1249
Crystals
Until the XVIII century, this element is often mistaken for tin or lead. It is two times more than gold, and it is a part of the popular drug against digestive disorders Pepto-Bismol.

Bismuth has been known to mankind since ancient times, first mentioned in written sources in 1450 as a Wismutton or Bisemutum. For a long time it was considered a kind of metal antimony, lead or tin. The first information about the metal bismuth, its mining and processing are found in the writings of the largest metallurgist and mineralogist Georgius Agricola Middle Ages, dated 1529 Representation of the bismuth as an independent chemical element formed only in the XVIII century. Bi Symbol first introduced into chemical nomenclature outstanding Swedish chemist Jens Jakob Berzelius.
The origin of the word "Bi" there are several versions. According to one of them believe that it is based on German roots «wis» and «mat» (distorted weisse masse and weisse materia) -White metal (or rather, a white mass of white matter). On the other - the word "Bi" - not that other, as an Arab "bi ismid," that is similar to the antimony.

The bismuth content in the crust of 2 * 10-5% by weight in seawater - 2 * 10-5 mg / l. Bismuth ores containing 1% or more of bismuth, rare, usually its source are lead, tin and other ores, where it is contained as an impurity. Bismuth minerals that are part of such ores are native bismuth (contains 98, 5-99% Bi), bismuthine - Bi2S3, bismite - Bi2O3 and others.
About 90% of the bismuth produced is removed simultaneously with the metallurgical processing of lead-zinc, copper, tin ores and concentrates. Bismuth sulfide is prepared by melting iron: Bi2S3 + 3Fe = 2Bi + 3FeS,
or consistent application of processes:
2Bi2S3 + 9O2 = 2Bi2O3 + 6SO2; Bi2O3 + 3C = 2Bi + 3CO.

In contrast, antimony, bismuth metal properties clearly prevail over non-metallic. He attaches a strong metallic luster and white pinkish tint. Bismuth simultaneously rather fragile and soft, heavy (density of 9, 8 g / cm3) legkoplavok (melting point 271 ° C). Upon melting bismuth shrinks (as ice), i.e. solid bismuth lighter fluid. Among other metals, bismuth emit low thermal conductivity (heat worse than it spends only mercury) and the strongest diamagneticheskie properties.
Natural bismuth consists of one stable isotope 209Bi.

In dry air bismuth is not oxidized in humid atmosphere is gradually covered with an oxide film. When heated above 1000 ° C is burned to form the basic oxide Bi2O3. When alloying bismuth with sulfur formed Bi2S3.
Reacts with halogens (the most studied trihalides): 2Bi + 3Hal2 = 2BiHal3
Does not react with H2, C, N2, ... Si
The interaction with the metals bismuth bismuthides formed, for example, sodium bismuthides Na3Bi, bismuthides Mg3Bi magnesium, etc.. The action of acids such alloys of bismuth formed bismuthine BiH3.
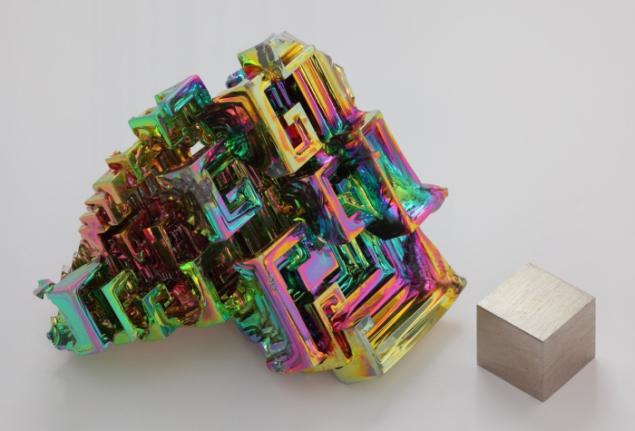

The main application of bismuth - its use as a component of the fusible alloy. Bismuth includes, for example, known Wood's alloy having a melting point below the boiling point of water, many other alloys used, for example, in the manufacture of fusible fuses. Alloys of bismuth and manganese (Mn) characterized ferromagnetic properties and hence are powerful for the manufacture of permanent magnets.
Small additions of Bismuth (0, 003% -0, 01%) in the steel and aluminum-based alloys improves the plastic properties of the metal, greatly simplifies processing.
Bismuth has some value in nuclear technology in the preparation of polonium - an important element of radioisotope industry. Bismuth compounds, especially Bi2O3, used in glass and ceramics, in the pharmaceutical industry, as a catalyst, and others.
Bismuth is a toxic ultramicroelements.
On the physiological role of bismuth is little known. Perhaps it induces the synthesis of low molecular weight proteins, is involved in the ossification process forms intracellular inclusion in epithelium of renal tubules. Perhaps this element has genotoxic and mutagenic.
Despite the fact that the bismuth is classified as heavy metals, it is moderately toxic element. Soluble bismuth salts are toxic and the nature of its impact (albeit to a lesser extent) are similar to those of mercury salts.

Bismuth salts used with the 1700s years. for the treatment of diseases such as diarrhea, as well as to alleviate the symptoms of cholera.

During the oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, seabirds forced to swallow this stuff, to bring the oil that got into their bodies.
Although this substance has been known since ancient times, the word "Bi" first appeared in the late XVII century. Alchemists used it in their experiments in the Middle Ages. Miners, mine, called him tectum argenti. It translates as "production of silver." The miners thought that bismuth was half silver.
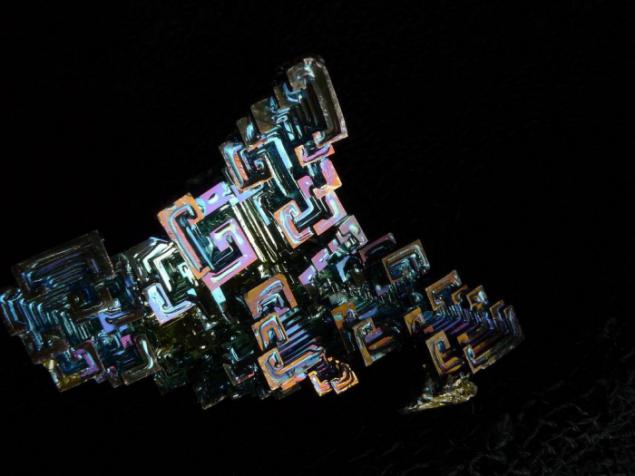
And the beauty of its crystals, of course, indicates why they thought so.
Name bismuth considered Latinized version starogermanskogo word "vissmut", and only in 1546 a German scientist Georgius Agricola (father of mineralogy) said that Bi - a separate metal.
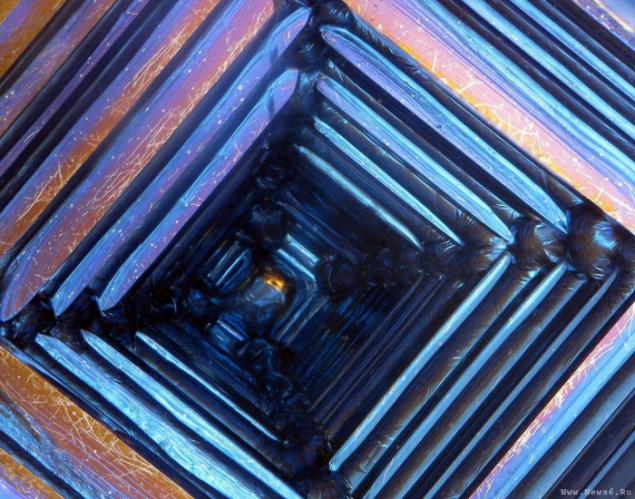
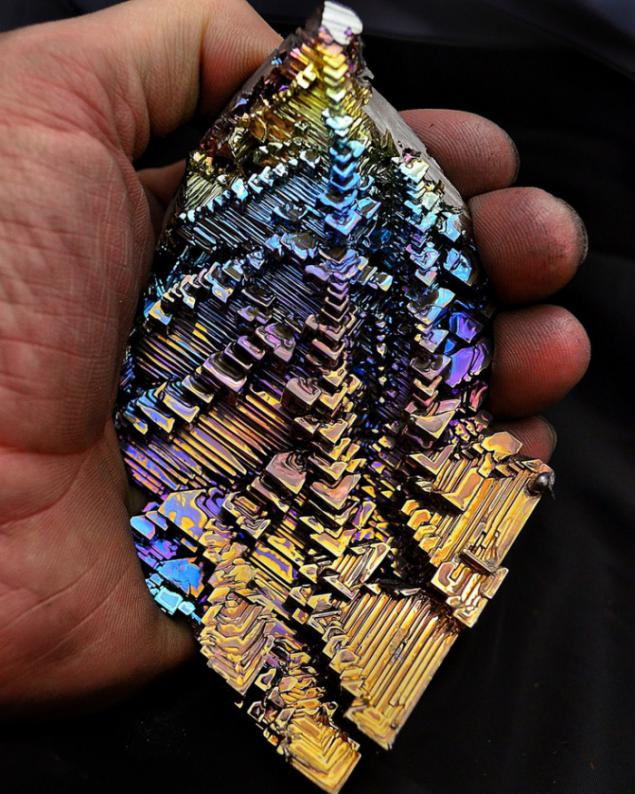
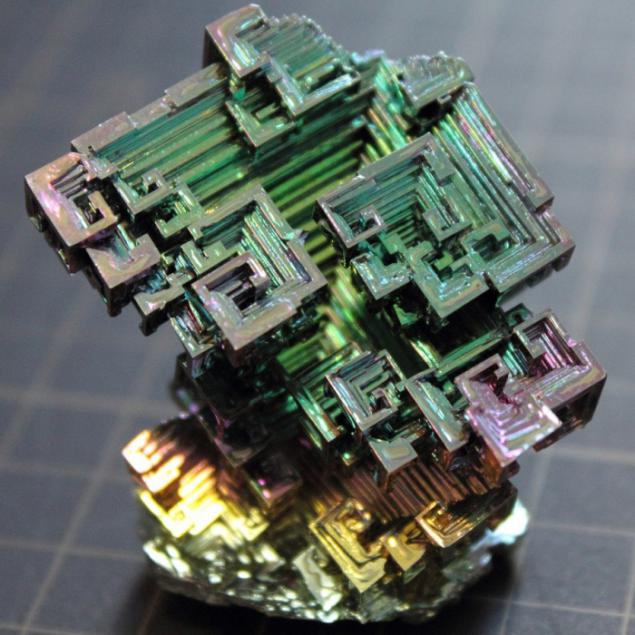
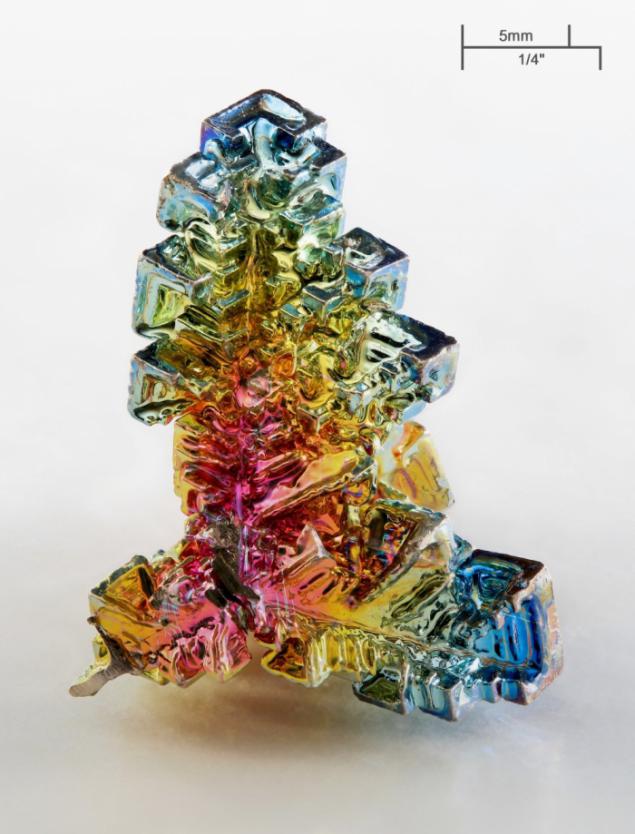
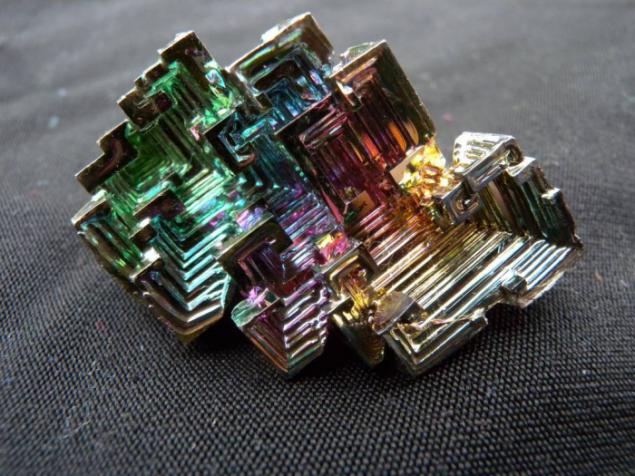
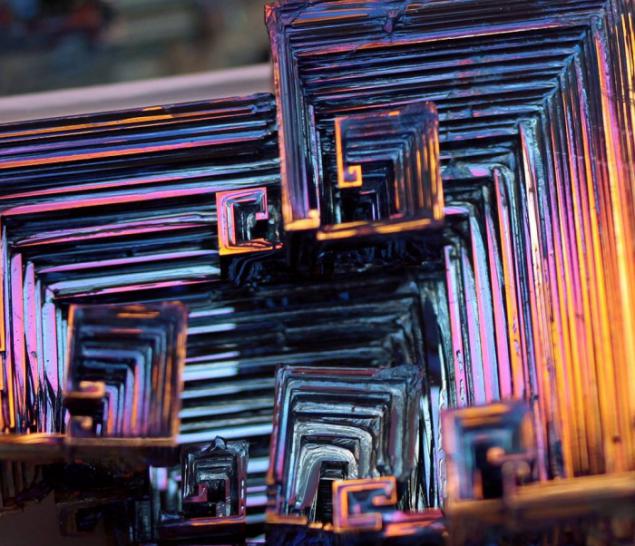
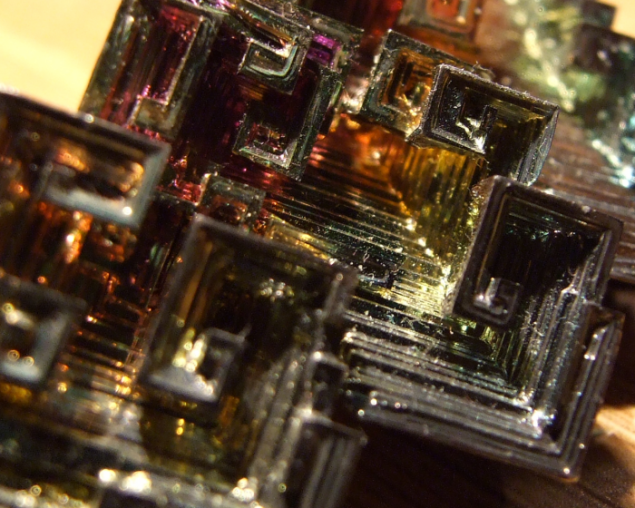
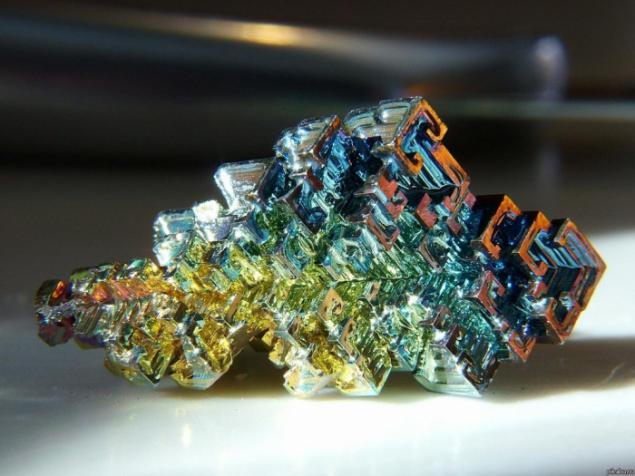
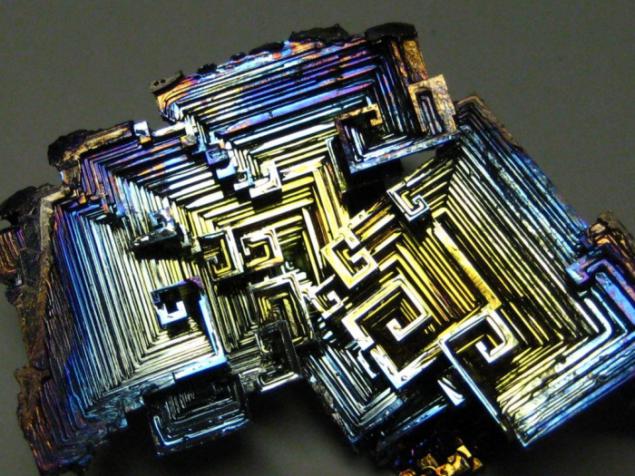
Bismuth is used not only in Europe, although the Andean name was lost, the Incas used a bismuth for the manufacture of knives. Because of this, the swords of the Incas were very beautiful, and it was the result of an iridescent glow oxidation - a chemical reaction with oxygen. Differences in color - this is the result of different thickness oxide layer on top of the crystal. When bismuth crystals exposed to direct light, these variations in thickness lead to different wavelengths to interrupt reflection. So we get a beautiful rainbow effect.
In the periodic table, bismuth has several neighbors (his number - 81), and if we take them in, can cause serious damage to health. The list includes lead, antimony and polonium. Although bismuth has a high atomic weight, he has always been stable (many years he even considered the most stable element in terms of weight).
However, recently discovered to be slightly radioactive element. But do not worry, bismuth can not kill. In fact, bismuth alloys have long been replaced by lead (in subjects such as valves for drinking water supply systems).

Bullion lead bullion contains up to 10% of bismuth, and its production is necessary to go through several stages. However, after the two main processes, the mixture is still a lot of other metals.
To obtain a clean bismuth, to melt processed mixture, and then add chlorine gas. Other metals mined in the form of chloride, then is pure bismuth. Bismuth has some amazing characteristics. As you know, the water - one of the few materials that are more dense in the liquid form than in the solid. This bismuth like water - in solid form, it is increased by 3%.
It is also more diamagnetic than any other metal in the world. Diamagnetism is present in all the materials - a feature that creates a magnetic field. On the other hand, bismuth has the lowest thermal conductivity than any other metal. It is believed that bismuth has a low environmental impact. This is because its components are not very soluble in water, so it can not hurt people. However, in terms of influence on the environment bismuth were conducted only limited studies.

Generally, bismuth - a fusible metal which expands upon solidification, ingots therefore have shrinkage cavity, but instead have a convex surface. Suitable bismuth, mainly for the production of low-melting alloys and solders.
Clean, unoxidized bismuth has a silver-white color with a slight reddish tinge. Rainbow color of the crystal due to the presence of a thin oxide film on his Turn. If desired, the color is easy to remove. Simply wash the crystal with dilute hydrochloric acid, and its surface is silver.
If you pour molten metal into a mold and let it harden, then turn the ingot. But bismuth crystals obtained a little differently.
Get these fantastic crystals of bismuth (Bi only! With another metal such will not work!), You can. We need a very clean bismuth. How is it cleaner, more beautiful crystals are obtained. The molten metal is poured out on the burner in a heated tank. After some time, when it is about one third solidified, the molten metal is poured, and still at the bottom of such crystals. Such a beautiful color crystals of bismuth acquire as a result of oxidation of the metal surface layer, the higher the purity of the parent metal, the more beautifully colored crystal.


©

Bismuth has been known to mankind since ancient times, first mentioned in written sources in 1450 as a Wismutton or Bisemutum. For a long time it was considered a kind of metal antimony, lead or tin. The first information about the metal bismuth, its mining and processing are found in the writings of the largest metallurgist and mineralogist Georgius Agricola Middle Ages, dated 1529 Representation of the bismuth as an independent chemical element formed only in the XVIII century. Bi Symbol first introduced into chemical nomenclature outstanding Swedish chemist Jens Jakob Berzelius.
The origin of the word "Bi" there are several versions. According to one of them believe that it is based on German roots «wis» and «mat» (distorted weisse masse and weisse materia) -White metal (or rather, a white mass of white matter). On the other - the word "Bi" - not that other, as an Arab "bi ismid," that is similar to the antimony.

The bismuth content in the crust of 2 * 10-5% by weight in seawater - 2 * 10-5 mg / l. Bismuth ores containing 1% or more of bismuth, rare, usually its source are lead, tin and other ores, where it is contained as an impurity. Bismuth minerals that are part of such ores are native bismuth (contains 98, 5-99% Bi), bismuthine - Bi2S3, bismite - Bi2O3 and others.
About 90% of the bismuth produced is removed simultaneously with the metallurgical processing of lead-zinc, copper, tin ores and concentrates. Bismuth sulfide is prepared by melting iron: Bi2S3 + 3Fe = 2Bi + 3FeS,
or consistent application of processes:
2Bi2S3 + 9O2 = 2Bi2O3 + 6SO2; Bi2O3 + 3C = 2Bi + 3CO.

In contrast, antimony, bismuth metal properties clearly prevail over non-metallic. He attaches a strong metallic luster and white pinkish tint. Bismuth simultaneously rather fragile and soft, heavy (density of 9, 8 g / cm3) legkoplavok (melting point 271 ° C). Upon melting bismuth shrinks (as ice), i.e. solid bismuth lighter fluid. Among other metals, bismuth emit low thermal conductivity (heat worse than it spends only mercury) and the strongest diamagneticheskie properties.
Natural bismuth consists of one stable isotope 209Bi.

In dry air bismuth is not oxidized in humid atmosphere is gradually covered with an oxide film. When heated above 1000 ° C is burned to form the basic oxide Bi2O3. When alloying bismuth with sulfur formed Bi2S3.
Reacts with halogens (the most studied trihalides): 2Bi + 3Hal2 = 2BiHal3
Does not react with H2, C, N2, ... Si
The interaction with the metals bismuth bismuthides formed, for example, sodium bismuthides Na3Bi, bismuthides Mg3Bi magnesium, etc.. The action of acids such alloys of bismuth formed bismuthine BiH3.

The main application of bismuth - its use as a component of the fusible alloy. Bismuth includes, for example, known Wood's alloy having a melting point below the boiling point of water, many other alloys used, for example, in the manufacture of fusible fuses. Alloys of bismuth and manganese (Mn) characterized ferromagnetic properties and hence are powerful for the manufacture of permanent magnets.
Small additions of Bismuth (0, 003% -0, 01%) in the steel and aluminum-based alloys improves the plastic properties of the metal, greatly simplifies processing.
Bismuth has some value in nuclear technology in the preparation of polonium - an important element of radioisotope industry. Bismuth compounds, especially Bi2O3, used in glass and ceramics, in the pharmaceutical industry, as a catalyst, and others.
Bismuth is a toxic ultramicroelements.
On the physiological role of bismuth is little known. Perhaps it induces the synthesis of low molecular weight proteins, is involved in the ossification process forms intracellular inclusion in epithelium of renal tubules. Perhaps this element has genotoxic and mutagenic.
Despite the fact that the bismuth is classified as heavy metals, it is moderately toxic element. Soluble bismuth salts are toxic and the nature of its impact (albeit to a lesser extent) are similar to those of mercury salts.

Bismuth salts used with the 1700s years. for the treatment of diseases such as diarrhea, as well as to alleviate the symptoms of cholera.

During the oil spill in the Gulf of Mexico, seabirds forced to swallow this stuff, to bring the oil that got into their bodies.
Although this substance has been known since ancient times, the word "Bi" first appeared in the late XVII century. Alchemists used it in their experiments in the Middle Ages. Miners, mine, called him tectum argenti. It translates as "production of silver." The miners thought that bismuth was half silver.
And the beauty of its crystals, of course, indicates why they thought so.
Name bismuth considered Latinized version starogermanskogo word "vissmut", and only in 1546 a German scientist Georgius Agricola (father of mineralogy) said that Bi - a separate metal.

Bismuth is used not only in Europe, although the Andean name was lost, the Incas used a bismuth for the manufacture of knives. Because of this, the swords of the Incas were very beautiful, and it was the result of an iridescent glow oxidation - a chemical reaction with oxygen. Differences in color - this is the result of different thickness oxide layer on top of the crystal. When bismuth crystals exposed to direct light, these variations in thickness lead to different wavelengths to interrupt reflection. So we get a beautiful rainbow effect.
In the periodic table, bismuth has several neighbors (his number - 81), and if we take them in, can cause serious damage to health. The list includes lead, antimony and polonium. Although bismuth has a high atomic weight, he has always been stable (many years he even considered the most stable element in terms of weight).
However, recently discovered to be slightly radioactive element. But do not worry, bismuth can not kill. In fact, bismuth alloys have long been replaced by lead (in subjects such as valves for drinking water supply systems).

Bullion lead bullion contains up to 10% of bismuth, and its production is necessary to go through several stages. However, after the two main processes, the mixture is still a lot of other metals.
To obtain a clean bismuth, to melt processed mixture, and then add chlorine gas. Other metals mined in the form of chloride, then is pure bismuth. Bismuth has some amazing characteristics. As you know, the water - one of the few materials that are more dense in the liquid form than in the solid. This bismuth like water - in solid form, it is increased by 3%.
It is also more diamagnetic than any other metal in the world. Diamagnetism is present in all the materials - a feature that creates a magnetic field. On the other hand, bismuth has the lowest thermal conductivity than any other metal. It is believed that bismuth has a low environmental impact. This is because its components are not very soluble in water, so it can not hurt people. However, in terms of influence on the environment bismuth were conducted only limited studies.

Generally, bismuth - a fusible metal which expands upon solidification, ingots therefore have shrinkage cavity, but instead have a convex surface. Suitable bismuth, mainly for the production of low-melting alloys and solders.
Clean, unoxidized bismuth has a silver-white color with a slight reddish tinge. Rainbow color of the crystal due to the presence of a thin oxide film on his Turn. If desired, the color is easy to remove. Simply wash the crystal with dilute hydrochloric acid, and its surface is silver.
If you pour molten metal into a mold and let it harden, then turn the ingot. But bismuth crystals obtained a little differently.
Get these fantastic crystals of bismuth (Bi only! With another metal such will not work!), You can. We need a very clean bismuth. How is it cleaner, more beautiful crystals are obtained. The molten metal is poured out on the burner in a heated tank. After some time, when it is about one third solidified, the molten metal is poured, and still at the bottom of such crystals. Such a beautiful color crystals of bismuth acquire as a result of oxidation of the metal surface layer, the higher the purity of the parent metal, the more beautifully colored crystal.


©






















