436
Scientists have developed a battery powered by bacteria
Scientists have developed a battery powered by bacteria, the entire battery is very thin, its thickness is comparable to the sheet. According to the developers this battery can be used for medical purposes.
The researchers say that the materials for such batteries can take in any, even the most underdeveloped area, which makes it really affordable.
"Papertronics has recently emerged as a simple and inexpensive way to supply disposable medical diagnostic sensors," says engineer Seochon Sean Choi from the University of Binghamton.
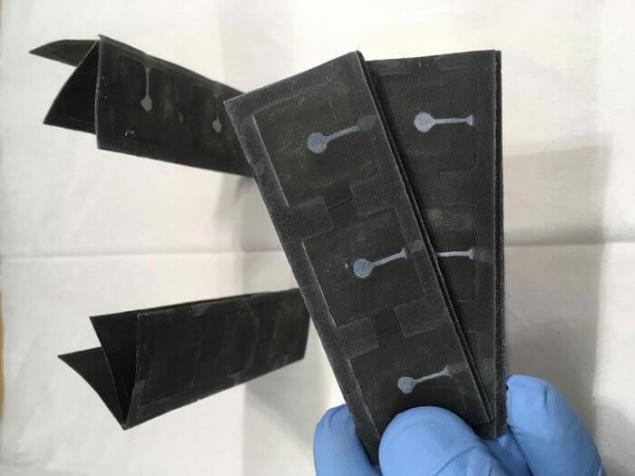

The battery is made of ribbons of silver nitrate is placed on paper on top the researchers placed a thin layer of wax to create the cathode..on the other side of the paper the team made a reservoir of conductive polymer, it pours liquid with bacteria, which acts as the anode. When the paper is folded together, the anode and the cathode must be in contact, the process known as "cell respiration."
Testing of the battery showed that it is possible to create 31.51 — 44.85 microwatt on 125.53-105.89 µa from six batteries stacked on top of each other.
The researchers acknowledge that performance has not an exact value and an indicator of its not so great. The scientists also noted that this paper should be a lot to power from her 40-watt bulb, because the use of such paper can only see the sensors that do not require large amounts of energy. published
Source: www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161221110606.htm
The researchers say that the materials for such batteries can take in any, even the most underdeveloped area, which makes it really affordable.
"Papertronics has recently emerged as a simple and inexpensive way to supply disposable medical diagnostic sensors," says engineer Seochon Sean Choi from the University of Binghamton.

The battery is made of ribbons of silver nitrate is placed on paper on top the researchers placed a thin layer of wax to create the cathode..on the other side of the paper the team made a reservoir of conductive polymer, it pours liquid with bacteria, which acts as the anode. When the paper is folded together, the anode and the cathode must be in contact, the process known as "cell respiration."
Testing of the battery showed that it is possible to create 31.51 — 44.85 microwatt on 125.53-105.89 µa from six batteries stacked on top of each other.
The researchers acknowledge that performance has not an exact value and an indicator of its not so great. The scientists also noted that this paper should be a lot to power from her 40-watt bulb, because the use of such paper can only see the sensors that do not require large amounts of energy. published
Source: www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2016/12/161221110606.htm
60% of Chinese manufacturers of solar panels will close in 2017
Solar Pines - urban structure relaxation, producing clean energy