519
IBM increases solar cell efficiency 2000 times
Existing technologies for converting solar energy provide for the disposal of only a small part of the spectrum of solar radiation, and with an efficiency not higher than 15% for the most advanced (and very expensive) development. A large part of the spectrum attributable to the low energy red and infrared radiation is wasted.
Created by members of the IBM system high concentration photovoltaic and thermal (HCPVT) enables utilization of solar energy in a wide spectrum range of solar radiation, increasing the efficiency of its use in 2000. According to the developers, in the future they are able to raise the ceiling of the effectiveness of safe production of electric and thermal energy 5000 times! In the process of trapping the sunlight produces additional desalination of cooling water, which can also go for air conditioning, so a relatively small unit can power the whole village.
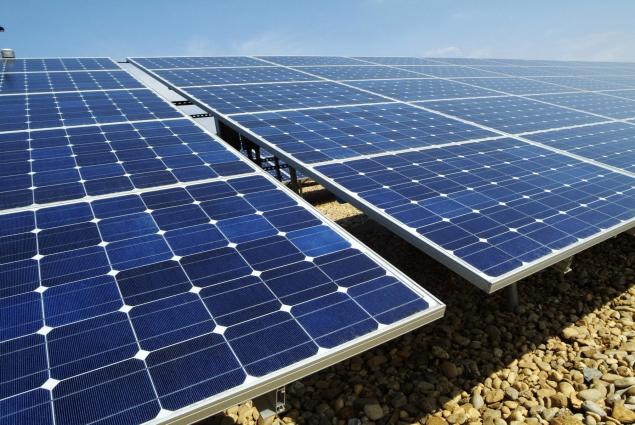

In the HCPVT system the heat is absorbed by the hundreds of tiny solar photovoltaic chips. Chips collect energy and then cooled by water circulating through the microchannels, so they're able to concentrate a large amount of solar energy.
Each chip size 1X1 cm can convert into a Sunny region of about 200-250 watts over a normal eight-hour working day. In the HCPVT system the cooling water is heated to 90 degrees Celsius, then the water passes through a porous membrane distillation system where it then evaporates and opasnaya. Such a system could provide 30-40 liters of drinkable water per square meter of the receiver on the day, at the same time, the production of electricity with an efficiency of more than 25 percent will be about two kilowatt hours a day.

According to Greenpeace, this technology can establish itself as the third largest source of sustainable industrial energy production. In a study published in 2009, proved that solar energy can cover the entire global energy demand. According to calculations by Greenpeace, it is enough only two percent of the area of the Sahara desert. This project is funded by the Swiss Commission for technology and innovation. It provided a three year grant for $ 2.4 million to develop the technology. Prototypes have already been developed and tested.
Source: brainswork.ru
Created by members of the IBM system high concentration photovoltaic and thermal (HCPVT) enables utilization of solar energy in a wide spectrum range of solar radiation, increasing the efficiency of its use in 2000. According to the developers, in the future they are able to raise the ceiling of the effectiveness of safe production of electric and thermal energy 5000 times! In the process of trapping the sunlight produces additional desalination of cooling water, which can also go for air conditioning, so a relatively small unit can power the whole village.

In the HCPVT system the heat is absorbed by the hundreds of tiny solar photovoltaic chips. Chips collect energy and then cooled by water circulating through the microchannels, so they're able to concentrate a large amount of solar energy.
Each chip size 1X1 cm can convert into a Sunny region of about 200-250 watts over a normal eight-hour working day. In the HCPVT system the cooling water is heated to 90 degrees Celsius, then the water passes through a porous membrane distillation system where it then evaporates and opasnaya. Such a system could provide 30-40 liters of drinkable water per square meter of the receiver on the day, at the same time, the production of electricity with an efficiency of more than 25 percent will be about two kilowatt hours a day.

According to Greenpeace, this technology can establish itself as the third largest source of sustainable industrial energy production. In a study published in 2009, proved that solar energy can cover the entire global energy demand. According to calculations by Greenpeace, it is enough only two percent of the area of the Sahara desert. This project is funded by the Swiss Commission for technology and innovation. It provided a three year grant for $ 2.4 million to develop the technology. Prototypes have already been developed and tested.
Source: brainswork.ru
Created nanofibers that are 15 times stronger than steel
Creative vegetable gardening: greenhouse-garden furniture from plastic bottles