560
Insecure Internet: the rules of online behavior
The revelations of Edward Snowden, the recent leak of private photos of Hollywood stars "drain" database with the email addresses of Gmail users, Mail.ru and Yandex has made the Internet a new force to talk about security issues in the Network. How burglars work and how the average user to protect themselves from unwanted interference by outsiders in personal digital life, "the Daily" has learned from Vladimir Ulyanov, head of the analytical center Zecurion Analytics. This Russian developer of DLP-systems (Data Loss Prevention technology, leak prevention) provides information protection of major domestic and foreign companies, including Gazprom, Allianz, "Aeroflot", "Tupolev", "Rostelecom" and the Ministry of Finance, Ministry of defense and other agencies. 
Vladimir Ulyanov. — In late August, the network got personal photos of foreign celebrities who hackers get from iCloud. How serious the work was carried out for hacking?
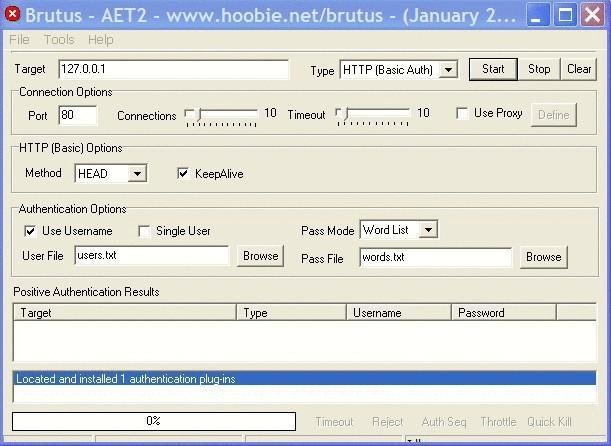
— It was not used no tricky software. Just someone who found that the service is vulnerable to a simple hacker attack, called brute force password, or brute force. Utility, able to cycle through passwords, you can "write on the knee" for five minutes. With the help of such software, and were hacked accounts of celebrities in iCloud.
Weak password security is one of the main problems. Statistics show that most people use primitive passwords: 12345, qwerty, aaaaaa, and so on. There are even dictionaries of passwords — programs that with great speed sorted out such are a popular combination.
In the case of the iCloud service was vulnerable. If you try to hack thus, for example, Windows, you have nothing. After the third or fifth attempt Windows makes the delay of, say, half a minute. Therefore, a brute force attack would be ineffective, since to sort through thousands of passwords, it will take several days. If the system allows for a second to pick up ten, twenty or even thousands of passwords, problems with the selection of the attacker will not occur.
Recently shared was usernames and passwords from mailbox Gmail Mail.ru and Yandex. Some of them were inactive. How, in your opinion, who, how and why did it?
Even now it is not absolutely clear what happened. There are a few working versions. One of them, the base was going a few months or even years (it includes pieces previously published in other places in the database). To me it seems unlikely. Indeed, among the compromised accounts were inactive. If it was a legacy database, the number of active accounts does not exceed 20-30%, and they were more than half. That got her non-working', there is nothing surprising — most users have "left" the accounts which they brought and left.
If it has more than half of working addresses, it can be used. For example, the spammers behind it can give good money. Usually they buy for cheap a huge base, where the percentage of live users is minimal.
Perhaps it was a leak from the companies...
— Once out of three?
— Information could be stolen at different times, and published it all in a moment. In addition, the database could steal from third services. If you use the email you signed into the same iCloud or other similar resources, the information could leak out. And then just ' divided into Mail.ru, Gmail and Yandex. In favor of this version says that, apparently, was able to steal only the addresses, and passwords were selected according to the so-called "rainbow tables". Typically, the services to protect user does not use the password in its pure form, and encrypt it. That is, instead of a password cracker got a certain combination of symbols, which he gave nothing. But there are "rainbow tables", they help with this resultant combination to establish the initial password. Judging by the fact that in these databases, a large number of duplicate passwords, like 12345 and qwerty, it is highly likely they picked up separately.

© Pawel Kopczynski/Reuters — whether employees of companies access to the passwords? If they can, when leaving the company to "merge" to someone that base?
Is one of the biggest problems of corporate security. This applies not only to the situation of leak of passwords, but any classified information. The easiest example is sales. They have their own customer base, and, when they move from company to company, they take with them. It can be sold, to from the new bosses some bonuses or to use in a new place. Zecurion Analytics recently conducted a study and found that the majority of employees do not believe that this information belongs to the employer. They believe that it is their personal information: they got access to the database, added her and believe her.
The problem is much deeper than it seems, because we interviewed not only workers but also students — the future specialists, personnel reserve of the country for the next 15-20 years. The vast majority of these people feel that stealing information is not shameful. They don't consider it stealing, because we are talking about using information, which they partially gained. In the employment contract probably will indicate what information they do not have the right to distribute and why it is the property of the employer, not the employee. But usually these agreements no one is watching sign the papers the crowd at the job, not getting a grasp on the details. This situation is not beneficial for the employee and the employer. Therefore, when we talk about information security, we must bear in mind not only technical tools, but also organizational issues.

— And whether the employees of companies access to data stored in the cloud? Roughly speaking, can one of them just for fun to get into the account to the same Jennifer Lawrence and to see what kind of photos she stores?
— It depends on the company. But we don't know. Of course, the company hedged staff sign a non-disclosure agreement information, but it does not guarantee.
First and foremost, we must understand that the cloud service itself is a big security risk. Still no real controls over what got there. When you send data to the cloud, they are lost to you — you don't know where they are stored and how carefully the provider that owns a cloud-based technology, will protect them. In the cloud, you can store non-critical leak information, otherwise it is necessary to think ten times before using this technology.
Jennifer Lawrence
© vk.com — recently it became known that the American intelligence services put pressure on Yahoo! requiring to disclose the personal data of users. How do intelligence agencies are interested in reading personal correspondence of ordinary citizens?
— They are not interested. For them it is garbage, noise. Simple user interesting commercial companies who will sell him the boots, diapers or fancy gadgets. Intelligence services are interested in a very small number of users. But to identify such a person, they have "wool" huge amounts of information on the Internet.
— Can protect you from this services, to provide anonymity, like TOR?
— Most likely, and TOR the security services can read the technical capability to do this, they need to be. But again, the users are conditional, the CIA is not interested.
— But that ordinary users are most screaming about invasion of privacy.
Really, talk about Big brother are the place to be. But, judging on the cold head, special services you are not interested. At least, today. Tomorrow if you join a terrorist organization, you certainly will be interested. Most people are worried about is not that they are being watched, and the fact that it is theoretically possible. It is a violation of their constitutional rights.

— As an ordinary user best protect your information?
— Most importantly, when working in a network to understand that any information you submit there, no longer belongs to you. Even if it's a draft email. Until recently the company strongly deny the rumors that they are reading someone else's mail. Now they do not hide it, but in another way it's positioned. For example, there were cases when the major postal services have announced the capture of pedophiles. They found some photos or correspondence in relation to the person of pedophilia, and passed this information to law enforcement agencies. How was it done? By scanning the mails of all users. So now about privacy, however.
Generally it makes sense to hold three mailboxes: for work, for personal needs or to register for third-party services. Simple passwords can be used only on the "left" accounts. Even if the box is hacked, and there comes the spam for you, it is not critical. Important email accounts that you use for registration in payment systems or online stores, have to protect complex passwords of ten or twelve characters of different case and numbers.
Do not use the same password on multiple services, for example, in the mail Yandex and Gmail, in Facebook and "Vkontakte". Especially if you are not sure what a particular service will protect your information.
Ideally, it is necessary to change the password every three months, but it is difficult, especially if a lot of accounts on different services. In this case, you can use a password Manager — special programs that collect your passwords and encrypt them in a special vault. But then again, if the attacker can hack a Manager, he will get access to your entire digital life.
It is not necessary to record the password on paper and sculpt it under the keyboard or on the monitor. It's like that write the pin code from the Bank card and keep it in your wallet.
If the account is not required to enter the real personal data, specify the "left" — can a date of birth to change. If anything, it will help to figure out where a leak has occurred and to take action.
With the development of Internet banking there is a risk of losing your money in case of leakage of personal data. If possible, keep a separate laptop for use with such systems. This can be the simplest car for two or three thousand a flea market. Don't even need antivirus, the main thing that was fresh operating system. From this computer you will only to go to the Internet Bank.
If a separate device to buy expensive, you can use a special bootable USB stick with an operating system (Live USB). Inserted the flash drive, downloaded from her computer, went to the Internet-Bank, carried out the necessary operations, took the flash drive and everything. You came just to the website of their Bank, and therefore the chance that information can be intercepted or substitute hackers are much less.
With regard to mobile phones, it is better to use a simple tube without operating systems (Vladimir uses this camera, approx. ed.). They are more robust because it is protected from hacking and viruses. If you are a fan of fashionable smartphones, then get a separate phone for Internet banking wherever you came codes to confirm the operation.
As always, when it comes to security, it is best to use all of these solutions in the complex.
Source: ridus.ru

Vladimir Ulyanov. — In late August, the network got personal photos of foreign celebrities who hackers get from iCloud. How serious the work was carried out for hacking?
— It was not used no tricky software. Just someone who found that the service is vulnerable to a simple hacker attack, called brute force password, or brute force. Utility, able to cycle through passwords, you can "write on the knee" for five minutes. With the help of such software, and were hacked accounts of celebrities in iCloud.
Weak password security is one of the main problems. Statistics show that most people use primitive passwords: 12345, qwerty, aaaaaa, and so on. There are even dictionaries of passwords — programs that with great speed sorted out such are a popular combination.
In the case of the iCloud service was vulnerable. If you try to hack thus, for example, Windows, you have nothing. After the third or fifth attempt Windows makes the delay of, say, half a minute. Therefore, a brute force attack would be ineffective, since to sort through thousands of passwords, it will take several days. If the system allows for a second to pick up ten, twenty or even thousands of passwords, problems with the selection of the attacker will not occur.

Recently shared was usernames and passwords from mailbox Gmail Mail.ru and Yandex. Some of them were inactive. How, in your opinion, who, how and why did it?
Even now it is not absolutely clear what happened. There are a few working versions. One of them, the base was going a few months or even years (it includes pieces previously published in other places in the database). To me it seems unlikely. Indeed, among the compromised accounts were inactive. If it was a legacy database, the number of active accounts does not exceed 20-30%, and they were more than half. That got her non-working', there is nothing surprising — most users have "left" the accounts which they brought and left.
If it has more than half of working addresses, it can be used. For example, the spammers behind it can give good money. Usually they buy for cheap a huge base, where the percentage of live users is minimal.
Perhaps it was a leak from the companies...
— Once out of three?
— Information could be stolen at different times, and published it all in a moment. In addition, the database could steal from third services. If you use the email you signed into the same iCloud or other similar resources, the information could leak out. And then just ' divided into Mail.ru, Gmail and Yandex. In favor of this version says that, apparently, was able to steal only the addresses, and passwords were selected according to the so-called "rainbow tables". Typically, the services to protect user does not use the password in its pure form, and encrypt it. That is, instead of a password cracker got a certain combination of symbols, which he gave nothing. But there are "rainbow tables", they help with this resultant combination to establish the initial password. Judging by the fact that in these databases, a large number of duplicate passwords, like 12345 and qwerty, it is highly likely they picked up separately.

© Pawel Kopczynski/Reuters — whether employees of companies access to the passwords? If they can, when leaving the company to "merge" to someone that base?
Is one of the biggest problems of corporate security. This applies not only to the situation of leak of passwords, but any classified information. The easiest example is sales. They have their own customer base, and, when they move from company to company, they take with them. It can be sold, to from the new bosses some bonuses or to use in a new place. Zecurion Analytics recently conducted a study and found that the majority of employees do not believe that this information belongs to the employer. They believe that it is their personal information: they got access to the database, added her and believe her.
The problem is much deeper than it seems, because we interviewed not only workers but also students — the future specialists, personnel reserve of the country for the next 15-20 years. The vast majority of these people feel that stealing information is not shameful. They don't consider it stealing, because we are talking about using information, which they partially gained. In the employment contract probably will indicate what information they do not have the right to distribute and why it is the property of the employer, not the employee. But usually these agreements no one is watching sign the papers the crowd at the job, not getting a grasp on the details. This situation is not beneficial for the employee and the employer. Therefore, when we talk about information security, we must bear in mind not only technical tools, but also organizational issues.

— And whether the employees of companies access to data stored in the cloud? Roughly speaking, can one of them just for fun to get into the account to the same Jennifer Lawrence and to see what kind of photos she stores?
— It depends on the company. But we don't know. Of course, the company hedged staff sign a non-disclosure agreement information, but it does not guarantee.
First and foremost, we must understand that the cloud service itself is a big security risk. Still no real controls over what got there. When you send data to the cloud, they are lost to you — you don't know where they are stored and how carefully the provider that owns a cloud-based technology, will protect them. In the cloud, you can store non-critical leak information, otherwise it is necessary to think ten times before using this technology.
Jennifer Lawrence
© vk.com — recently it became known that the American intelligence services put pressure on Yahoo! requiring to disclose the personal data of users. How do intelligence agencies are interested in reading personal correspondence of ordinary citizens?
— They are not interested. For them it is garbage, noise. Simple user interesting commercial companies who will sell him the boots, diapers or fancy gadgets. Intelligence services are interested in a very small number of users. But to identify such a person, they have "wool" huge amounts of information on the Internet.
— Can protect you from this services, to provide anonymity, like TOR?
— Most likely, and TOR the security services can read the technical capability to do this, they need to be. But again, the users are conditional, the CIA is not interested.
— But that ordinary users are most screaming about invasion of privacy.
Really, talk about Big brother are the place to be. But, judging on the cold head, special services you are not interested. At least, today. Tomorrow if you join a terrorist organization, you certainly will be interested. Most people are worried about is not that they are being watched, and the fact that it is theoretically possible. It is a violation of their constitutional rights.

— As an ordinary user best protect your information?
— Most importantly, when working in a network to understand that any information you submit there, no longer belongs to you. Even if it's a draft email. Until recently the company strongly deny the rumors that they are reading someone else's mail. Now they do not hide it, but in another way it's positioned. For example, there were cases when the major postal services have announced the capture of pedophiles. They found some photos or correspondence in relation to the person of pedophilia, and passed this information to law enforcement agencies. How was it done? By scanning the mails of all users. So now about privacy, however.
Generally it makes sense to hold three mailboxes: for work, for personal needs or to register for third-party services. Simple passwords can be used only on the "left" accounts. Even if the box is hacked, and there comes the spam for you, it is not critical. Important email accounts that you use for registration in payment systems or online stores, have to protect complex passwords of ten or twelve characters of different case and numbers.
Do not use the same password on multiple services, for example, in the mail Yandex and Gmail, in Facebook and "Vkontakte". Especially if you are not sure what a particular service will protect your information.
Ideally, it is necessary to change the password every three months, but it is difficult, especially if a lot of accounts on different services. In this case, you can use a password Manager — special programs that collect your passwords and encrypt them in a special vault. But then again, if the attacker can hack a Manager, he will get access to your entire digital life.
It is not necessary to record the password on paper and sculpt it under the keyboard or on the monitor. It's like that write the pin code from the Bank card and keep it in your wallet.
If the account is not required to enter the real personal data, specify the "left" — can a date of birth to change. If anything, it will help to figure out where a leak has occurred and to take action.
With the development of Internet banking there is a risk of losing your money in case of leakage of personal data. If possible, keep a separate laptop for use with such systems. This can be the simplest car for two or three thousand a flea market. Don't even need antivirus, the main thing that was fresh operating system. From this computer you will only to go to the Internet Bank.
If a separate device to buy expensive, you can use a special bootable USB stick with an operating system (Live USB). Inserted the flash drive, downloaded from her computer, went to the Internet-Bank, carried out the necessary operations, took the flash drive and everything. You came just to the website of their Bank, and therefore the chance that information can be intercepted or substitute hackers are much less.
With regard to mobile phones, it is better to use a simple tube without operating systems (Vladimir uses this camera, approx. ed.). They are more robust because it is protected from hacking and viruses. If you are a fan of fashionable smartphones, then get a separate phone for Internet banking wherever you came codes to confirm the operation.
As always, when it comes to security, it is best to use all of these solutions in the complex.
Source: ridus.ru