrichment looks just like any other mineral. Initially, the factory get big chunks of rock the size of a few meters. After primary crushing in jaw or cone crushers ore fed to the mill wet autogenous (pictured), where using water rock fragments up to 1, 5 m crushed to a size of 0, 5 m or less.

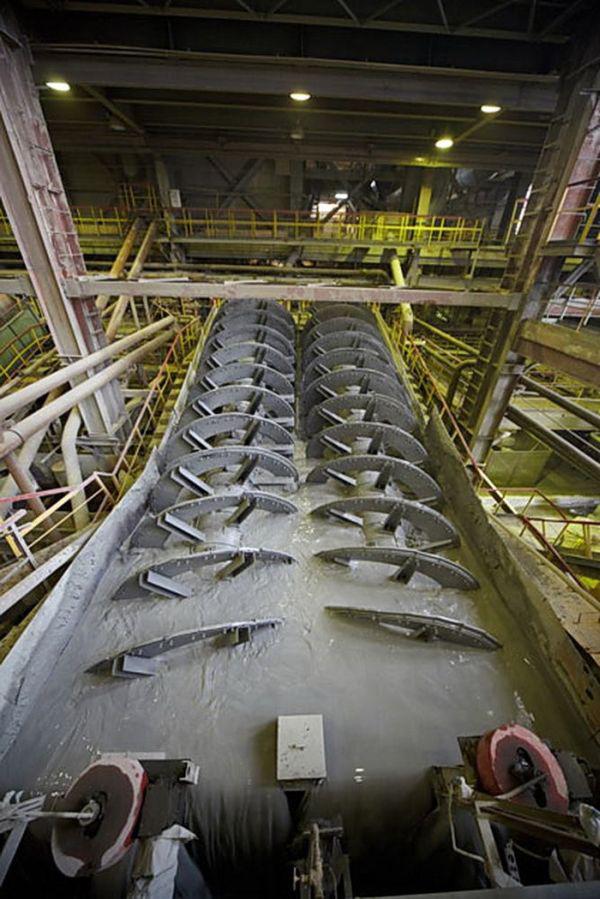
In the next step the raw materials separated spiral classifiers, depending on its size and density. The principle of operation is very simple. Water picks up fine particles and carries the drain. Large particles (up to a few centimeters) did not carry the water to be - they settle in the lower part of the tank, and then picks them up coil.

The next stage of enrichment - crashing, so named for the noise that accompanies the work. "Rumble" - a huge vibrating sieve different sizes allows you to sort the raw materials for various fractions. Separation of raw materials by size groups is necessary because in the future, each of them will be enriched in different ways.
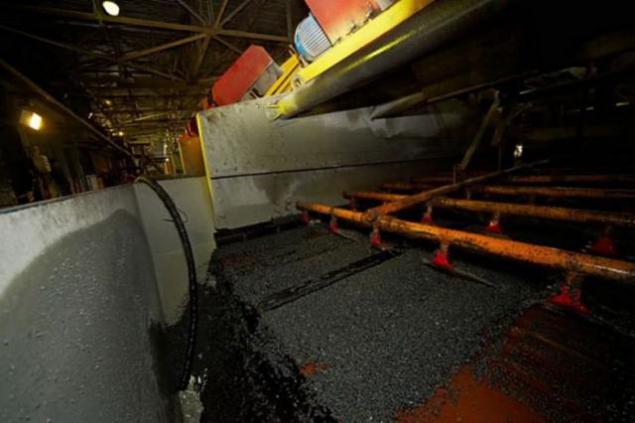

Now we have to somehow isolate diamonds from small pieces of ore, obtained after crushing. Medium size pieces of ore sent to the jigs and heavy medium enrichment: under the influence of water ripple diamond crystals are singled out and settle the heavy fraction. Fine "powder" passes through pnevmoflotatsiyu, during which, interacting with the reagents, fine diamond crystals adhere to the foam bubbles.
At the next stage, all the raw materials pass the basic procedure - separation of X-ray (RLS).
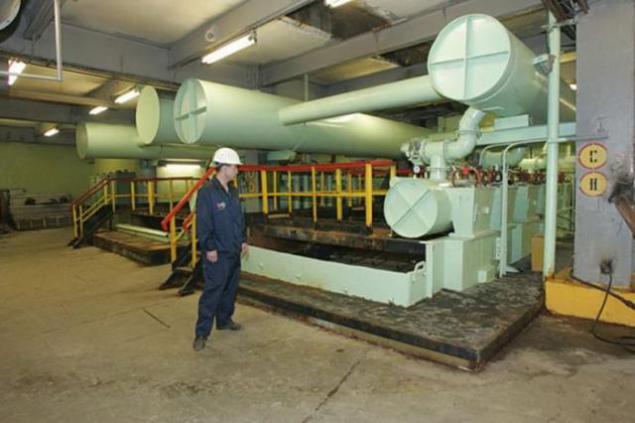

That's just to show what is going on inside the separator in the course of its work, will not work: the principle of radar is based on the continuous X-rays. Look inside at the time of the separator, to put it mildly, is not safe. If we describe in words, the method is based on the unique properties of diamond - it's the only mineral that fluoresces in X-rays.
On the conveyor belt inside the separator is constantly moving ground ore is irradiated with X-rays. As soon as the irradiation zone enters the diamond, photocells fixed fluorescent flash and air flow "knocks" lighteneth fragment into a separate container.
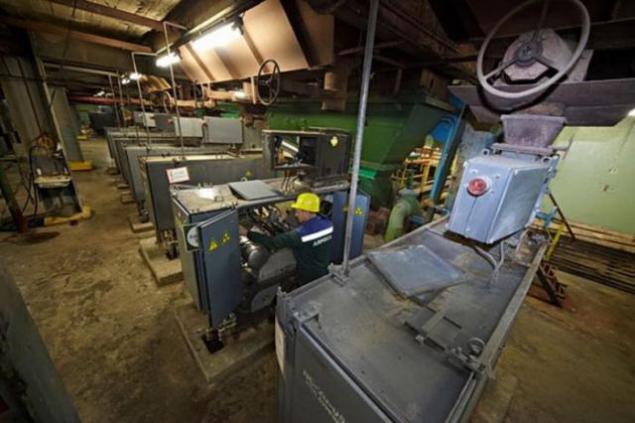

Of course, the air flow inside the separator can separate only one small crystal - with it is eliminated and a certain amount of waste rock. In fact, the whole process ore is directed only to minimize the number of "empty" and then the material to facilitate manual handling. And the "manual" in the literal sense of the word: professionals choose crystals, clean them and carry out the so-called "final finishing».
No matter how popular now, was the desire to automate all production processes in general, but in the diamond mining do without the human factor is absolutely impossible.
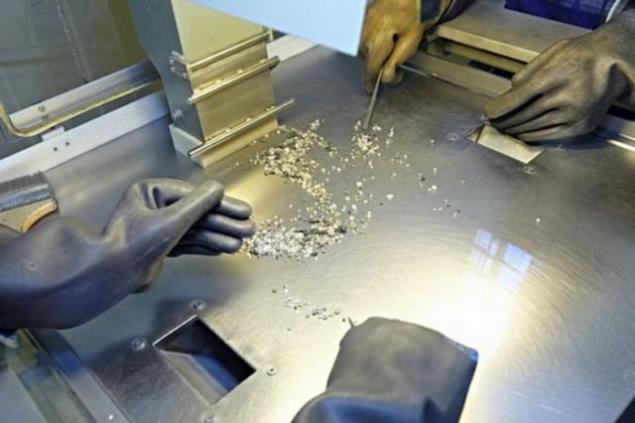
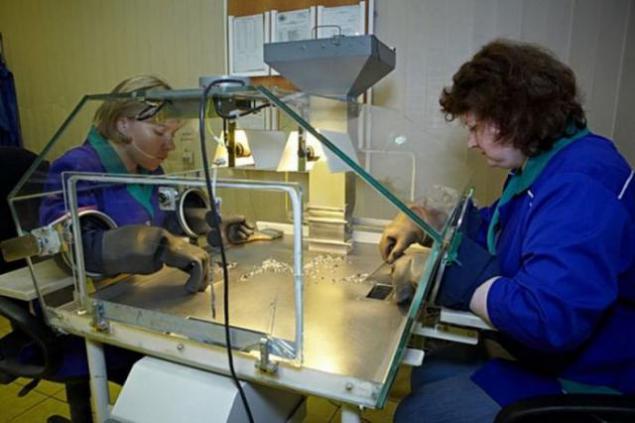


From the shop ultimate finishing all rough diamonds sent to the sorting center in Peace. Here the raw material is divided by the main groups and give it an initial evaluation, after which it can be sent for sale through the United Selling Organization "ALROSA».
By the way, about half of the production of "ALROSA" sold outside Russia. Until recently, the company was selling its diamonds on the world market, using the services of a monopolist De Beers. However, in early 2009 they ceased cooperation and "Alrosa" began reorganizing its distribution system, providing for the sale through direct contracts and equal treatment of foreign and Russian buyers, worked its customer base and introduced the practice of "long" contracts.
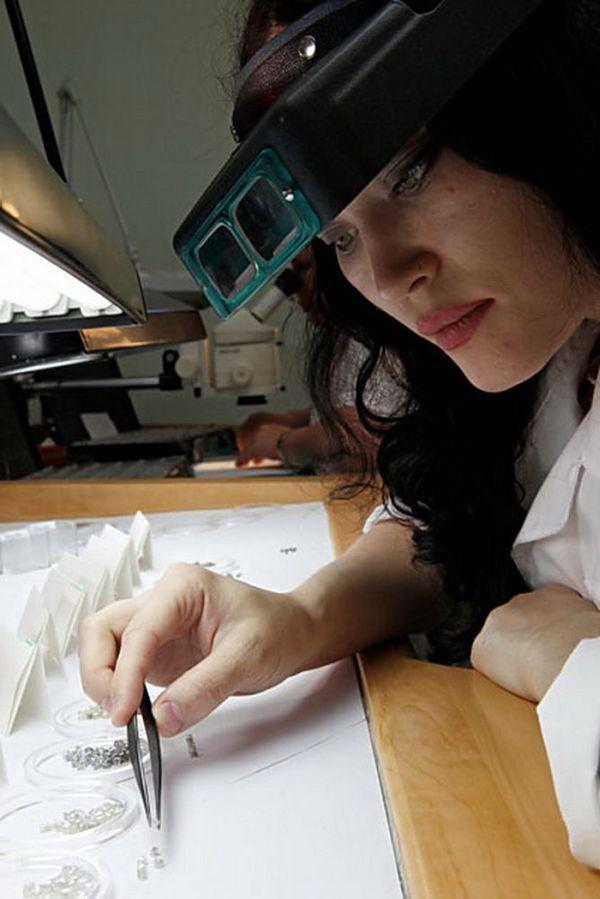

In general, the raw material from each of the fields has its own distinctive features. Experienced experts when looking at a diamond can identify with what is mine he arrived. But this applies only to the common symptoms. Two identical diamonds does not exist. Because there is no organized exchange trading and diamonds, such as gold or copper - it is not a standardized product, every stone has unique characteristics.
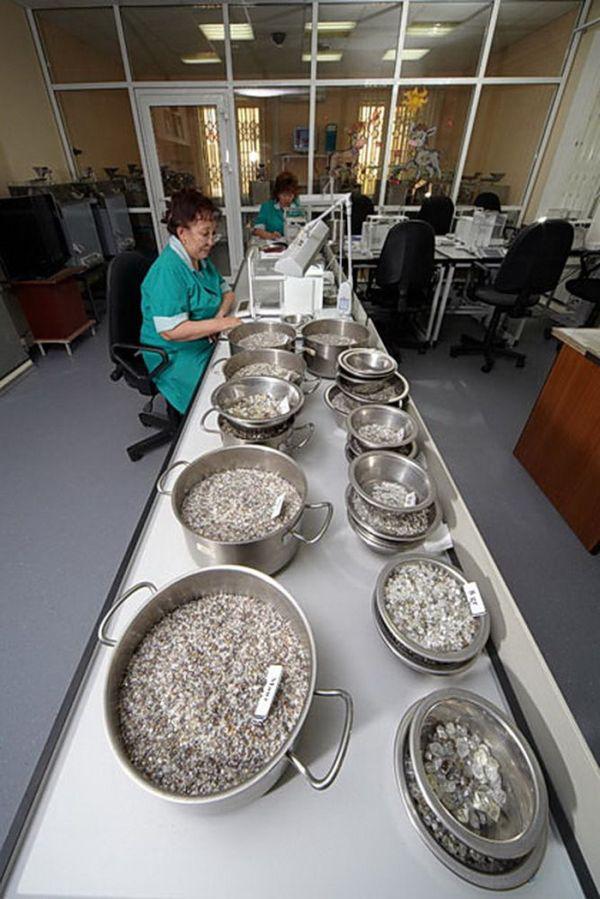

This significantly complicates the uniqueness and sorting, and evaluation. In assessing the experts take the basis of three characteristics: size, color and clarity (no inclusions inside, transparency). The most expensive stones - "clean water" absolutely transparent and do not have distinct colors. Each has different characteristics graduation. As a result, depending on the size, color and other parameters would be about 8000 possible positions rough.
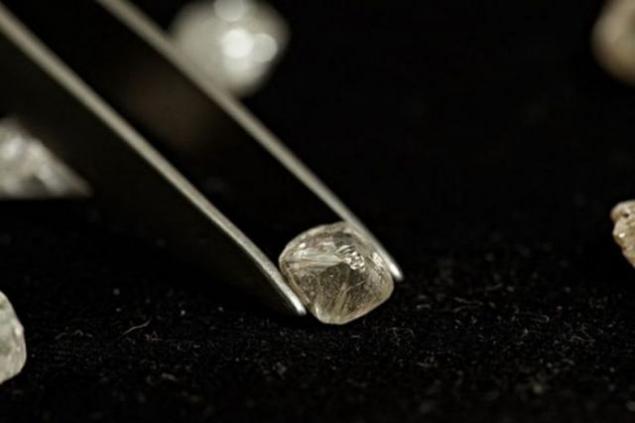

Hence

In the photo - view of the main career Udachninsky ore processing plant - "Lucky." Mining operations on the same field were started in 1971 and over the past 25 years Plant is a leading diamond mining company in Russia and one of the largest open-pit mines in the world. In 2010, the share of Udachninsky GOK had 33, 8% of diamond production in terms of value and 12, 5% of mining operations from the total in the group "Alrosa».

The first large-scale commercial production of diamonds began in southern Africa about a hundred years ago. In Russia, the kimberlite pipes were discovered only in the middle of the last century - in Yakutia. This discovery marked the beginning of "ALROSA" - today a world leader in diamond mining. So, probable reserves of the company amount to about a third of the world's, and explored enough to maintain current production levels for 25 years without reducing the quality of raw materials. If the figures, the reserves of diamonds belonging to the "ALROSA" fields is (according to data released in May 2011) 1, 23 billion carat under Russian classification (1, 014 billion - proven and 0 211 000 000 000 - possible).

The past five years, the company annually sends Exploration 2, 5 and 3, 5 billion rubles. In 2011, exploration costs amounted to about 4 billion rubles., In 2012 - more than 5, 36 billion rubles.
In their fields "Alrosa" produces about 35 million carats of diamonds per year, being the world's largest producer of this raw material in physical terms: it accounts for about 97% of Russian oil production and 25% of the world. The content of the diamond grade kimberlite pipes are traditionally small - usually a few carats per tonne. Yakut deposits are advantageous in this respect, and is considered one of the richest in content.

In 2010, the volume of sales of diamonds and diamond raw materials "ALROSA" was $ 3, 48 billion, and in 2011, according to preliminary data, the company sold products worth $ 5 billion - a record number in its history. The company's revenue in the first half of 2011 under IFRS was 66, 15 billion rubles. (+ 3% the previous year), and net profit increased fivefold to 26, 27 billion.
Kimberlite pipes are cone-shaped, extending up, so they usually start practicing with quarrying. The project depth of the quarry "Lucky" depicted in these photographs - 600 m. In order to rise from the bottom of the quarry to the surface, dump on the "serpentine" overcomes the path length of about 10 km.

But so are mined in quarries. The rig is doing well, which laid the explosive (pictured - the process of laying). By the way, even though the diamond is the hardest mineral, it is quite fragile. Therefore, when blasting uses soft technologies, allowing to preserve the integrity of the crystals. After the explosion of rock fragments are loaded into dump trucks and transported to the processing plant.

Major companies are located in Western Yakutia, in four districts of the Republic of Sakha (Yakutia) - Mirny, Lena, Anabarskiy, Nurbinskogo - in one of the harshest regions of the planet, with a sharply continental climate, with large temperature differences in the permafrost zone. In a good winter lasts up to 8 months, winter temperatures sometimes drop to -60 C.
Therefore, most of the equipment is made to order - a machine adapted for use in low temperature conditions. As a result of work carried out in the fields all year round in all weather conditions. In quarrying simultaneously involves a large amount of equipment - wheel loaders, dump trucks, excavators. Heavy trucks in the park "ALROSA" only about 300, with capacity from 40 to 136 m. - Basically, "BelAZ", there is also a Cat and Komatsu.

After reaching a certain depth within the open pit reserves are exhausted, the development of open pit becomes unprofitable. The average career developed to a depth of about 600 m. However, kimberlite pipes lie under the ground to a depth of 1, 5 km. For further mining built mine. Underground mining is more costly compared to the quarry, but it is the only cost-effective way to reach deeply buried reserves. In the future, "Alrosa" is going to significantly increase the share of underground mining of diamonds. Now the company completes the open quarrying "Lucky" and is building a parallel underground mine. He is expected to be launched in 2014
The cost of the transition to underground mining of diamonds valued at $ 4.3 billion, but in the future it should lead to a reduction in costs. Largely due to the construction of underground mines duty "ALROSA" to the acute phase of the crisis in 2008 grew by 64% to 134, 4 billion rubles. But the state company in trouble will not leave: she got into the list of strategic enterprises, non-core gas assets VTB bought for $ 620 million, and when the demand for diamonds fell, production of "ALROSA" began to buy Gokhran.
Controlling stake "ALROSA" (51%) is federally owned (from 2006 to 2008, 10% of the package belonged VTB), 32% of the shares owned by the government of Yakutia, 8% of the ulus control of the Federation. In April 2011, the company was transformed from JSC JSC to be able to raise funds on the market. From the middle of last year, the campaign "ALROSA" are traded on the Russian stock exchanges, but the volume of transactions on them is small due to low liquidity (the stock market were only the shares of minority shareholders). In the autumn of 2011, the number of shareholders "ALROSA" entered "Nafta-Moscow" Suleiman Kerimov, skimp on the market for about 1% of the company.

At the word "diamond mines" involuntarily imagine a beautiful picture: cave walls which gems are iridescent. In fact, diamond mine - not the most romantic place on earth. The walls are not sparkle with diamond glitter, and looking for ore, generally hard to imagine that it hid the future "girl's best friend." In the photo - working in one of the vent horizontal workings of the future underground mine, depth - 380 meters.
Mine development takes place in the unique geological conditions. In addition to the permafrost, it is complicated by aggressive groundwater, which due to the high salinity are not only able to wash out the walls of mine workings, but also eat away (!) Wheel tire dump. In addition, the fields "ALROSA" present bitumo- and oil shows that also complicate the extraction of diamonds.

Parallel is building the future of the mine surface facilities - such as ventilation and air heater installations. Underground mine "Lucky" will become one of the largest in the world - its performance is expected to reach 4 million tonnes of ore per year. This is not the first underground mine company: 1999 "Alrosa" works at the mine "International". In addition, in August 2009, the company has commissioned an underground mine "Mir».
It is expected that when all mines are at full capacity, the share of underground mining in total operations "ALROSA" will rise to 40%. Total in Russia, the company has been producing diamonds on indigenous 9 and 10 placer deposits located in Yakutia and Arkhangelsk region. In addition, the company owns a diamond mining company "Catoca" in Angola - together with the local state-owned company "ENDIAMA».

How will the underground mining on the "good" in 2-3 years? For example - the picture is already working mine "Mir". Diamond mining ore under the ground is conducted mainly shearer penetration (see photo). The company's staff are studying the possibility of using traditional mining shpurovyh breaking - when the rock is broken explosives planted in drilled wells. Next scheme is the same: take the ore loaders and transported to the surface where it gets to the processing plant. Now it will go and we will.

The initial stage of the diamond ore enrichment looks just like any other mineral. Initially, the factory get big chunks of rock the size of a few meters. After primary crushing in jaw or cone crushers ore fed to the mill wet autogenous (pictured), where using water rock fragments up to 1, 5 m crushed to a size of 0, 5 m or less.

In the next step the raw materials separated spiral classifiers, depending on its size and density. The principle of operation is very simple. Water picks up fine particles and carries the drain. Large particles (up to a few centimeters) did not carry the water to be - they settle in the lower part of the tank, and then picks them up coil.

The next stage of enrichment - crashing, so named for the noise that accompanies the work. "Rumble" - a huge vibrating sieve different sizes allows you to sort the raw materials for various fractions. Separation of raw materials by size groups is necessary because in the future, each of them will be enriched in different ways.

Now we have to somehow isolate diamonds from small pieces of ore, obtained after crushing. Medium size pieces of ore sent to the jigs and heavy medium enrichment: under the influence of water ripple diamond crystals are singled out and settle the heavy fraction. Fine "powder" passes through pnevmoflotatsiyu, during which, interacting with the reagents, fine diamond crystals adhere to the foam bubbles.
At the next stage, all the raw materials pass the basic procedure - separation of X-ray (RLS).

That's just to show what is going on inside the separator in the course of its work, will not work: the principle of radar is based on the continuous X-rays. Look inside at the time of the separator, to put it mildly, is not safe. If we describe in words, the method is based on the unique properties of diamond - it's the only mineral that fluoresces in X-rays.
On the conveyor belt inside the separator is constantly moving ground ore is irradiated with X-rays. As soon as the irradiation zone enters the diamond, photocells fixed fluorescent flash and air flow "knocks" lighteneth fragment into a separate container.

Of course, the air flow inside the separator can separate only one small crystal - with it is eliminated and a certain amount of waste rock. In fact, the whole process ore is directed only to minimize the number of "empty" and then the material to facilitate manual handling. And the "manual" in the literal sense of the word: professionals choose crystals, clean them and carry out the so-called "final finishing».
No matter how popular now, was the desire to automate all production processes in general, but in the diamond mining do without the human factor is absolutely impossible.


From the shop ultimate finishing all rough diamonds sent to the sorting center in Peace. Here the raw material is divided by the main groups and give it an initial evaluation, after which it can be sent for sale through the United Selling Organization "ALROSA».
By the way, about half of the production of "ALROSA" sold outside Russia. Until recently, the company was selling its diamonds on the world market, using the services of a monopolist De Beers. However, in early 2009 they ceased cooperation and "Alrosa" began reorganizing its distribution system, providing for the sale through direct contracts and equal treatment of foreign and Russian buyers, worked its customer base and introduced the practice of "long" contracts.

In general, the raw material from each of the fields has its own distinctive features. Experienced experts when looking at a diamond can identify with what is mine he arrived. But this applies only to the common symptoms. Two identical diamonds does not exist. Because there is no organized exchange trading and diamonds, such as gold or copper - it is not a standardized product, every stone has unique characteristics.

This significantly complicates the uniqueness and sorting, and evaluation. In assessing the experts take the basis of three characteristics: size, color and clarity (no inclusions inside, transparency). The most expensive stones - "clean water" absolutely transparent and do not have distinct colors. Each has different characteristics graduation. As a result, depending on the size, color and other parameters would be about 8000 possible positions rough.

Hence