1661
The role of mushrooms in nature
The role of fungi in nature and the human economy can not be overestimated. Fungi are present in all biological niches - in the water and on land, in the soil and at various other substrates. A very high biological and ecological diversity of fungi. This is one of the largest and most diverse group of living organisms, has become an integral part of all the aquatic and terrestrial ecosystems. According to the current estimates, in the world there are 100 to 250 thousand, and by some estimates up to 1, 5 million species of fungi.
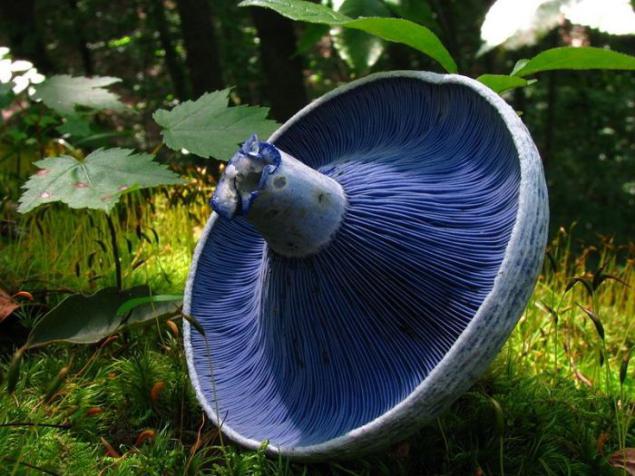

Lactarius indigo (Lactarius indigo). Fairly common type of fungus, grows in eastern North America, East Asia and Central America. It grows on the ground in deciduous and coniferous forests. The color varies from dark blue at the fresh mushrooms to pale blue-gray in old. Milk, which identifies fungus if its cut or break, too blue. Cap is 5-15 cm, leg - 2-8 cm in height and 1-2, 5 cm in thickness. Edible fungus and sold in rural markets in Mexico, Guatemala and China.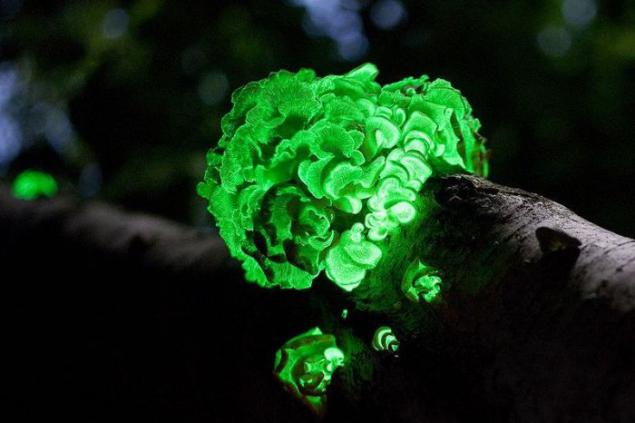
Panellyus kind Panellus stipticus. A common view is growing in Asia, Australia, Europe and North America. It grows in groups on logs, stumps and trunks of deciduous trees, especially on oaks, beeches and birches. This is one of the bioluminescent species of fungi, although fungi of this species from the Pacific region, North America, no.
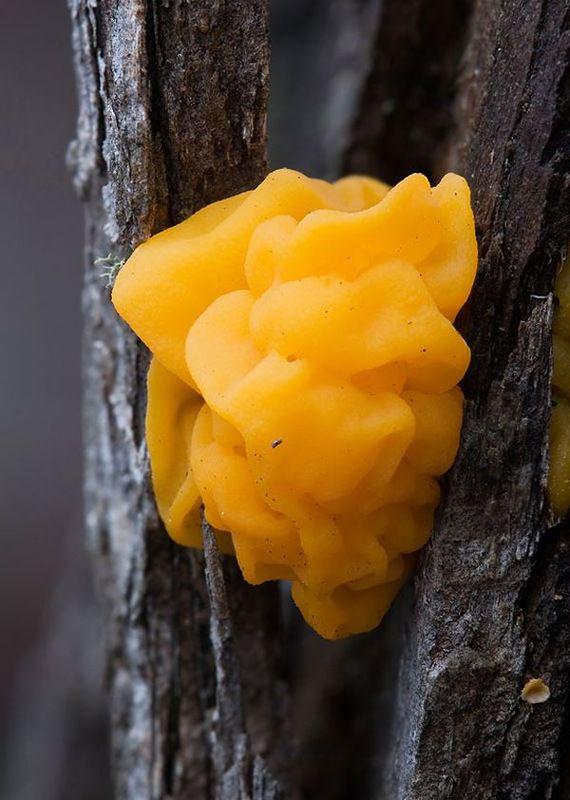

Tremella Mesenterica (Tremella mesenterica). This fungus often grows on dead trees, but also on the recently fallen branches. Orange-yellow gelatinous body of the fungus (7, 5 cm in diameter) has a winding surface which during rain becomes sticky and slippery. The fungus grows in the cracks of the bark, appearing in the rain. A few days after the rain it dries and turns into a thin film or a wrinkled mass capable revived after the rain. This fungus is commonly found in mixed forests and distributed in temperate and tropical regions, including Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, North and South America. The mushroom is edible, although it is tasteless. This fungus produces carbohydrates that are valuable for research.
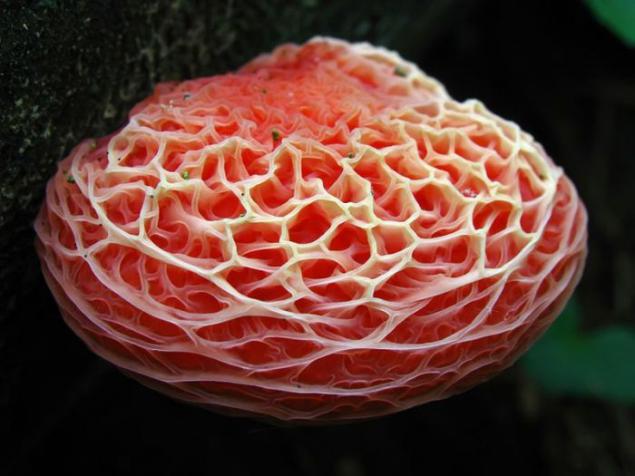

Rhodotus (Rhodotus palmatus). This fungus - the only representative of the genus in the family Physalacriaceae. Not very common. The fungus collected in eastern North America, North Africa, Europe and Asia. In Europe, the number of fungi is rapidly falling, so rhodotus made in the Red Book. Usually it grows on stumps and rotting logs solid wood. Mature mushroom differ pinkish color and the characteristic "venoobraznoy" surface.
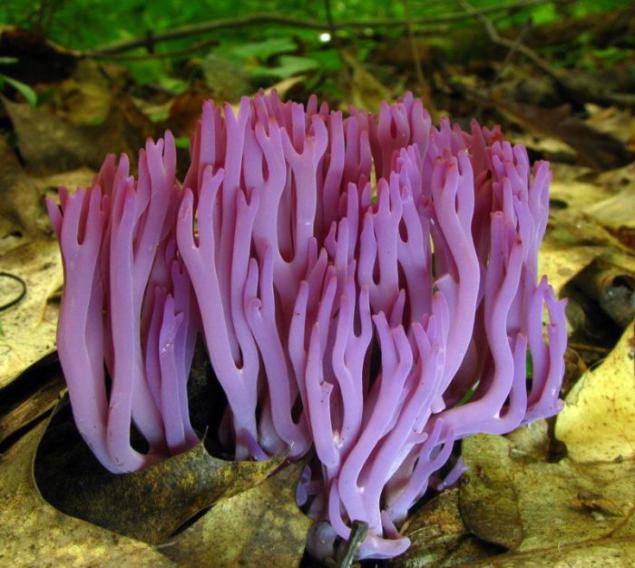

Klavariya pale brown (Clavaria zollingeri). Widespread species of fungi. It has a tube-shaped purple or pinkish-lavender body that grows up to 10 cm high and 7 cm wide. The tips of the fragile and thin branches are usually rounded and brownish. It saprobity kind of mushroom, it absorbs nutrients, breaking down organic matter. Usually it grows on the ground.
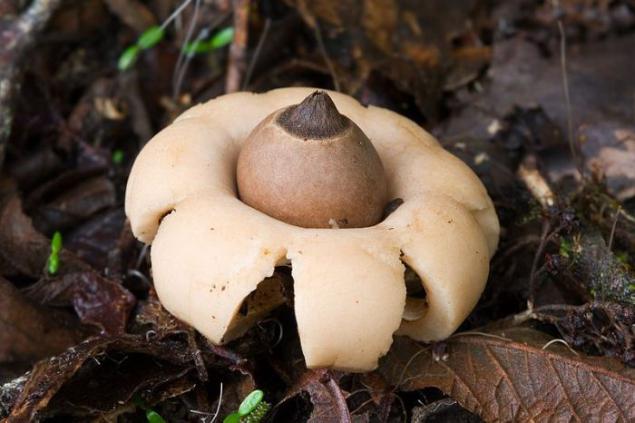

Geastrum bag-shaped (Geastrum saccatum). It grows in North America and Europe on decaying trees. Mushroom pickers believe it inedible because of its taste slides. Pretty common form of the peak gathering comes at the end of the summer. It is believed that the hole in the outer layer of the mushroom body has a star shape due to the gathering of calcium oxalate crystals in front of the opening. In Brazil, a mushroom called the "Star of the earth».
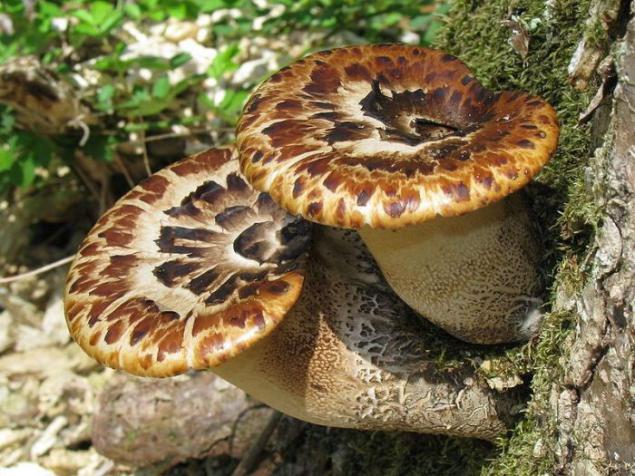

Scaly Polypore (Polyporus squamosus). Widespread species of fungus growing in North America, Australia, Asia and Europe. It causes white rot on the hard wood. Alternative name of the fungus - the saddle Dryad - refers to Greek mythology and the Dryads who supposedly could ride on these fungi.
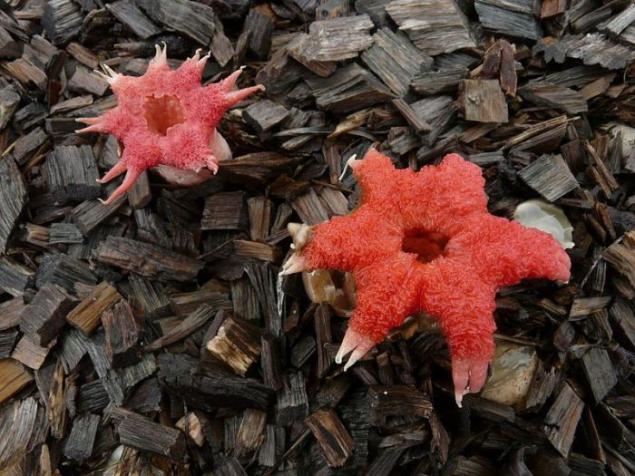

Aseroe rubra. The so-called sea anemone is widespread and recognizable due to its unpleasant smell of rot and shape of starfish. It grows in the gardens of the forest floor in grassy areas, reminiscent of the red star, covered with brownish slime, and has a white foot. Attracts flies.
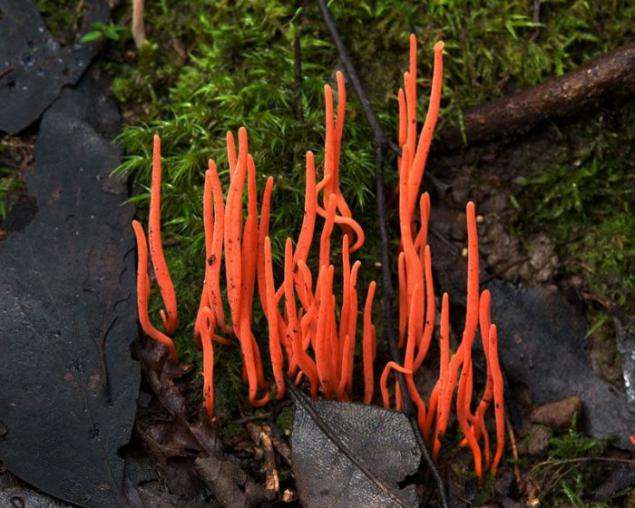

Coral mushroom (Clavulinopsis corallinorosacea). The fungus is called so because of the similarity with sea corals. These mushrooms have bright colors, mostly orange, yellow or red. Usually they grow older lesah.odni saprotrophic coral fungi, and other symbiotic or parasitic.
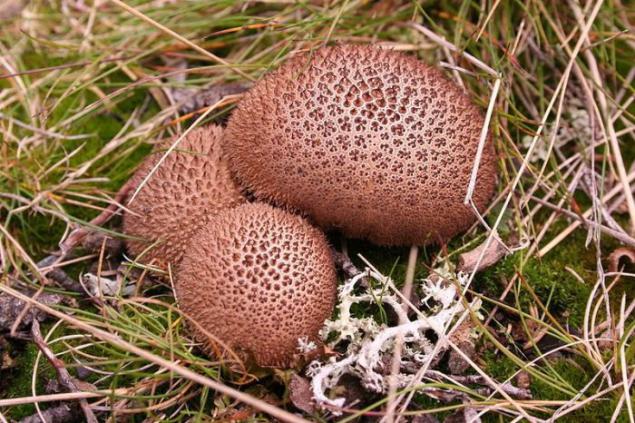

Brown Puffball (Lycoperdon umbrinum). This type of fungus grows in China, Europe and North America. These mushrooms are not open hats disputes. Instead, disputes occur within in a spherical body. Ripening, spores form Hleb in the center of the body, which has a distinctive color and texture.
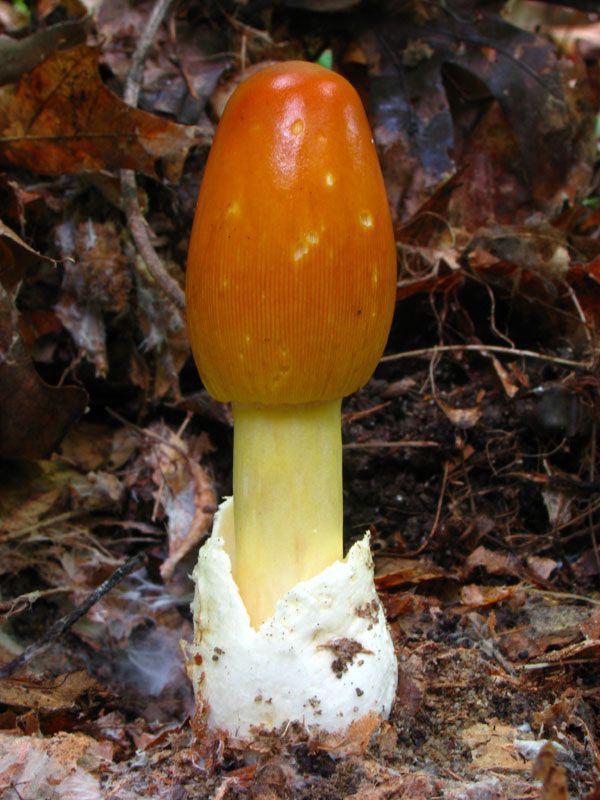

Amanita Caesarea (Amanita caesarea). Very valuable edible mushroom that grows in southern Europe and North America. For the first time this fungus described by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in 1772. He was very fond of the rulers of the Roman Empire. He has a distinctive orange cap, yellow spore-bearing plate and the leg. This fungus is very much appreciated by the Romans, who called it Boletus.
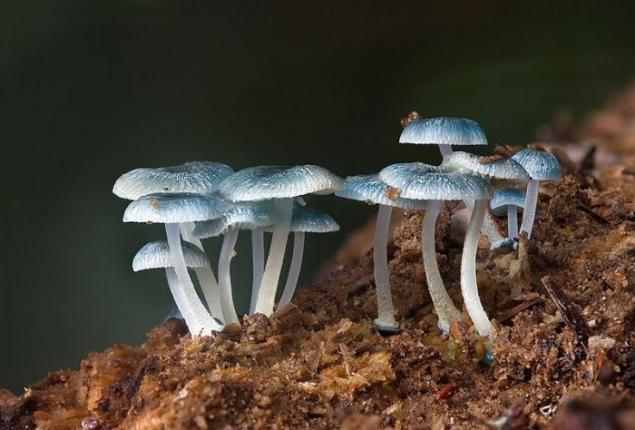

Mycena interrupta. This mushroom grows in Australia, New Zealand, Chile and New Caledonia. In Australia, it is increasing in Victoria, Tasmania, New South Wales and South Australia and Queensland, but only at The National Park Lamington. Cap mushroom is 0, 6-2 cm, and they have a bright blue color. When they appear, they have a spherical shape, but as they mature become wider. Hats sticky and slimy in appearance, especially in the rain.
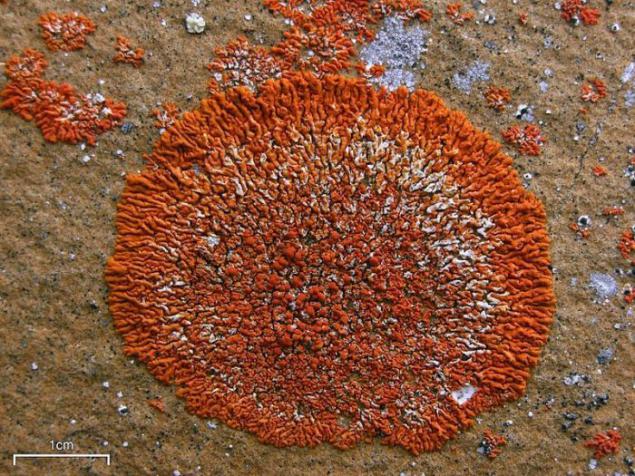

Ksantor elegant (Xanthoria elegans). This fungus grows on rocks, often near bird perches or mink rodents. By the nature of this lichen. He became one of the first lichens, who used the method of dating the rock surfaces, known as lihenometriya. Growing at a rate of 0, 5 mm per year during the first century, then its growth slows down a bit.
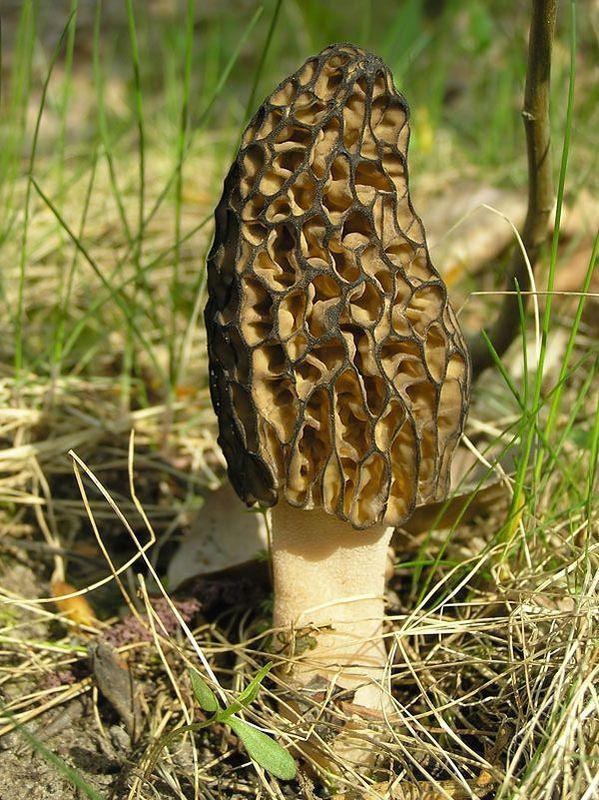

Conical Morel (Morchella conica). Edible mushroom, in the upper part resembling a honeycomb. It consists of the entire network wavy bands with cavities therebetween. It is appreciated by gourmets, particularly in French cuisine. The fungus is very popular with mushroom pickers, not only from a commercial point of view but also because of the pleasant taste.
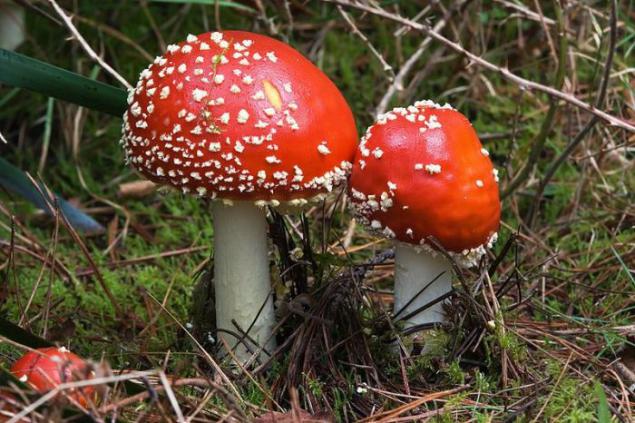

Amanita muscaria (Amanita muscaria). All known amanita - poisonous and psychoactive basidiomycete. It grows in the northern hemisphere, but also was introduced to the countries of the southern hemisphere, first as a symbiont in coniferous forests, and then as a full species. Red hat with white dots - who do not know the mushroom? This is one of the most recognizable of fungi in the world. Although considered a poisonous mushroom, Amanita muscaria confirmed cases of poisoning is not, and in some parts of Europe, Asia and North America, and it does eat after blanching. Amanita has hallucinogenic properties, its main psychoactive component - is muscimol. Some peoples of Siberia used it as entheogen, and it has great religious significance in these cultures.

Lactarius indigo (Lactarius indigo). Fairly common type of fungus, grows in eastern North America, East Asia and Central America. It grows on the ground in deciduous and coniferous forests. The color varies from dark blue at the fresh mushrooms to pale blue-gray in old. Milk, which identifies fungus if its cut or break, too blue. Cap is 5-15 cm, leg - 2-8 cm in height and 1-2, 5 cm in thickness. Edible fungus and sold in rural markets in Mexico, Guatemala and China.

Panellyus kind Panellus stipticus. A common view is growing in Asia, Australia, Europe and North America. It grows in groups on logs, stumps and trunks of deciduous trees, especially on oaks, beeches and birches. This is one of the bioluminescent species of fungi, although fungi of this species from the Pacific region, North America, no.

Tremella Mesenterica (Tremella mesenterica). This fungus often grows on dead trees, but also on the recently fallen branches. Orange-yellow gelatinous body of the fungus (7, 5 cm in diameter) has a winding surface which during rain becomes sticky and slippery. The fungus grows in the cracks of the bark, appearing in the rain. A few days after the rain it dries and turns into a thin film or a wrinkled mass capable revived after the rain. This fungus is commonly found in mixed forests and distributed in temperate and tropical regions, including Africa, Asia, Australia, Europe, North and South America. The mushroom is edible, although it is tasteless. This fungus produces carbohydrates that are valuable for research.

Rhodotus (Rhodotus palmatus). This fungus - the only representative of the genus in the family Physalacriaceae. Not very common. The fungus collected in eastern North America, North Africa, Europe and Asia. In Europe, the number of fungi is rapidly falling, so rhodotus made in the Red Book. Usually it grows on stumps and rotting logs solid wood. Mature mushroom differ pinkish color and the characteristic "venoobraznoy" surface.

Klavariya pale brown (Clavaria zollingeri). Widespread species of fungi. It has a tube-shaped purple or pinkish-lavender body that grows up to 10 cm high and 7 cm wide. The tips of the fragile and thin branches are usually rounded and brownish. It saprobity kind of mushroom, it absorbs nutrients, breaking down organic matter. Usually it grows on the ground.

Geastrum bag-shaped (Geastrum saccatum). It grows in North America and Europe on decaying trees. Mushroom pickers believe it inedible because of its taste slides. Pretty common form of the peak gathering comes at the end of the summer. It is believed that the hole in the outer layer of the mushroom body has a star shape due to the gathering of calcium oxalate crystals in front of the opening. In Brazil, a mushroom called the "Star of the earth».

Scaly Polypore (Polyporus squamosus). Widespread species of fungus growing in North America, Australia, Asia and Europe. It causes white rot on the hard wood. Alternative name of the fungus - the saddle Dryad - refers to Greek mythology and the Dryads who supposedly could ride on these fungi.

Aseroe rubra. The so-called sea anemone is widespread and recognizable due to its unpleasant smell of rot and shape of starfish. It grows in the gardens of the forest floor in grassy areas, reminiscent of the red star, covered with brownish slime, and has a white foot. Attracts flies.

Coral mushroom (Clavulinopsis corallinorosacea). The fungus is called so because of the similarity with sea corals. These mushrooms have bright colors, mostly orange, yellow or red. Usually they grow older lesah.odni saprotrophic coral fungi, and other symbiotic or parasitic.

Brown Puffball (Lycoperdon umbrinum). This type of fungus grows in China, Europe and North America. These mushrooms are not open hats disputes. Instead, disputes occur within in a spherical body. Ripening, spores form Hleb in the center of the body, which has a distinctive color and texture.

Amanita Caesarea (Amanita caesarea). Very valuable edible mushroom that grows in southern Europe and North America. For the first time this fungus described by Giovanni Antonio Scopoli in 1772. He was very fond of the rulers of the Roman Empire. He has a distinctive orange cap, yellow spore-bearing plate and the leg. This fungus is very much appreciated by the Romans, who called it Boletus.

Mycena interrupta. This mushroom grows in Australia, New Zealand, Chile and New Caledonia. In Australia, it is increasing in Victoria, Tasmania, New South Wales and South Australia and Queensland, but only at The National Park Lamington. Cap mushroom is 0, 6-2 cm, and they have a bright blue color. When they appear, they have a spherical shape, but as they mature become wider. Hats sticky and slimy in appearance, especially in the rain.

Ksantor elegant (Xanthoria elegans). This fungus grows on rocks, often near bird perches or mink rodents. By the nature of this lichen. He became one of the first lichens, who used the method of dating the rock surfaces, known as lihenometriya. Growing at a rate of 0, 5 mm per year during the first century, then its growth slows down a bit.

Conical Morel (Morchella conica). Edible mushroom, in the upper part resembling a honeycomb. It consists of the entire network wavy bands with cavities therebetween. It is appreciated by gourmets, particularly in French cuisine. The fungus is very popular with mushroom pickers, not only from a commercial point of view but also because of the pleasant taste.

Amanita muscaria (Amanita muscaria). All known amanita - poisonous and psychoactive basidiomycete. It grows in the northern hemisphere, but also was introduced to the countries of the southern hemisphere, first as a symbiont in coniferous forests, and then as a full species. Red hat with white dots - who do not know the mushroom? This is one of the most recognizable of fungi in the world. Although considered a poisonous mushroom, Amanita muscaria confirmed cases of poisoning is not, and in some parts of Europe, Asia and North America, and it does eat after blanching. Amanita has hallucinogenic properties, its main psychoactive component - is muscimol. Some peoples of Siberia used it as entheogen, and it has great religious significance in these cultures.