1769
Soviet antitank cumulative ammunition
For the most active accusers accordions - And this article is published on the website topwar.ru 8 February 2014.
The cumulative effect of directed explosion became known in the 19th century, shortly after the start of mass production of high explosives. His first scientific papers on the subject, was published in 1915 in the UK.
20 photo.
Author Sergei Linnik
Source

This effect is achieved by giving a special form explosive charge. Usually, for this purpose, the charges are made with a groove on the opposite side from its detonator. When initiating an explosion convergent flow of detonation products is formed into a high cumulative jet, with the cumulative effect is increased by lining the recess with a metal layer (1-2 mm thick). The rate of the metal stream reaches 10 km / s. Compared with the expanding detonation products of conventional charges in applying the product stream shaped charge pressure and density of matter and energy is much higher that provides a directed action of explosion and high penetrating power of a cumulative jet.
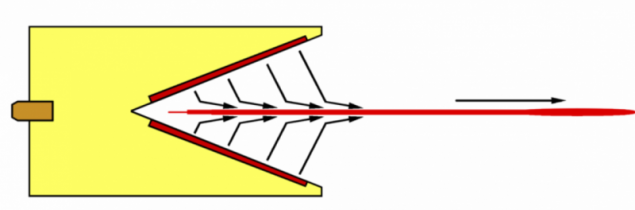
During the collapse of the conical shell speed jet parts are somewhat different, as a result of the jet in flight stretched. Therefore, a small increase in the gap between the charge and the target increases the depth of penetration due to the elongation of the jet. The thickness of the armor punctured cumulative projectiles, does not depend on the firing range and is approximately equal to their caliber. At greater distances between the charge and the target jet is torn apart, and the effect of penetration is reduced.
In 30-ies of XX century there was a mass saturation of troops tanks and armored vehicles. In addition to the traditional means of dealing with them, before the war in some countries were developing cumulative projectiles.
Especially attractive was that the armor penetration of such munitions are not dependent on the speed of a meeting with the armor. This allowed them to successfully apply for the destruction of tanks in artillery systems, originally not intended for this, as well as to create high-performance anti-tank mines and grenades. Most of all in the creation of advanced anti-tank weapons cumulative Germany, at the time of the attack on the Soviet Union there were created and put into service the cumulative artillery shells caliber 75-105 mm.

Unfortunately, in the Soviet Union before the war, this area has not been given due attention. In our country, the improvement of anti-tank weapons went through capacity-caliber anti-tank guns and an increase in the initial velocity armor-piercing shells. It is fair to say that in the USSR in the late 30's has been released and tested by shooting a pilot batch of 76-mm HEAT projectiles. During the tests, it turned out that the cumulative projectiles equipped with fuses staff from shrapnel shells are usually not penetrate the armor and give bounce. Obviously, it was detonated, but the military already has shown little interest in such projectiles, after unsuccessful firing finally they were rejected.
At the same time the Soviet Union had made a significant number of recoilless (dinamoreaktivny) Kurchevsky guns.

The advantage of these systems is light weight and lower cost compared to the "classical" instruments. Bezotkatki in conjunction with cumulative projectiles quite well could show itself as anti-tank weapons.
Since the beginning of the fighting from the front were reports that German artillery previously unknown uses so-called "broneprozhigayuschie" shells, effectively destroy tanks. When viewed from destroyed tanks noticed the characteristic form of holes with fused edges. At first it was suggested version that unidentified projectiles used ', fast-thermite "accelerated powder gases. However, experimentally this hypothesis was soon disproved. It has been found that the processes of burning thermite incendiary composition and interaction of the jet with the metal slag tank armor is too slow and can not be implemented in a very short time armor penetration projectile. At this time, from the front it was taken samples captured from the Germans' broneprozhigayuschih "shells. It turned out that their design is based on the cumulative effect of the explosion.
In early 1942, the designers MJ Vasilyev, ZV Vladimirov and N. Jitka designed 76-mm projectile with a cumulative charge hollow cone, lined steel shell. Was used artillery shell casing with bottom gear, the chamber is further tapered bore in the head part. The projectile used the powerful explosive - an alloy of TNT and hexogen. Bottom hole and the plug is used to install additional detonator and radiation blasting cap. The big problem was the lack of an appropriate fuse in the production. After a series of experiments was chosen Aviation fuse instantaneous AM-6.
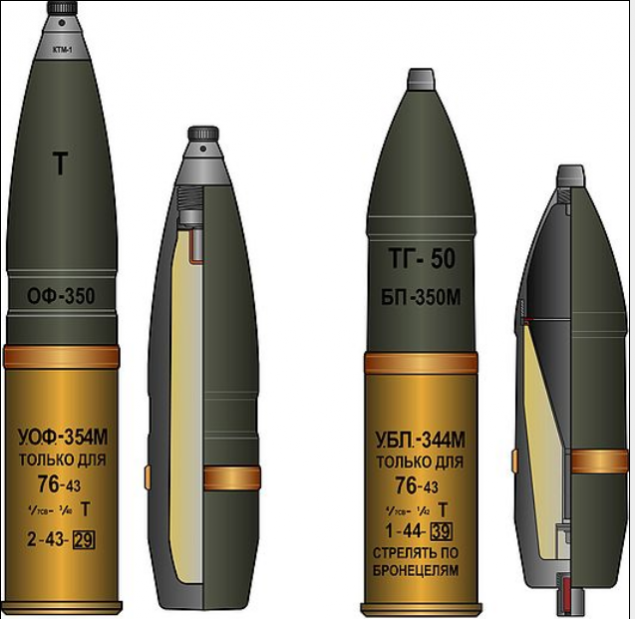

Cumulative shells had about 70-75 mm armor piercing, ammunition appeared in the regimental guns since 1943, and manufactures standard throughout the war.

The industry has put about 1 front, 1 million. 76 mm cumulative anti-tank shells. Unfortunately, to use them in tank and 76-mm divisional guns because of unreliable operation fuse and the risk of explosion in the trunk was forbidden. Fuses for cumulative artillery shells, meet safety requirements when shooting long-barreled guns were set up only in late 1944.
In 1942, a group of designers as part of IP Dziuba, NP Kazeikin, IP Kucherenko, VY Matyushkina and AA Greenberg developed a cumulative anti-tank missiles to the 122 mm howitzer.
Posted in [mergetime] 1391850227 [/ mergetime]
122 mm howitzer shells for a cumulative sample of 1938 had a housing stalistogo iron equip an effective explosive composition based on RDX and powerful heaters detonator. 122mm HEAT projectile equipped with snap-action fuse B-229, which was developed in a very short time in the CDB-22, led by AJ Karpov.

122 mm howitzer shells for a cumulative sample of 1938 had a housing stalistogo iron equip an effective explosive composition based on RDX and powerful heaters detonator. 122mm HEAT projectile equipped with snap-action fuse B-229, which was developed in a very short time in the CDB-22, led by AJ Karpov.

The projectile was adopted, put into mass production in early 1943, and managed to take part in the Battle of Kursk. By the end of the war produced more than 100 thousand. 122mm shaped-charge projectiles. The shell pierced the armor thickness up to 150 mm normal, ensuring the defeat of the German heavy tank "Tiger" and "Panther". However, the effective range of the howitzer of maneuvering tanks was suicidal - 400 meters.
Creating a cumulative shells opened up great opportunities for the use of artillery shells with relatively small initial velocities - 76 mm regimental cannon samples in 1927 and 1943. and 122 mm howitzers of the sample in 1938 that large amounts were in the army. Availability cumulative rounds of ammunition in these instruments greatly increased the effectiveness of their anti-tank fire. This significantly increased the anti-Soviet defense infantry divisions.
One of the main tasks put into service in early 1941 armored Il-2 was a fight with armored vehicles.
However, the existing armed attack aircraft cannons effectively allowed to hit only lightly armored vehicles.
Reactive 82-132 mm shells did not have the required accuracy. However, for the weapons of IL-2 in 1942, it was designed cumulative RBSK-82.
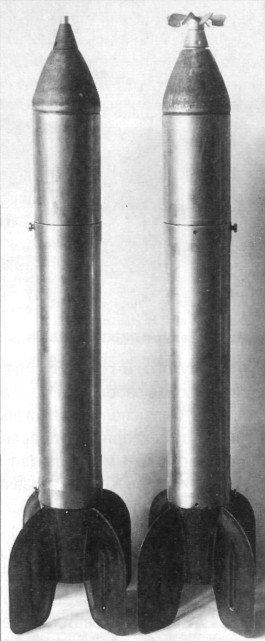
Nosecone missile RBSK-82 consisted of a steel cylinder having a wall thickness of 8 mm. In the front part of the cylinder broke out into a cone of sheet metal, creating the recess in the explosive poured into the cylinder head of the projectile. In the center of the cylinder tube is passed, which served as "to transmit the beam fire from nakolnogo capsule to the detonator cap TAT-1." The shells were tested in two equipment BB: TNT and Alloy 70/30 (TNT and hexogen). The shells with TNT had a point for the AM-A fuse, and shells with alloy 70/30 - the fuse M-50. Fuses were blasting nakolnogo class action APUV. Missile parts RBSK-82 - standard, from the rockets M-8 filled with pyroxylin powder.
In total, during the test was spent RBSK 40 pieces 82, 18 of them - firing in the air, the rest - on the ground. Shelled captured German tanks Pz. III, StuG III and Czech tank Pz.38 (t) with enhanced reservation. Shooting in the air was carried out on the tank StuG III dive at an angle of 30 ° volleys 2-4 projectile in one go. Shooting distance of 200 m. The shells have shown good resistance to the flight path, but no falling off the tank could not be obtained.
Reactive armor-piercing shell cumulative effect RBSK-82, filled alloy 70/30, pierced the armor thickness of 30 mm at any angle of the meeting, and armor thickness of 50 mm punched at a right angle, but does not break the meeting at an angle of 30 °. Apparently, low armor penetration is a consequence of the delay in the activation fuse "on the rebound, and the jet stream is formed by a deformed cone."
Shells RBSK 82 TNT gear pierced the armor thickness of 30 mm only at the angles of the meeting not less than 30 °, and 50 mm armor - did not break under any circumstances hit. Holes produced in the through-penetration of armor, had a diameter of 35 mm. In most cases, armor penetration accompanied by splitting off of metal around the outlet.
Adopt cumulative RSy not accepted due to the lack of explicit advantages over regular rockets. On the approach it has had a new, much more powerful weapon - PTAB.
The priority in the development of small bombs cumulative effect belongs to Russian scientists and designers. In mid-1942 a well-known developer of fuses IA Larionov, proposed the construction of a light anti-tank bombs cumulative effects. The Air Force has expressed interest in the proposal. CDB-22 quickly conducted design work and testing new bombs began in late 1942. The final version represented PTAB 2, 5-1, 5, i.e. anti-aircraft bomb the cumulative effect of weight 1, 5 kg in size 2, 5 kg aviation bomb fragment. ICT has decided to urgently adopt PTAB-2, 5-1, 5, and organize its mass production.
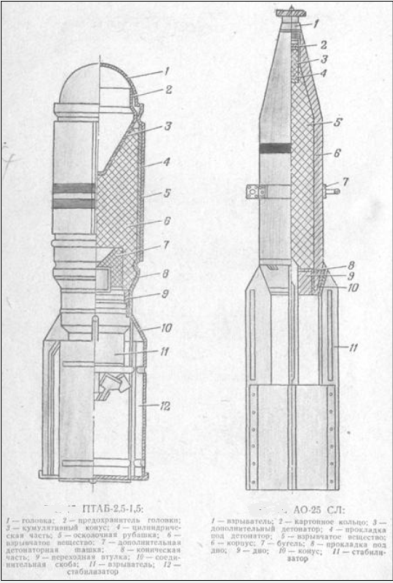
At first PTAB-2, 5-1, 5 riveted hull and stabilizers pinnate-cylindrical shape manufactured from sheet steel with a thickness 0, 6 mm. To increase fragmentation on the cylindrical part of the bomb put an additional 1 steel, 5 mm-shirt. PTAB warhead consisted of smesevogo BB type of TGA, the loaded through the bottom point. To protect the fan fuse BP-A spontaneous clotting to wear special stabilizer bomb fuse from a tin plate with a square-shaped plug attached to it two wire whiskers extending between the blades. After dropping it from an airplane PTAB frustrated with bombs oncoming airflow.

Upon impact, the armor of the tank breakdowns fuse that through tetrilovuyu detonator bomb detonates an explosive charge. Upon detonation of the charge, thanks to the cumulative funnel and a metal cone in it, create the jet stream, which, as shown by field testing, armor penetration up to 60 mm at an angle of meeting 30 ° followed by destructive influence of the armor: the defeat of the crew of the tank, initiate detonation of munitions and ignition of fuel or vapors.
The bomb charging IL-2 included 192 aerial bombs PTAB-2, 5-1, 5, 4 cassettes small bombs (48 pieces each) or up to 220 pieces at their rational distribution in bulk in 4 bomb bay. < br />
Adopting PTAB some time kept secret, their use without the permission of the High Command was forbidden. It is possible to use the effect of surprise and effectively apply the new weapon in the battle of Kursk.

The massive use of PTAB had a stunning effect of tactical surprise and had a strong impact on the morale of the enemy. German tank crews, however, as the Soviet, the third year of the war have become accustomed to the relatively low efficiency bomboshturmovyh air strikes. In the initial phase of the battle the Germans did not apply the dispersed camping and pre-battle orders, that is, on routes of movement in convoys in the areas of concentration and starting positions, for which they were severely punished - lane expansion of the tank 2-3 PTAB overlaps removed from one another 60-75 m, so that the past carried significant losses, even in the absence of massive use of IL-2. One IL-2 with a height of 75-100 meters could cover the area 15h75 meters, destroying her entire enemy technology.
On average, during the war, irrecoverable losses of tanks from air operations did not exceed 5%, after the application of PTAB in some parts of the front is the figure exceeded 20%.
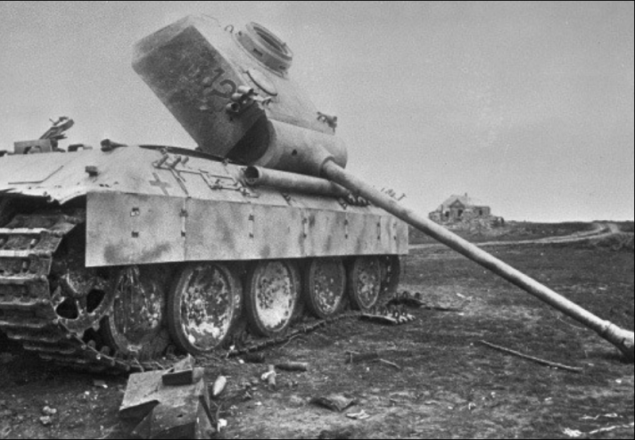

After recovering from the shock of the German tank crews soon moved exclusively to the march dispersed and pre-battle orders. Naturally, it is very difficult control of tank units, increased the timing of their deployment, redeployment and concentration, complicated interaction between them. At stops German tank crews began to have their cars under trees, awnings and light grid installed on the roof of the tower and light metal mesh body. Efficiency impacts of IL-2 with PTAB declined approximately 4-4 5 times, remaining, however, on average 2-3 times higher than when using a high explosive and high-explosive bombs.

In 1944 he was accepted into service a more powerful anti-tank bomb PTAB-10-2, 5, in dimensions of 10-kg aircraft bomb. It provided armor penetration thickness up to 160 mm. According to the principle of action and purpose of the major components and elements PTAB 10-2, 5 was similar PTAB-2, 5-1, 5, and differs from it only by the shape and dimensions.
On arms of the Red Army in 1920-1930-ies was dulnozaryadny "grenade Dyakonova", created at the end of the First World War, and subsequently upgraded.
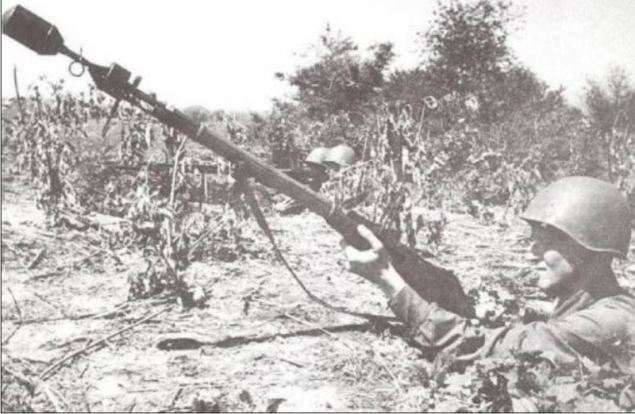

It was a 41-caliber mortars mm that fits over the barrel of the rifle, fixing at gunpoint cut. On the eve of World War II there was a grenade in each rifle and cavalry unit. Then there was a question of giving the rifle grenade "anti" properties.
During World War II, in 1944, adopted the Red Army entered the cumulative pomegranate VCG-40. Fires pomegranate special blank cartridge 2, 75 g of powder brand VI or P-45. Reduced charge blank cartridge allow direct fire grenade fire with an emphasis butt in the shoulder at a distance up to 150 meters.
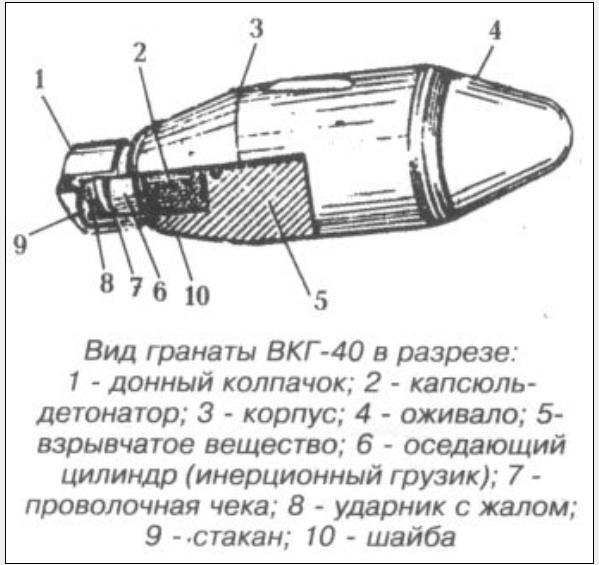
Rifle Grenade cumulative designed to deal with light armored vehicles and mobile enemy means not protected by armor, as well as gun emplacements. We used the CWS-40 is very limited, due to the low accuracy of fire and weak armor penetration.
During the war, the Soviet Union was released a significant amount of manual anti-tank grenades. Originally it was a grenade explosive action, increasing the thickness and weight of armor, increases anti-tank grenades. However, it still did not provide armor penetration of medium tanks, because a grenade RPG-41 with a weight of 1400 g of explosives could penetrate 25mm armor.

Needless to say, the danger represented antitank weapon is for the one who applied it.
In mid-1943, the Red Army adopted a fundamentally new pomegranate cumulative action RPG-43, developed by NP Belyakov. It was the first cumulative grenade, developed in the Soviet Union.
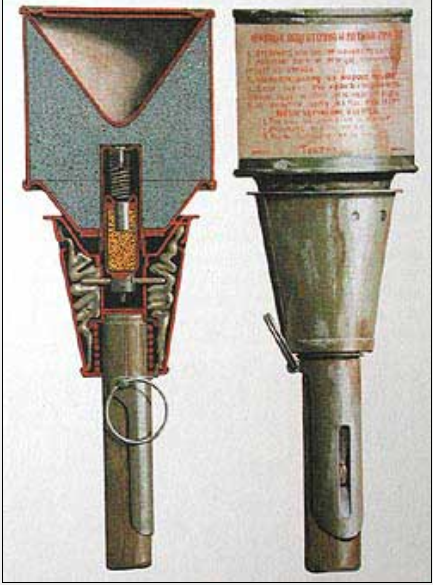
RPG-43 was a body with a flat bottom and a conical lid, wooden handle with a safety mechanism, tape stabilizer and shock-flammable fuse mechanism. Inside the housing placed with burster charge hollow conical lined with a thin layer of metal, glass, and fixed with its bottom a safety spring and a tip.
On its front end of the handle is attached a metal sleeve, which is located inside the fuse holder and hold it in the rearmost position pin. Outside in the bush wearing the spring and stacked cloth tape, attached to the cover of the stabilizer. The safety mechanism consists of folding strips and checks.
operation-barbarossa.narod.ru/artel...76-mm-m1927.htm
ser-sarajkin.narod2.ru/ALL_OUT/AiKO.../RBSK-82002.htm
Source:
The cumulative effect of directed explosion became known in the 19th century, shortly after the start of mass production of high explosives. His first scientific papers on the subject, was published in 1915 in the UK.
20 photo.
Author Sergei Linnik
Source

This effect is achieved by giving a special form explosive charge. Usually, for this purpose, the charges are made with a groove on the opposite side from its detonator. When initiating an explosion convergent flow of detonation products is formed into a high cumulative jet, with the cumulative effect is increased by lining the recess with a metal layer (1-2 mm thick). The rate of the metal stream reaches 10 km / s. Compared with the expanding detonation products of conventional charges in applying the product stream shaped charge pressure and density of matter and energy is much higher that provides a directed action of explosion and high penetrating power of a cumulative jet.

During the collapse of the conical shell speed jet parts are somewhat different, as a result of the jet in flight stretched. Therefore, a small increase in the gap between the charge and the target increases the depth of penetration due to the elongation of the jet. The thickness of the armor punctured cumulative projectiles, does not depend on the firing range and is approximately equal to their caliber. At greater distances between the charge and the target jet is torn apart, and the effect of penetration is reduced.
In 30-ies of XX century there was a mass saturation of troops tanks and armored vehicles. In addition to the traditional means of dealing with them, before the war in some countries were developing cumulative projectiles.
Especially attractive was that the armor penetration of such munitions are not dependent on the speed of a meeting with the armor. This allowed them to successfully apply for the destruction of tanks in artillery systems, originally not intended for this, as well as to create high-performance anti-tank mines and grenades. Most of all in the creation of advanced anti-tank weapons cumulative Germany, at the time of the attack on the Soviet Union there were created and put into service the cumulative artillery shells caliber 75-105 mm.

Unfortunately, in the Soviet Union before the war, this area has not been given due attention. In our country, the improvement of anti-tank weapons went through capacity-caliber anti-tank guns and an increase in the initial velocity armor-piercing shells. It is fair to say that in the USSR in the late 30's has been released and tested by shooting a pilot batch of 76-mm HEAT projectiles. During the tests, it turned out that the cumulative projectiles equipped with fuses staff from shrapnel shells are usually not penetrate the armor and give bounce. Obviously, it was detonated, but the military already has shown little interest in such projectiles, after unsuccessful firing finally they were rejected.
At the same time the Soviet Union had made a significant number of recoilless (dinamoreaktivny) Kurchevsky guns.

The advantage of these systems is light weight and lower cost compared to the "classical" instruments. Bezotkatki in conjunction with cumulative projectiles quite well could show itself as anti-tank weapons.
Since the beginning of the fighting from the front were reports that German artillery previously unknown uses so-called "broneprozhigayuschie" shells, effectively destroy tanks. When viewed from destroyed tanks noticed the characteristic form of holes with fused edges. At first it was suggested version that unidentified projectiles used ', fast-thermite "accelerated powder gases. However, experimentally this hypothesis was soon disproved. It has been found that the processes of burning thermite incendiary composition and interaction of the jet with the metal slag tank armor is too slow and can not be implemented in a very short time armor penetration projectile. At this time, from the front it was taken samples captured from the Germans' broneprozhigayuschih "shells. It turned out that their design is based on the cumulative effect of the explosion.
In early 1942, the designers MJ Vasilyev, ZV Vladimirov and N. Jitka designed 76-mm projectile with a cumulative charge hollow cone, lined steel shell. Was used artillery shell casing with bottom gear, the chamber is further tapered bore in the head part. The projectile used the powerful explosive - an alloy of TNT and hexogen. Bottom hole and the plug is used to install additional detonator and radiation blasting cap. The big problem was the lack of an appropriate fuse in the production. After a series of experiments was chosen Aviation fuse instantaneous AM-6.

Cumulative shells had about 70-75 mm armor piercing, ammunition appeared in the regimental guns since 1943, and manufactures standard throughout the war.

The industry has put about 1 front, 1 million. 76 mm cumulative anti-tank shells. Unfortunately, to use them in tank and 76-mm divisional guns because of unreliable operation fuse and the risk of explosion in the trunk was forbidden. Fuses for cumulative artillery shells, meet safety requirements when shooting long-barreled guns were set up only in late 1944.
In 1942, a group of designers as part of IP Dziuba, NP Kazeikin, IP Kucherenko, VY Matyushkina and AA Greenberg developed a cumulative anti-tank missiles to the 122 mm howitzer.
Posted in [mergetime] 1391850227 [/ mergetime]
122 mm howitzer shells for a cumulative sample of 1938 had a housing stalistogo iron equip an effective explosive composition based on RDX and powerful heaters detonator. 122mm HEAT projectile equipped with snap-action fuse B-229, which was developed in a very short time in the CDB-22, led by AJ Karpov.

122 mm howitzer shells for a cumulative sample of 1938 had a housing stalistogo iron equip an effective explosive composition based on RDX and powerful heaters detonator. 122mm HEAT projectile equipped with snap-action fuse B-229, which was developed in a very short time in the CDB-22, led by AJ Karpov.

The projectile was adopted, put into mass production in early 1943, and managed to take part in the Battle of Kursk. By the end of the war produced more than 100 thousand. 122mm shaped-charge projectiles. The shell pierced the armor thickness up to 150 mm normal, ensuring the defeat of the German heavy tank "Tiger" and "Panther". However, the effective range of the howitzer of maneuvering tanks was suicidal - 400 meters.
Creating a cumulative shells opened up great opportunities for the use of artillery shells with relatively small initial velocities - 76 mm regimental cannon samples in 1927 and 1943. and 122 mm howitzers of the sample in 1938 that large amounts were in the army. Availability cumulative rounds of ammunition in these instruments greatly increased the effectiveness of their anti-tank fire. This significantly increased the anti-Soviet defense infantry divisions.
One of the main tasks put into service in early 1941 armored Il-2 was a fight with armored vehicles.
However, the existing armed attack aircraft cannons effectively allowed to hit only lightly armored vehicles.
Reactive 82-132 mm shells did not have the required accuracy. However, for the weapons of IL-2 in 1942, it was designed cumulative RBSK-82.

Nosecone missile RBSK-82 consisted of a steel cylinder having a wall thickness of 8 mm. In the front part of the cylinder broke out into a cone of sheet metal, creating the recess in the explosive poured into the cylinder head of the projectile. In the center of the cylinder tube is passed, which served as "to transmit the beam fire from nakolnogo capsule to the detonator cap TAT-1." The shells were tested in two equipment BB: TNT and Alloy 70/30 (TNT and hexogen). The shells with TNT had a point for the AM-A fuse, and shells with alloy 70/30 - the fuse M-50. Fuses were blasting nakolnogo class action APUV. Missile parts RBSK-82 - standard, from the rockets M-8 filled with pyroxylin powder.
In total, during the test was spent RBSK 40 pieces 82, 18 of them - firing in the air, the rest - on the ground. Shelled captured German tanks Pz. III, StuG III and Czech tank Pz.38 (t) with enhanced reservation. Shooting in the air was carried out on the tank StuG III dive at an angle of 30 ° volleys 2-4 projectile in one go. Shooting distance of 200 m. The shells have shown good resistance to the flight path, but no falling off the tank could not be obtained.
Reactive armor-piercing shell cumulative effect RBSK-82, filled alloy 70/30, pierced the armor thickness of 30 mm at any angle of the meeting, and armor thickness of 50 mm punched at a right angle, but does not break the meeting at an angle of 30 °. Apparently, low armor penetration is a consequence of the delay in the activation fuse "on the rebound, and the jet stream is formed by a deformed cone."
Shells RBSK 82 TNT gear pierced the armor thickness of 30 mm only at the angles of the meeting not less than 30 °, and 50 mm armor - did not break under any circumstances hit. Holes produced in the through-penetration of armor, had a diameter of 35 mm. In most cases, armor penetration accompanied by splitting off of metal around the outlet.
Adopt cumulative RSy not accepted due to the lack of explicit advantages over regular rockets. On the approach it has had a new, much more powerful weapon - PTAB.
The priority in the development of small bombs cumulative effect belongs to Russian scientists and designers. In mid-1942 a well-known developer of fuses IA Larionov, proposed the construction of a light anti-tank bombs cumulative effects. The Air Force has expressed interest in the proposal. CDB-22 quickly conducted design work and testing new bombs began in late 1942. The final version represented PTAB 2, 5-1, 5, i.e. anti-aircraft bomb the cumulative effect of weight 1, 5 kg in size 2, 5 kg aviation bomb fragment. ICT has decided to urgently adopt PTAB-2, 5-1, 5, and organize its mass production.

At first PTAB-2, 5-1, 5 riveted hull and stabilizers pinnate-cylindrical shape manufactured from sheet steel with a thickness 0, 6 mm. To increase fragmentation on the cylindrical part of the bomb put an additional 1 steel, 5 mm-shirt. PTAB warhead consisted of smesevogo BB type of TGA, the loaded through the bottom point. To protect the fan fuse BP-A spontaneous clotting to wear special stabilizer bomb fuse from a tin plate with a square-shaped plug attached to it two wire whiskers extending between the blades. After dropping it from an airplane PTAB frustrated with bombs oncoming airflow.

Upon impact, the armor of the tank breakdowns fuse that through tetrilovuyu detonator bomb detonates an explosive charge. Upon detonation of the charge, thanks to the cumulative funnel and a metal cone in it, create the jet stream, which, as shown by field testing, armor penetration up to 60 mm at an angle of meeting 30 ° followed by destructive influence of the armor: the defeat of the crew of the tank, initiate detonation of munitions and ignition of fuel or vapors.
The bomb charging IL-2 included 192 aerial bombs PTAB-2, 5-1, 5, 4 cassettes small bombs (48 pieces each) or up to 220 pieces at their rational distribution in bulk in 4 bomb bay. < br />
Adopting PTAB some time kept secret, their use without the permission of the High Command was forbidden. It is possible to use the effect of surprise and effectively apply the new weapon in the battle of Kursk.

The massive use of PTAB had a stunning effect of tactical surprise and had a strong impact on the morale of the enemy. German tank crews, however, as the Soviet, the third year of the war have become accustomed to the relatively low efficiency bomboshturmovyh air strikes. In the initial phase of the battle the Germans did not apply the dispersed camping and pre-battle orders, that is, on routes of movement in convoys in the areas of concentration and starting positions, for which they were severely punished - lane expansion of the tank 2-3 PTAB overlaps removed from one another 60-75 m, so that the past carried significant losses, even in the absence of massive use of IL-2. One IL-2 with a height of 75-100 meters could cover the area 15h75 meters, destroying her entire enemy technology.
On average, during the war, irrecoverable losses of tanks from air operations did not exceed 5%, after the application of PTAB in some parts of the front is the figure exceeded 20%.

After recovering from the shock of the German tank crews soon moved exclusively to the march dispersed and pre-battle orders. Naturally, it is very difficult control of tank units, increased the timing of their deployment, redeployment and concentration, complicated interaction between them. At stops German tank crews began to have their cars under trees, awnings and light grid installed on the roof of the tower and light metal mesh body. Efficiency impacts of IL-2 with PTAB declined approximately 4-4 5 times, remaining, however, on average 2-3 times higher than when using a high explosive and high-explosive bombs.

In 1944 he was accepted into service a more powerful anti-tank bomb PTAB-10-2, 5, in dimensions of 10-kg aircraft bomb. It provided armor penetration thickness up to 160 mm. According to the principle of action and purpose of the major components and elements PTAB 10-2, 5 was similar PTAB-2, 5-1, 5, and differs from it only by the shape and dimensions.
On arms of the Red Army in 1920-1930-ies was dulnozaryadny "grenade Dyakonova", created at the end of the First World War, and subsequently upgraded.

It was a 41-caliber mortars mm that fits over the barrel of the rifle, fixing at gunpoint cut. On the eve of World War II there was a grenade in each rifle and cavalry unit. Then there was a question of giving the rifle grenade "anti" properties.
During World War II, in 1944, adopted the Red Army entered the cumulative pomegranate VCG-40. Fires pomegranate special blank cartridge 2, 75 g of powder brand VI or P-45. Reduced charge blank cartridge allow direct fire grenade fire with an emphasis butt in the shoulder at a distance up to 150 meters.

Rifle Grenade cumulative designed to deal with light armored vehicles and mobile enemy means not protected by armor, as well as gun emplacements. We used the CWS-40 is very limited, due to the low accuracy of fire and weak armor penetration.
During the war, the Soviet Union was released a significant amount of manual anti-tank grenades. Originally it was a grenade explosive action, increasing the thickness and weight of armor, increases anti-tank grenades. However, it still did not provide armor penetration of medium tanks, because a grenade RPG-41 with a weight of 1400 g of explosives could penetrate 25mm armor.

Needless to say, the danger represented antitank weapon is for the one who applied it.
In mid-1943, the Red Army adopted a fundamentally new pomegranate cumulative action RPG-43, developed by NP Belyakov. It was the first cumulative grenade, developed in the Soviet Union.

RPG-43 was a body with a flat bottom and a conical lid, wooden handle with a safety mechanism, tape stabilizer and shock-flammable fuse mechanism. Inside the housing placed with burster charge hollow conical lined with a thin layer of metal, glass, and fixed with its bottom a safety spring and a tip.
On its front end of the handle is attached a metal sleeve, which is located inside the fuse holder and hold it in the rearmost position pin. Outside in the bush wearing the spring and stacked cloth tape, attached to the cover of the stabilizer. The safety mechanism consists of folding strips and checks.
operation-barbarossa.narod.ru/artel...76-mm-m1927.htm
ser-sarajkin.narod2.ru/ALL_OUT/AiKO.../RBSK-82002.htm
Source:























