2403
Deep space through the eyes of the artist (21 photos)
American artist Walter Myers (Walter Myers) was born in 1958, a child is interested in astronomy. Through his paintings, drawn in accordance with the scientific data, we can admire the scenery of the other planets. Here is a selection of works Myers with his informative commentary.

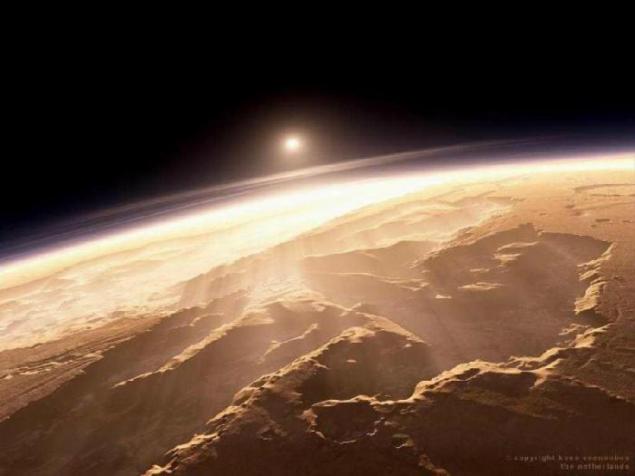
1. Sunrise on Mars.
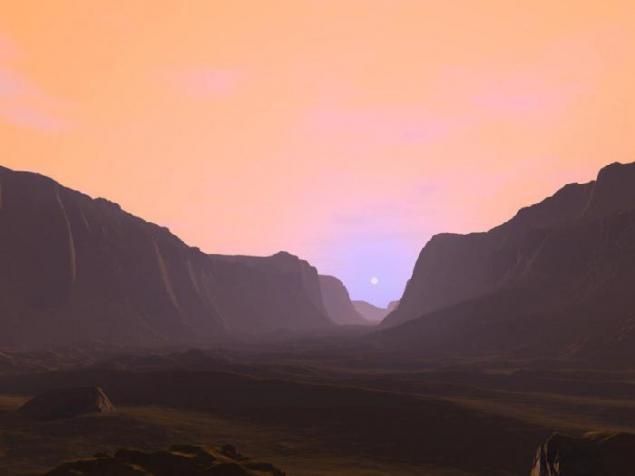

Sunrise on the bottom of one of the canyons in the Labyrinth of Night Tharsis on Mars. The reddish color of the sky gives the scattered dust in the atmosphere, which consists mainly of "rust" - iron oxides (if to real photographs taken rovers using an automatic color correction in image editor, the sky on them will be "normal" blue. Stones surface, however, will acquire a greenish hue, which is not true, so right all the same as here). This dust scatters and refracts light in part, as a result of the Sun in the sky appears blue halo.
2. Dawn on Io.
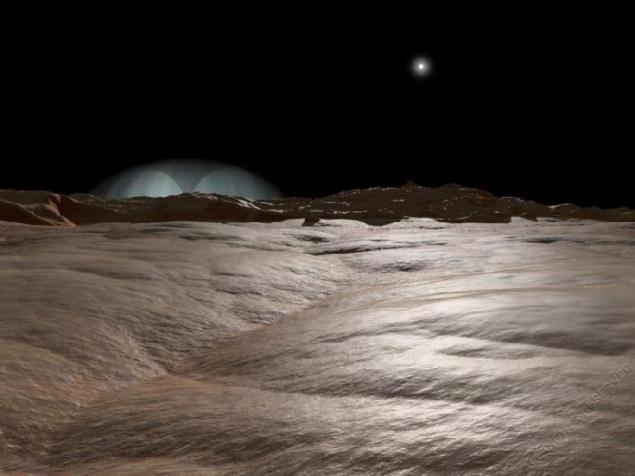

Dawn on Io, Jupiter's moon. Surface, similar to the snow in the foreground consists of crystals of sulfur dioxide emitted to the surface of geysers, like now rising above the close horizon. There is no atmosphere, creating turbulence, so geyser has the correct shape.
3. Dawn on Mars

4. The solar eclipse on Callisto.
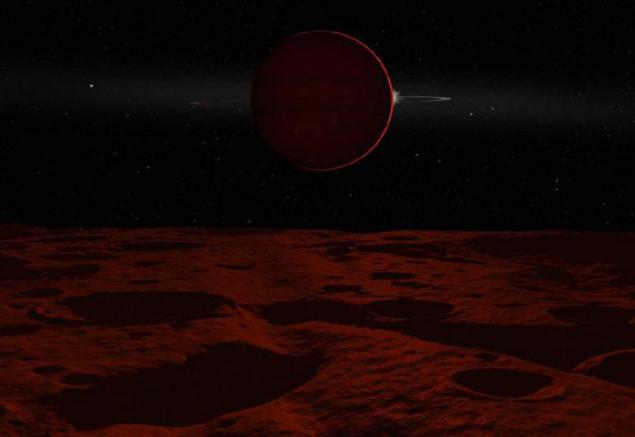

This is the farthest of the four large moons of Jupiter. It's smaller than Ganymede, but more than Io and Europa. Callisto is also covered with a crust of ice mixed with rocks, beneath which contains an ocean of water (the closer to the outskirts of the solar system, the greater the proportion of oxygen in the material planets, and, hence, water), but the tidal interaction of the satellite hardly plagued so superficial ice thickness can reach one hundred km, and volcanism absent, so that the presence of life here is unlikely. In this photo we look at Jupiter from a position about 5 ° from the north pole of Callisto. The sun will soon be over the right edge of Jupiter; and its rays are refracted atmosphere of the giant planet. Blue dot to the left of Jupiter - is the Earth, yellowish right - Venus and right and above it - Mercury. Whitish band Jupiter - not the Milky Way, and the gas-dust disk in the plane of the ecliptic the inner solar system, known as the terrestrial observer "zodiacal light"
5. Jupiter - satellite view of Europe.
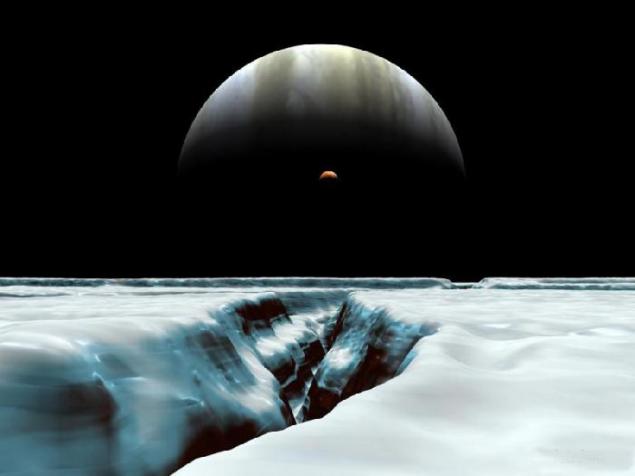

Crescent Jupiter varies slowly over the horizon of Europe. The eccentricity of its orbit is constantly exposed to disturbances due to the orbital resonance with Io, which is now just against the backdrop of Jupiter. Tidal deformation causes the surface of Europa covered with deep cracks and provides satellite warm, stimulating underground geological processes, allowing you to stay subsurface ocean of liquid.
6. Sunrise on Mercury.
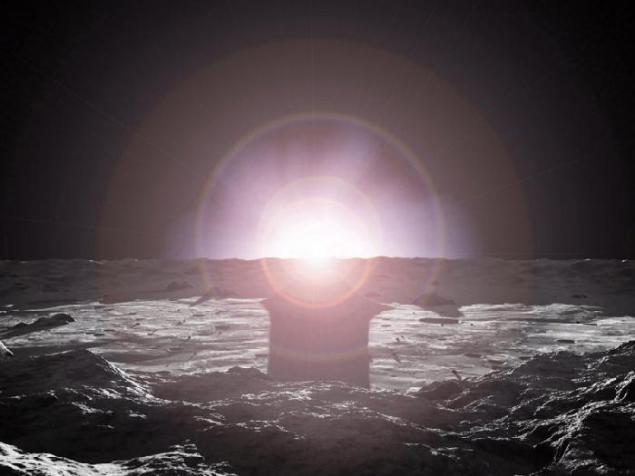

Disk of the sun appears to Mercury three times larger than the Earth, and many times brighter, especially in an airless sky.
7. Given the slowness of the rotation of the planet, to this for a few weeks with the same point could be seen slowly creeps over the horizon solar corona
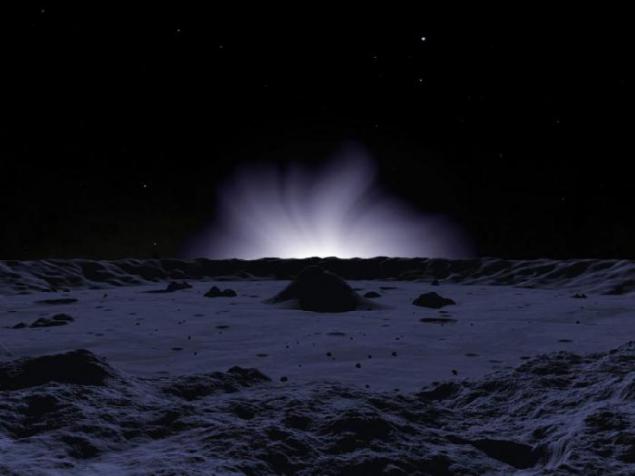

8. Triton.
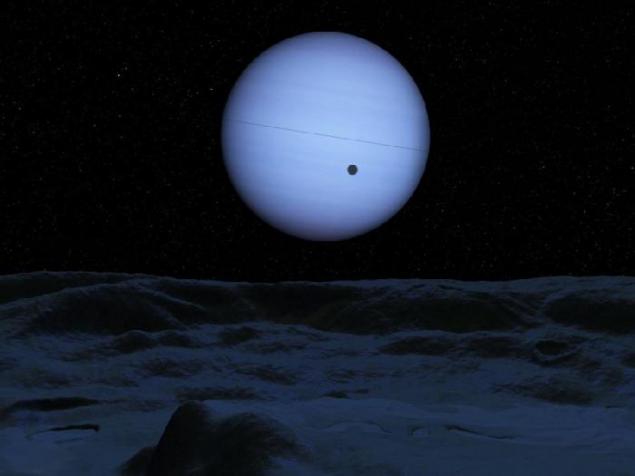

Full Neptune in the sky - the only source of light for the night side of Triton. A thin line across the disk of Neptune - this is his ring, visible edge and dark circle - the shadow of the Triton. The opposite edge of the depression in the middle ground is about 15 kilometers.
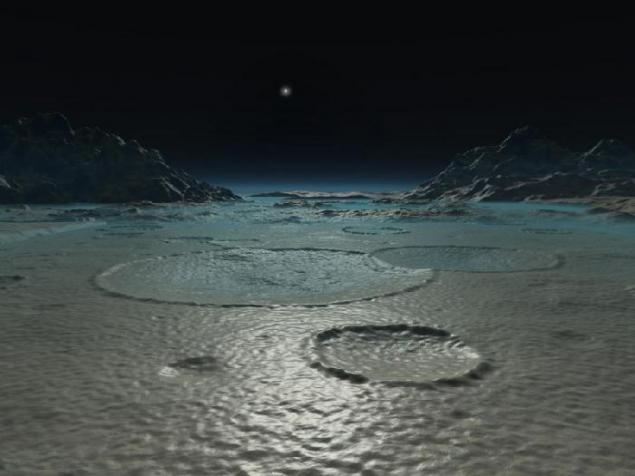
9. sunrise on Triton is no less impressive:

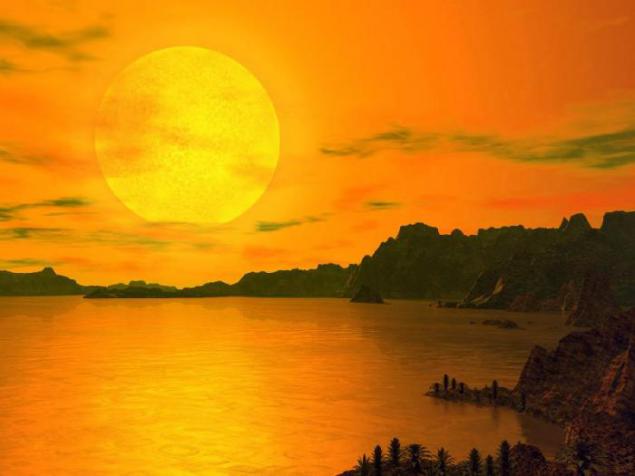
10. "Summer" on Pluto.
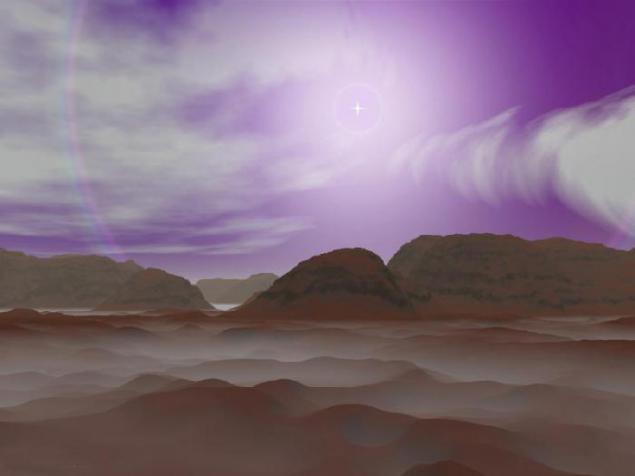

Despite its small size and great distance from the Sun, Pluto has an atmosphere at times. This happens when Pluto is moving along its elongated orbit, fits closer to the Sun Neptune. During this period, about twenty of the methane-nitrogen ice surface evaporates, enveloping the planet atmosphere, the density of the Martian rival. February 11, 1999, Pluto has once again crossed the orbit of Neptune, and it once again became further from the Sun (and now would be the ninth, the farthest from the sun, planets, if in 2006 with the adoption of the definition of "planet" was not "demoted") . Now up to 2231 goda.on will be the usual (though large) the frozen planetoid Kuiper Belt - a dark, covered with armor of frozen gases, in some places has acquired a reddish tint from the interaction of gamma rays with open space.
11. Dangerous dawn on Gliese 876d.

The danger in itself can carry sunrises on the planet Gliese 876d. Although, in fact, none of mankind does not know the actual conditions on this planet. It rotates at a very close distance from the variable star - a red dwarf star Gliese 876. This image shows how they imagined the artist. The mass of this planet several times the mass of Earth, and the size of its orbit is smaller than the orbit of Mercury. Gliese 876d rotates so slowly that the conditions on this planet day and night are very different. You can prevent the assumption that Gliese 876d possibility of a strong volcanic activity caused by gravitational tides that deformiruyuet and heating up the planet, and she is enhanced in the daytime.
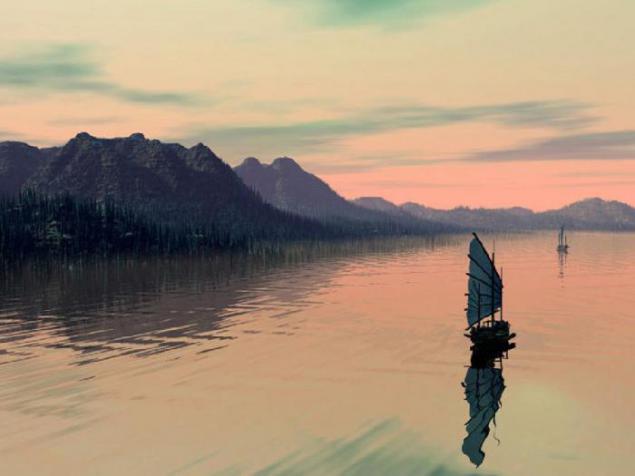
12. Ship sentient beings under the green sky unknown planet.

13. Gliese 581, she's Wolf 562 - class red dwarf star located in the constellation of Libra, 20, 4 St. years from Earth.

The main attraction of its system - the first open scientists exoplanet Gliese 581 C within the "habitable zone" - that is, not too close and not too far from the star that its surface could be liquid water. The surface temperature of the planet is from -3 ° C to + 40 ° C, which means that it can be inhabited. Gravity on the surface of one and a half times higher than Earth's, and "year" is only 13 days. As a result, such a short distance to the star Gliese 581 C is always turned to one side of it, so the change of day and night is not there (although the light can be raised and lowered relative to the horizon due to the eccentricity of the orbit and inclination of the planetary axis). The star Gliese 581 is half the diameter of the Sun and a hundred times fainter.
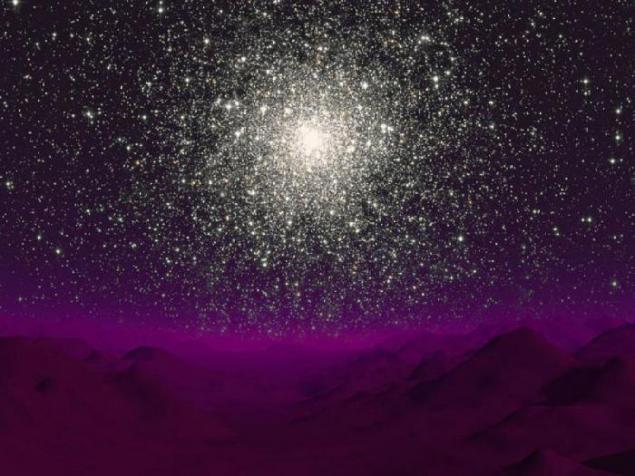
14. Planetarium or rogue planet called planet that do not revolve around the stars and drift freely in interstellar space. Some of them are formed like stars, as a result of gravitational contraction of gas and dust clouds, others are having, like ordinary planets in star systems, but were thrown out into interstellar space due to disturbances from neighboring planets. Planetarium to be fairly common in the galaxy, but they are almost impossible to find, and most of the wandering planets will likely never be opened. If the mass of the planetarium is 0, 6-0, 8 from the earth and above, it is able to retain an atmosphere, which will stop the heat generated by the subsoil and the temperature and pressure at the surface can be dvzhe acceptable for life. On the surface of their reigns eternal night. Globular cluster, which travels along the edge of the planetarium, contains about 50 000 stars and is close to our own galaxy. Perhaps in his heart, as in the nuclei of many galaxies, supermassive black hole lurks. Globular clusters typically contain very old stars, and the planetarium, probably too much older than the Earth.

15. When the life of a star like our sun nears the end, it expands to more than 200 times its original diameter, becoming a red giant and destroying the inner planets of the system. Then, within a few tens of thousands of years the star occasionally ejects its outer layers into space, sometimes with the formation of concentric shells, after which it remains small, very hot core, which cools and shrinks to become a white dwarf. Here we see the beginning of compression - star throws the first of its gas shells. This ghostly sphere will gradually expand, eventually leaving far beyond the orbit of this planet - "Pluto" this star system, almost all of its history - ten billion years - far carried through on its outskirts in a dark dead ball covered with a layer of frozen gases. The last hundred million years, it is bathed in streams of light and heat, thawed nitrogen-methane ice formed the atmosphere and on the surface of this water rivers flow. But soon - in astronomical terms - this planet once again plunged into darkness and cold - now forever.

16. The gloomy landscape nameless planet drifting with his star system in the depths of a dense absorbing nebula - an immense interstellar gas and dust clouds.
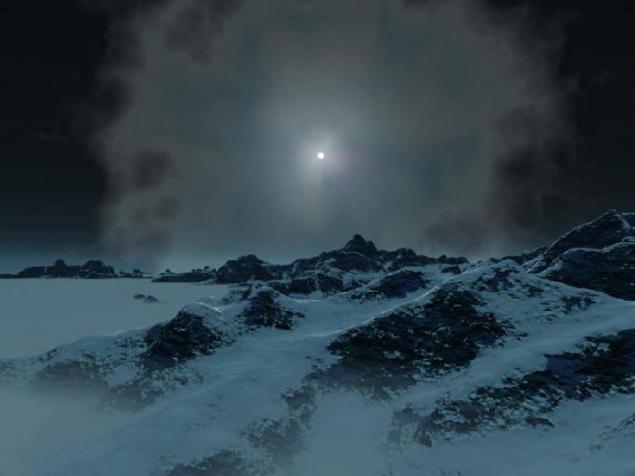

Light from other stars is hidden, while the solar wind from the central luminary system "inflates" the material of the nebula, creating a bubble around a star relative to free space, which can be seen in the sky as a light spot necessary, within about 160 million. Km - is a tiny tear in dark cloud, whose dimensions are measured in light years. Planet whose surface we see was once geologically active world with a significant atmosphere - as evidenced by the lack of impact craters - but after immersion in the nebula amount of sunlight and heat reaching the surface decreased so that a large part of the atmosphere is simply frozen and of snow. Life that once flourished here, disappeared.
17. Star in the sky this marsopodobnoy planet - it Teide 1.
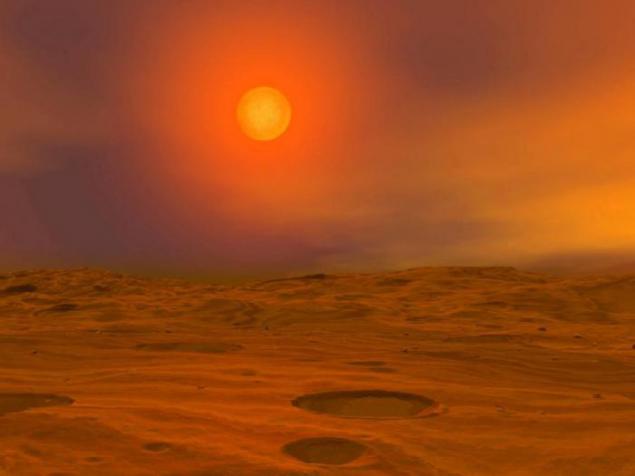

Discovered in 1995, the Teide 1 is one of the brown dwarfs - stars tiny mass of several tens of times smaller than the Sun - and is four hundred light-years from Earth in the Pleiades star cluster. Teide 1 has a mass of about 55 times greater than that of Jupiter, and is considered quite large for a brown dwarf. and, consequently, hot enough to maintain the synthesis of lithium in its bosom, but she is not able to start the process of nuclear fusion of hydrogen, like our sun. There is this substars probably only about 120 million years (compared to 4.5 billion years of existence of the Sun), and burns at a temperature of 2200 ° C - not half as hot as the sun. The planet, which we look at the Teide 1, is from her at a distance of about 6, 5 million km. There is an atmosphere and even clouds, but she's too young for life. Light in the sky looks dangerously large, but in fact it is only the diameter of two times more than Jupiter. All brown dwarfs in size comparable to Jupiter - the more massive of them are just more dense. As for life on this planet, then it probably just did not have time to develop in a short period of active life of a star - she meted out for about three hundred million years, after which another billion years it will slowly dotlevat at least a thousand degrees and stops already considered star.
18. Spring in Phoenix.
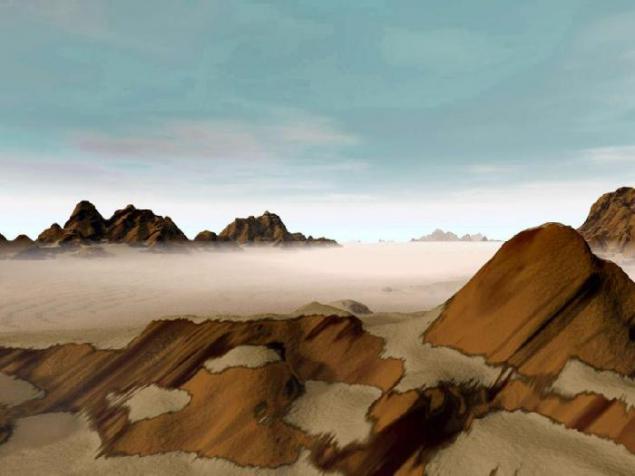

This world is similar to Earth ... but he deserted. Perhaps here, for some reason, did not have life, despite the favorable conditions, and maybe life just do not have time to produce advanced forms and get to dry land.
19. The frozen world.
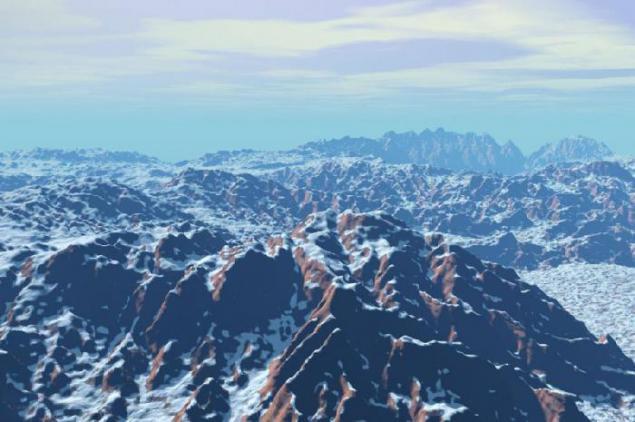

Some Earth-like planets may be located too far from the stars to their surface maintain an acceptable temperature for life. "Too far" in this case - is a relative concept, it all depends on the composition of the atmosphere and the presence or absence of the greenhouse effect. In the history of our Earth was a period (850-630 million years ago), when the whole it is a continuous ice desert from pole to pole and the equator was as cold as in modern Antarctica. By the beginning of this global glaciation on Earth already existed unicellular life, and if volcanoes millions of years is not saturated the atmosphere with carbon dioxide and methane so that the ice began to melt, life on Earth still would be represented by bacteria yutyaschimisya on rocky outcrops and in areas of volcanism
20. Ambler.
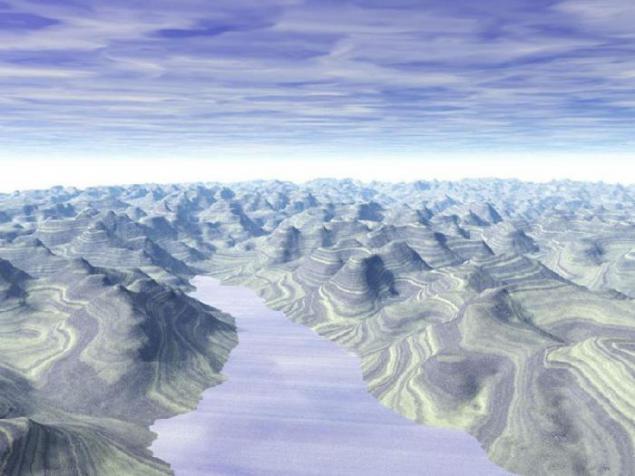

Alien world with different geology. Education resemble remnants of layered ice. Judging by the lack of sediment in the lowlands, they are formed by melting rather than weathering.

1. Sunrise on Mars.

Sunrise on the bottom of one of the canyons in the Labyrinth of Night Tharsis on Mars. The reddish color of the sky gives the scattered dust in the atmosphere, which consists mainly of "rust" - iron oxides (if to real photographs taken rovers using an automatic color correction in image editor, the sky on them will be "normal" blue. Stones surface, however, will acquire a greenish hue, which is not true, so right all the same as here). This dust scatters and refracts light in part, as a result of the Sun in the sky appears blue halo.
2. Dawn on Io.

Dawn on Io, Jupiter's moon. Surface, similar to the snow in the foreground consists of crystals of sulfur dioxide emitted to the surface of geysers, like now rising above the close horizon. There is no atmosphere, creating turbulence, so geyser has the correct shape.
3. Dawn on Mars

4. The solar eclipse on Callisto.

This is the farthest of the four large moons of Jupiter. It's smaller than Ganymede, but more than Io and Europa. Callisto is also covered with a crust of ice mixed with rocks, beneath which contains an ocean of water (the closer to the outskirts of the solar system, the greater the proportion of oxygen in the material planets, and, hence, water), but the tidal interaction of the satellite hardly plagued so superficial ice thickness can reach one hundred km, and volcanism absent, so that the presence of life here is unlikely. In this photo we look at Jupiter from a position about 5 ° from the north pole of Callisto. The sun will soon be over the right edge of Jupiter; and its rays are refracted atmosphere of the giant planet. Blue dot to the left of Jupiter - is the Earth, yellowish right - Venus and right and above it - Mercury. Whitish band Jupiter - not the Milky Way, and the gas-dust disk in the plane of the ecliptic the inner solar system, known as the terrestrial observer "zodiacal light"
5. Jupiter - satellite view of Europe.

Crescent Jupiter varies slowly over the horizon of Europe. The eccentricity of its orbit is constantly exposed to disturbances due to the orbital resonance with Io, which is now just against the backdrop of Jupiter. Tidal deformation causes the surface of Europa covered with deep cracks and provides satellite warm, stimulating underground geological processes, allowing you to stay subsurface ocean of liquid.
6. Sunrise on Mercury.

Disk of the sun appears to Mercury three times larger than the Earth, and many times brighter, especially in an airless sky.
7. Given the slowness of the rotation of the planet, to this for a few weeks with the same point could be seen slowly creeps over the horizon solar corona

8. Triton.

Full Neptune in the sky - the only source of light for the night side of Triton. A thin line across the disk of Neptune - this is his ring, visible edge and dark circle - the shadow of the Triton. The opposite edge of the depression in the middle ground is about 15 kilometers.
9. sunrise on Triton is no less impressive:

10. "Summer" on Pluto.

Despite its small size and great distance from the Sun, Pluto has an atmosphere at times. This happens when Pluto is moving along its elongated orbit, fits closer to the Sun Neptune. During this period, about twenty of the methane-nitrogen ice surface evaporates, enveloping the planet atmosphere, the density of the Martian rival. February 11, 1999, Pluto has once again crossed the orbit of Neptune, and it once again became further from the Sun (and now would be the ninth, the farthest from the sun, planets, if in 2006 with the adoption of the definition of "planet" was not "demoted") . Now up to 2231 goda.on will be the usual (though large) the frozen planetoid Kuiper Belt - a dark, covered with armor of frozen gases, in some places has acquired a reddish tint from the interaction of gamma rays with open space.
11. Dangerous dawn on Gliese 876d.

The danger in itself can carry sunrises on the planet Gliese 876d. Although, in fact, none of mankind does not know the actual conditions on this planet. It rotates at a very close distance from the variable star - a red dwarf star Gliese 876. This image shows how they imagined the artist. The mass of this planet several times the mass of Earth, and the size of its orbit is smaller than the orbit of Mercury. Gliese 876d rotates so slowly that the conditions on this planet day and night are very different. You can prevent the assumption that Gliese 876d possibility of a strong volcanic activity caused by gravitational tides that deformiruyuet and heating up the planet, and she is enhanced in the daytime.
12. Ship sentient beings under the green sky unknown planet.

13. Gliese 581, she's Wolf 562 - class red dwarf star located in the constellation of Libra, 20, 4 St. years from Earth.

The main attraction of its system - the first open scientists exoplanet Gliese 581 C within the "habitable zone" - that is, not too close and not too far from the star that its surface could be liquid water. The surface temperature of the planet is from -3 ° C to + 40 ° C, which means that it can be inhabited. Gravity on the surface of one and a half times higher than Earth's, and "year" is only 13 days. As a result, such a short distance to the star Gliese 581 C is always turned to one side of it, so the change of day and night is not there (although the light can be raised and lowered relative to the horizon due to the eccentricity of the orbit and inclination of the planetary axis). The star Gliese 581 is half the diameter of the Sun and a hundred times fainter.
14. Planetarium or rogue planet called planet that do not revolve around the stars and drift freely in interstellar space. Some of them are formed like stars, as a result of gravitational contraction of gas and dust clouds, others are having, like ordinary planets in star systems, but were thrown out into interstellar space due to disturbances from neighboring planets. Planetarium to be fairly common in the galaxy, but they are almost impossible to find, and most of the wandering planets will likely never be opened. If the mass of the planetarium is 0, 6-0, 8 from the earth and above, it is able to retain an atmosphere, which will stop the heat generated by the subsoil and the temperature and pressure at the surface can be dvzhe acceptable for life. On the surface of their reigns eternal night. Globular cluster, which travels along the edge of the planetarium, contains about 50 000 stars and is close to our own galaxy. Perhaps in his heart, as in the nuclei of many galaxies, supermassive black hole lurks. Globular clusters typically contain very old stars, and the planetarium, probably too much older than the Earth.

15. When the life of a star like our sun nears the end, it expands to more than 200 times its original diameter, becoming a red giant and destroying the inner planets of the system. Then, within a few tens of thousands of years the star occasionally ejects its outer layers into space, sometimes with the formation of concentric shells, after which it remains small, very hot core, which cools and shrinks to become a white dwarf. Here we see the beginning of compression - star throws the first of its gas shells. This ghostly sphere will gradually expand, eventually leaving far beyond the orbit of this planet - "Pluto" this star system, almost all of its history - ten billion years - far carried through on its outskirts in a dark dead ball covered with a layer of frozen gases. The last hundred million years, it is bathed in streams of light and heat, thawed nitrogen-methane ice formed the atmosphere and on the surface of this water rivers flow. But soon - in astronomical terms - this planet once again plunged into darkness and cold - now forever.

16. The gloomy landscape nameless planet drifting with his star system in the depths of a dense absorbing nebula - an immense interstellar gas and dust clouds.

Light from other stars is hidden, while the solar wind from the central luminary system "inflates" the material of the nebula, creating a bubble around a star relative to free space, which can be seen in the sky as a light spot necessary, within about 160 million. Km - is a tiny tear in dark cloud, whose dimensions are measured in light years. Planet whose surface we see was once geologically active world with a significant atmosphere - as evidenced by the lack of impact craters - but after immersion in the nebula amount of sunlight and heat reaching the surface decreased so that a large part of the atmosphere is simply frozen and of snow. Life that once flourished here, disappeared.
17. Star in the sky this marsopodobnoy planet - it Teide 1.

Discovered in 1995, the Teide 1 is one of the brown dwarfs - stars tiny mass of several tens of times smaller than the Sun - and is four hundred light-years from Earth in the Pleiades star cluster. Teide 1 has a mass of about 55 times greater than that of Jupiter, and is considered quite large for a brown dwarf. and, consequently, hot enough to maintain the synthesis of lithium in its bosom, but she is not able to start the process of nuclear fusion of hydrogen, like our sun. There is this substars probably only about 120 million years (compared to 4.5 billion years of existence of the Sun), and burns at a temperature of 2200 ° C - not half as hot as the sun. The planet, which we look at the Teide 1, is from her at a distance of about 6, 5 million km. There is an atmosphere and even clouds, but she's too young for life. Light in the sky looks dangerously large, but in fact it is only the diameter of two times more than Jupiter. All brown dwarfs in size comparable to Jupiter - the more massive of them are just more dense. As for life on this planet, then it probably just did not have time to develop in a short period of active life of a star - she meted out for about three hundred million years, after which another billion years it will slowly dotlevat at least a thousand degrees and stops already considered star.
18. Spring in Phoenix.

This world is similar to Earth ... but he deserted. Perhaps here, for some reason, did not have life, despite the favorable conditions, and maybe life just do not have time to produce advanced forms and get to dry land.
19. The frozen world.

Some Earth-like planets may be located too far from the stars to their surface maintain an acceptable temperature for life. "Too far" in this case - is a relative concept, it all depends on the composition of the atmosphere and the presence or absence of the greenhouse effect. In the history of our Earth was a period (850-630 million years ago), when the whole it is a continuous ice desert from pole to pole and the equator was as cold as in modern Antarctica. By the beginning of this global glaciation on Earth already existed unicellular life, and if volcanoes millions of years is not saturated the atmosphere with carbon dioxide and methane so that the ice began to melt, life on Earth still would be represented by bacteria yutyaschimisya on rocky outcrops and in areas of volcanism
20. Ambler.

Alien world with different geology. Education resemble remnants of layered ice. Judging by the lack of sediment in the lowlands, they are formed by melting rather than weathering.