562
Black hole inflates huge plasma bubble
The tiny black hole inflates huge fiery cosmic bubble.
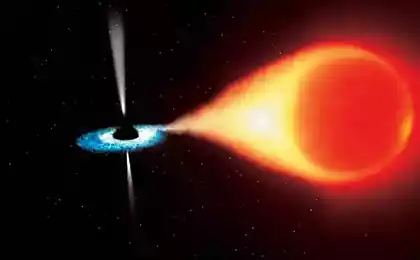
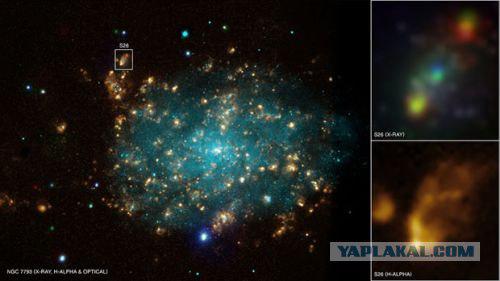
Scientists of the European Southern Observatory (European Southern Observatory, ESO), using data from the telescope Very Large Telescope (VLT), combining it with the data of NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory (NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory), discovered the phenomenon, located in the spiral galaxy NGC 7793 at a distance 12 million light years from Earth. This phenomenon is a miniature black hole that is classified as a microquasar, spewing a stream of matter is so strong and hot that in space "inflated" a real fire bubble size of 1000 light years.
Discovered gas bubble in its own way unique. It is at least twice and ten times denser than gas bubbles formed microquasars other. Jets of matter erupted microquasar NGC 7793 is so hot and fast, now the bubble is inflated at a rate of about one million kilometers per hour. Examining the data, and based on the size of the gas bubble, the scientists concluded that the activity of the black hole of "inflating" bubble continues, at least for 200 thousand years.

Of course, on a cosmic scale and magnitude of the specified size is not too large. But everything in the world is relative and Robert Soria (Robert Soria), one of the sponsors of an article in Nature, reports this discovery gives an example: "If the black hole is cut to the size of a soccer ball, the jet erupted matter has reached its orbit of Pluto."
Source:
Scientists of the European Southern Observatory (European Southern Observatory, ESO), using data from the telescope Very Large Telescope (VLT), combining it with the data of NASA's Chandra X-ray Observatory (NASA Chandra X-ray Observatory), discovered the phenomenon, located in the spiral galaxy NGC 7793 at a distance 12 million light years from Earth. This phenomenon is a miniature black hole that is classified as a microquasar, spewing a stream of matter is so strong and hot that in space "inflated" a real fire bubble size of 1000 light years.
Discovered gas bubble in its own way unique. It is at least twice and ten times denser than gas bubbles formed microquasars other. Jets of matter erupted microquasar NGC 7793 is so hot and fast, now the bubble is inflated at a rate of about one million kilometers per hour. Examining the data, and based on the size of the gas bubble, the scientists concluded that the activity of the black hole of "inflating" bubble continues, at least for 200 thousand years.

Of course, on a cosmic scale and magnitude of the specified size is not too large. But everything in the world is relative and Robert Soria (Robert Soria), one of the sponsors of an article in Nature, reports this discovery gives an example: "If the black hole is cut to the size of a soccer ball, the jet erupted matter has reached its orbit of Pluto."

Source: