599
Spectacular experiment Harvard medical school
Usually in laboratory experiments the bacteria is diluted in a homogeneous medium. Scientists from Harvard medical school went on. They organized an unusual experiment in the evolution of bacteria in a mixed environment — in the huge "dish" with a size of 120×60 cm
The space was divided into zones with different concentration of antibiotic, so the next area pass only the generation of bacteria with the appropriate mutations. As a result, in the final round in the center of the arena make their way "Supermicro", that is, the maximum changing their genotype and phenotype as the result of evolutionary selection (see about the isolation of the opportunists at the end of the article).
Frame demo video from Harvard medical school. With increasing resistance from the antibiotic in the bacterial population have the parallel lines of evolution, which differ in phenotype and genotype.
Arena battle the germs with antibiotics is called MEGA (microbial evolution and growth arena). Such an environment specially created to make, with exponential population growth of bacteria they did not compete with each other for scarce resources, as is customary in most scientific experiments. Here the resources are practically unlimited, and from bacteria only need to capture new territory and adapt to new conditions of life, multiplying their numbers with almost no restrictions.
In this sense, the movement of the bacterial front is reminiscent of the expansion of the human species on planet Earth in the middle ages with the colonization of new territories (presumably, the expansive development of the human race will continue beyond the home planet with the colonization of all the habitable territories in range).

Arena MEGA. Frame demo video from Harvard medical school
The experiment has scientific and educational value. The large space of the arena MEGA allows you to observe mutations and natural selection in the propagation of the front of bacterial population. An impressive sight.
SUBSCRIBE to OUR youtube channel that allows you to watch online, download from YouTube free video about the recovery, the rejuvenation of man. Love for others and ourselves, as the feeling of high vibrations — an important factor for improvement .
Previous research has shown that structured microenvironment of this type increase the rate of evolution in small populations of bacteria with changes in the genotype (Q. Zhang et al., Science 333, 1764-1767 (2011)). But until now remained unexplored question, as it happens in large populations.
For this experiment was constructed of a rectangular Petri dish with a size of 120×60 cm, structured by zones with the exponential increase in the concentration of the antibiotic trimethoprim from the periphery to the center, as well as nutrients for bacteria. A large area of the arena did not allow the E. coli to be mixed together, in order to more clearly observe what is happening mutation.
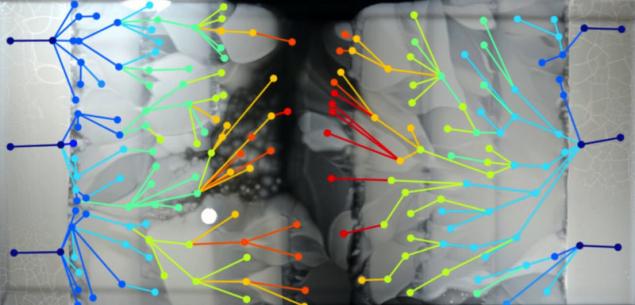
Design arena MEGA and the result of the spread of bacterial up front for the 12 days shown in figure B. Circles of different colors marked with 182 species of bacteria mutated, the color indicates the concentration of bacteria. The line between species correspond to the direction of the mutation, based on data from video.
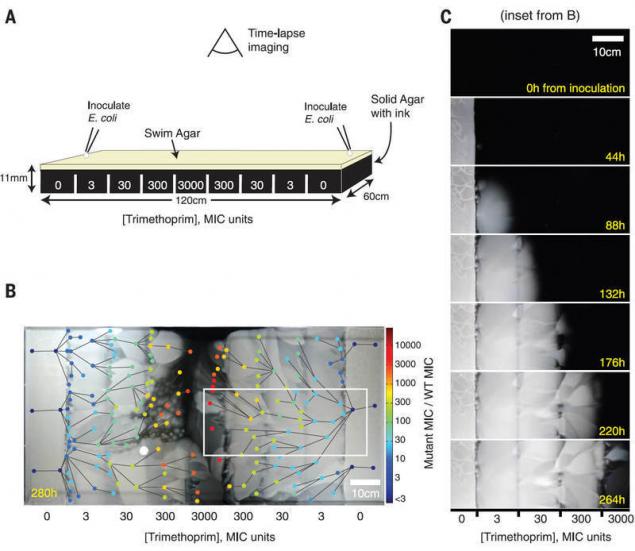
As the continuous increase in the resistance of antibiotic in the bacterial population, there are numerous parallel lines of evolution, which differ in phenotype and genotype.
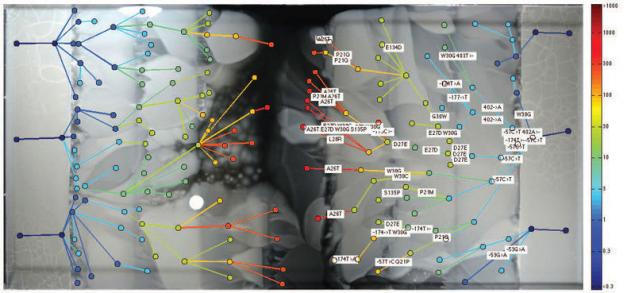
After studying the bacteria at the forefront and behind the front bacterial population, the scientists found some interesting things. It turned out that evolution does not always move forward bacteria most resistant to antibiotics. Ironically, sometimes the most stable hereditary line are locked behind the more sensitive bacteria. Apparently, this is due to the "premature" mutations, when some bacteria are able to survive in higher concentrations of antibiotic, which will appear in the future, but has not yet appeared. In such a situation potentially more adapted bacteria give way in front of their cousins, which are adapted exactly to the actual concentration existing at the moment.
To test this theory, scientists took samples of isolated bacterial colonies with the "premature" mutations and forcibly put them ahead of the front. As expected, they survived in the conditions in which the main bacterial front can not survive.
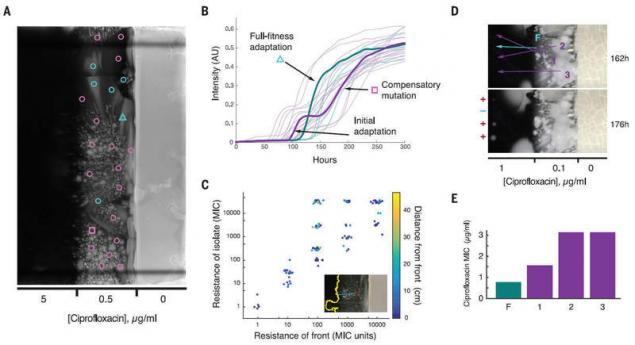
Illustration: Harvard medical school. The spatial trap of compensatory mutations — the bacteria that is so ahead of its time that even after the onset of suitable conditions they are already locked behind the coming front.
Scientists have extensively studied the genotype most mutated species of bacteria that managed to survive in a solution with a maximum concentration of trimethoprim. It turned out that these types of most often mutations were subjected to the gene folA, which encodes dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) and is the target of trimethoprim. The more resistance bacteria to the antibiotic, the more mutations in this gene.
Furthermore, the discovered mutations in several other genes, unrelated to the action of a specific antibiotic. Among them was the mar and sox operons, which are responsible for the stress response. Previously it was known that these "stress" genes play an important role in successful resistance to antibiotics.
Also interesting: the electron microscope has discovered how vitamin a enters the cells
What You did not know about epigenetics: genes and cellular memory
Scientists have also found that the best adaptation to the weak impact of antibiotic subsequently accelerates adaptation to higher concentrations (in the illustration below). All of the people who are able to adapt better to worsening conditions of life, when changes occur gradually and imperceptibly.
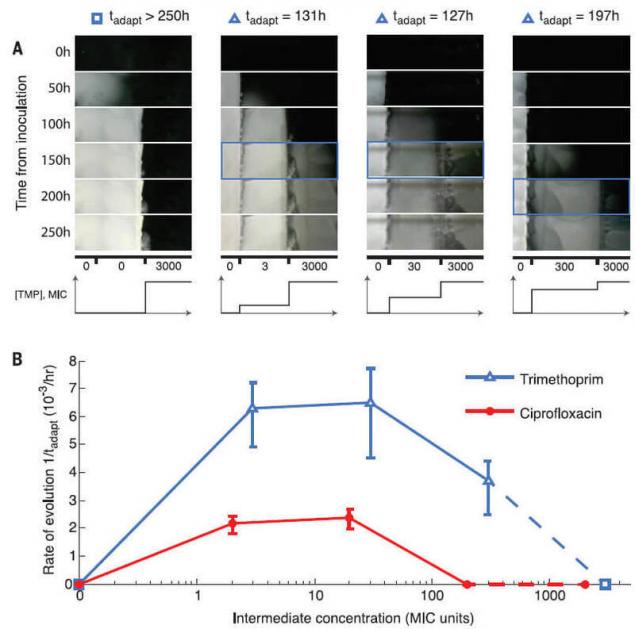
The experiment described in a scientific paper published on 9 September 2016 in the journal Science(doi:10.1126/science.aag0822). published
Author: Anatoly Alizar
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: geektimes.ru/post/280266/
The space was divided into zones with different concentration of antibiotic, so the next area pass only the generation of bacteria with the appropriate mutations. As a result, in the final round in the center of the arena make their way "Supermicro", that is, the maximum changing their genotype and phenotype as the result of evolutionary selection (see about the isolation of the opportunists at the end of the article).

Frame demo video from Harvard medical school. With increasing resistance from the antibiotic in the bacterial population have the parallel lines of evolution, which differ in phenotype and genotype.
Arena battle the germs with antibiotics is called MEGA (microbial evolution and growth arena). Such an environment specially created to make, with exponential population growth of bacteria they did not compete with each other for scarce resources, as is customary in most scientific experiments. Here the resources are practically unlimited, and from bacteria only need to capture new territory and adapt to new conditions of life, multiplying their numbers with almost no restrictions.
In this sense, the movement of the bacterial front is reminiscent of the expansion of the human species on planet Earth in the middle ages with the colonization of new territories (presumably, the expansive development of the human race will continue beyond the home planet with the colonization of all the habitable territories in range).

Arena MEGA. Frame demo video from Harvard medical school
The experiment has scientific and educational value. The large space of the arena MEGA allows you to observe mutations and natural selection in the propagation of the front of bacterial population. An impressive sight.
SUBSCRIBE to OUR youtube channel that allows you to watch online, download from YouTube free video about the recovery, the rejuvenation of man. Love for others and ourselves, as the feeling of high vibrations — an important factor for improvement .
Previous research has shown that structured microenvironment of this type increase the rate of evolution in small populations of bacteria with changes in the genotype (Q. Zhang et al., Science 333, 1764-1767 (2011)). But until now remained unexplored question, as it happens in large populations.
For this experiment was constructed of a rectangular Petri dish with a size of 120×60 cm, structured by zones with the exponential increase in the concentration of the antibiotic trimethoprim from the periphery to the center, as well as nutrients for bacteria. A large area of the arena did not allow the E. coli to be mixed together, in order to more clearly observe what is happening mutation.
Design arena MEGA and the result of the spread of bacterial up front for the 12 days shown in figure B. Circles of different colors marked with 182 species of bacteria mutated, the color indicates the concentration of bacteria. The line between species correspond to the direction of the mutation, based on data from video.

As the continuous increase in the resistance of antibiotic in the bacterial population, there are numerous parallel lines of evolution, which differ in phenotype and genotype.

After studying the bacteria at the forefront and behind the front bacterial population, the scientists found some interesting things. It turned out that evolution does not always move forward bacteria most resistant to antibiotics. Ironically, sometimes the most stable hereditary line are locked behind the more sensitive bacteria. Apparently, this is due to the "premature" mutations, when some bacteria are able to survive in higher concentrations of antibiotic, which will appear in the future, but has not yet appeared. In such a situation potentially more adapted bacteria give way in front of their cousins, which are adapted exactly to the actual concentration existing at the moment.
To test this theory, scientists took samples of isolated bacterial colonies with the "premature" mutations and forcibly put them ahead of the front. As expected, they survived in the conditions in which the main bacterial front can not survive.

Illustration: Harvard medical school. The spatial trap of compensatory mutations — the bacteria that is so ahead of its time that even after the onset of suitable conditions they are already locked behind the coming front.
Scientists have extensively studied the genotype most mutated species of bacteria that managed to survive in a solution with a maximum concentration of trimethoprim. It turned out that these types of most often mutations were subjected to the gene folA, which encodes dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) and is the target of trimethoprim. The more resistance bacteria to the antibiotic, the more mutations in this gene.
Furthermore, the discovered mutations in several other genes, unrelated to the action of a specific antibiotic. Among them was the mar and sox operons, which are responsible for the stress response. Previously it was known that these "stress" genes play an important role in successful resistance to antibiotics.
Also interesting: the electron microscope has discovered how vitamin a enters the cells
What You did not know about epigenetics: genes and cellular memory
Scientists have also found that the best adaptation to the weak impact of antibiotic subsequently accelerates adaptation to higher concentrations (in the illustration below). All of the people who are able to adapt better to worsening conditions of life, when changes occur gradually and imperceptibly.

The experiment described in a scientific paper published on 9 September 2016 in the journal Science(doi:10.1126/science.aag0822). published
Author: Anatoly Alizar
P. S. And remember, just changing your mind — together we change the world! ©
Source: geektimes.ru/post/280266/