573
Noble iris: the cultivation, care, breeding
Noble iris: the cultivation, care, breeding There are many species (more than 700) that include thousands of varieties of irises. According to European classification to this genus and the rank of bulbous irises, and Russian botanists have identified their self in childbirth (Juno, xiphium, iridodictyum), so the article about them not going.
The leaves of irises are flat broad sword-shaped, in some species narrow, mostly basal and assembled in a fan-shaped beam. Their surface is glossy or matte in various shades of green. Flowers solitary or in racemes have 6 perianth segments – 3 outer turned down, and 3 inside curved and directed upwards. The lower petals are different from the top color. The timing of flowering is early, middle and late – from late may until August.

Classification Given the form and color of flower, plant height and leaf width of his irises klassificeret to different sections, namely: bearded, beardless or limniris section ksiridion.
Bearded Bearded – have growths (fluffy hairs) on the folded down pubescent petals associated with a beard (hence the name). Mainly they are obtained by crossing different wild species. This is the largest group. Flowers irises come in all colors

The height of stems are subdivided into:
Low-growing or dwarf plants 40-50cm:
Miniature dwarfs – not above 20cm, ideal for rock gardens;
Standard dwarfs from 20 to 50cm tall, well grow. In two years the plant may be 10 or more stems;
Average height – the height varies from 50 to 70cm: InterMedia irises – flowers with a diameter of 7 to 10-12cm; border irises have flowers size 7-12cm in diameter; miniature high-irises – flower size of these varieties of 5-8cm in diameter.
Tall plants above 70 cm.
A very popular band, consisting of more than hundreds of varieties, is also called German iris. The flowers can be white, blue, pink, yellow, purple and blue, monochrome, dichroic or multicolor, with a border or with iridescent color. Beardless beardless irises Have thin, short-branched rhizomes. On the petals of the perianth are missing the barbs and the leaves narrowly ensiform flat. Flowers of all species of the section Limniris do not have a flavor.

They are also classified by groups depending on place of origin or some special characteristics. Siberian iris, up to 1 meter and above, frost-resistant and unpretentious. The flowers are mostly shades of blue and purple colors. The leaves are narrow, green. Little susceptible to diseases. Iris japonica (other names iris sword, iris Kempfer) has large flowers from 15 to 25cm in diameter. The flower is like a simple form, and Terry (multileaf), different shades of purple color. Unfortunately, bad winters in our latitudes, not per inosit severe frosts. Iris swamp (other names yellow iris, iris aerobicly) – height up to 120 cm Golden yellow flowers with brown stripes. Thermophilic species. Grows quickly, blooms in June-July. Grows exclusively in wet places, swamp iris Ksiridion Ksiridion – section includes 20 species of irises and more than 600 varieties, rare and little known group. Name the most common species is also referred to iris spuria. Durable plants with original and unusual flowers, different color. The flowers of these irises to confuse with other species is almost impossible, they have the most narrow petals. Tolerates drought and frost. A characteristic feature of Spurrier irises – they do not like transplanting and bloom for a long time in one place. Height are divided into short, medium and tall. Iris spuria

Landing
Can be planted from spring to autumn. The best time for dividing and transplanting in a few weeks after flowering. Land for planting it must be light and a good drainage. The soil is loamy with neutral or slightly acid reaction. It is desirable to transplant irises every 3 to 5 years. Siberian irises should be transplanted every 10 years so that they are not degenerated. Bearded irises to plant better-lit areas with good drainage. Bog irises grow best in moist soils. Before planting, very long roots should be shortened and remove the decaying parts of the rhizome. For disinfection can be soaked in solution of potassium permanganate 20-25 minutes after dry. Bearded irises are planted in a shallow hole in a pile of sand, straighten the roots and fall asleep earthy blend, not buried rhizome. Beardless irises same when landing needs a little bury and mulch with pine needles. Land is at a distance of 30-40 cm between the dwarf irises to 80 cm between the high irises. Planting irises telenok Care mainly due to timely weeding and hoeing, watering and fertilizing. Weeding is best done manually, as the root system of the plant is close to the soil surface and it can be a damage hoe. Watering. Irises – plants drought-resistant and long time without water. But to increase the flowering period requires regular watering, particularly during budding and flowering. After flowering, watering should be reduced.
Feeding.
Periodically irises should be fertilized. Nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer feed during the growing season and after flowering. A comprehensive — period of laying the flower buds. During flowering it is not recommended to fertilize. You can use compost and humus, but not the manure. Before the cold weather rhizome irises opening to the soil surface must be covered with earth or peat.
Reproduction
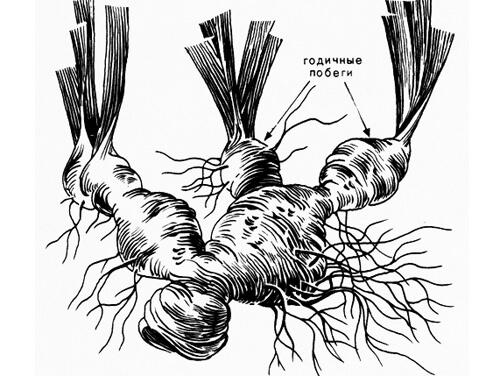
Reproduction of irises is carried out by dividing the Bush. It is best to divide in the spring before active growth or after flowering. It must be pre-watered to be broken from all sides with a fork and remove. Rhizomes are washed and divided into 1-2 year links with a fan of leaves, called "spatula". The rhizome should be cut with a sharp disinfected knife on a hard surface. The roots to shorten, the leaves to cut by 2/3. Put "spatula" in a tilted position, not buried below the rhizome with the Bud was on the surface. It is possible to hold the division without disturbing the entire hive, and Podkopaev on the one hand, to cut off part of the rhizome. The separated part of the roots are also divided into "spatula". And the land part are disinfected the ashes and sprinkled the ground. In this way it is possible not only to propagate the plant, but also to rejuvenate. When the reproduction of irises separates year links

Diseases and pests
One of the most dangerous diseases – bacterial blight or rot of the rhizomes. The leaves turn brown and wither, the fan is easily pulled out, fall off. The rot covers the rhizome, it collapses and becomes a white mass, covered with skin. The plant dies. Bacteriosis affected irises discarded. The damaged areas of the rhizome should be cut out down to healthy tissue, sprinkle with charcoal... Gray mold is a fungal disease. At high humidity the leaves become brown and rot, there is a gray patina. Rot spreading to the rhizome. When symptoms occur, it is necessary to use fungicides. Heterosporous. Can be recognized by brown spots with yellow edging on the leaves. Diseased leaves should be cut off and burned. The plant should be treated with a solution of copper sulfate or other fungicide drug. Iris, stricken heterosporium Of pests are the most annoying – winter shovels. In winter, gray caterpillars burrow into the soil and crawl out in the spring, pupate and turn into butterflies that lay eggs on the iris. After 1-2 weeks the eggs appear again and the caterpillars eat up the stems and leaves. To prevent these invasions should in early may, spray the plant with Uktelecom, according to instructions, and when there are caterpillars Cinecom. In recent years, plants often suffer from iris flies. Winters in the ground, leaves in the spring and lay eggs in unopened buds. The eggs hatch into larvae and eat the Bud. Spraying can be carried out by the medicines recommended to control the Colorado potato beetle. For irises dangerous mole crickets, podgryzayuschie rhizomes. Bronze beetle loves regales unopened buds. Gladiolus caused great damage in hot weather.

Composition with irises Use in landscape design In our country are very much lovers of irises, probably, in every second section you can see them. Slides are suitable for dwarf varieties, on the banks of artificial reservoirs often planted swamp iris. Very impressive look irises of different heights and colors, planted close together. Irises appropriate in any composition, can play as main role and secondary. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: 101dizain.ru/rasteniya/cveti/klumb/iris.html
The leaves of irises are flat broad sword-shaped, in some species narrow, mostly basal and assembled in a fan-shaped beam. Their surface is glossy or matte in various shades of green. Flowers solitary or in racemes have 6 perianth segments – 3 outer turned down, and 3 inside curved and directed upwards. The lower petals are different from the top color. The timing of flowering is early, middle and late – from late may until August.

Classification Given the form and color of flower, plant height and leaf width of his irises klassificeret to different sections, namely: bearded, beardless or limniris section ksiridion.
Bearded Bearded – have growths (fluffy hairs) on the folded down pubescent petals associated with a beard (hence the name). Mainly they are obtained by crossing different wild species. This is the largest group. Flowers irises come in all colors

The height of stems are subdivided into:
Low-growing or dwarf plants 40-50cm:
Miniature dwarfs – not above 20cm, ideal for rock gardens;
Standard dwarfs from 20 to 50cm tall, well grow. In two years the plant may be 10 or more stems;
Average height – the height varies from 50 to 70cm: InterMedia irises – flowers with a diameter of 7 to 10-12cm; border irises have flowers size 7-12cm in diameter; miniature high-irises – flower size of these varieties of 5-8cm in diameter.
Tall plants above 70 cm.
A very popular band, consisting of more than hundreds of varieties, is also called German iris. The flowers can be white, blue, pink, yellow, purple and blue, monochrome, dichroic or multicolor, with a border or with iridescent color. Beardless beardless irises Have thin, short-branched rhizomes. On the petals of the perianth are missing the barbs and the leaves narrowly ensiform flat. Flowers of all species of the section Limniris do not have a flavor.

They are also classified by groups depending on place of origin or some special characteristics. Siberian iris, up to 1 meter and above, frost-resistant and unpretentious. The flowers are mostly shades of blue and purple colors. The leaves are narrow, green. Little susceptible to diseases. Iris japonica (other names iris sword, iris Kempfer) has large flowers from 15 to 25cm in diameter. The flower is like a simple form, and Terry (multileaf), different shades of purple color. Unfortunately, bad winters in our latitudes, not per inosit severe frosts. Iris swamp (other names yellow iris, iris aerobicly) – height up to 120 cm Golden yellow flowers with brown stripes. Thermophilic species. Grows quickly, blooms in June-July. Grows exclusively in wet places, swamp iris Ksiridion Ksiridion – section includes 20 species of irises and more than 600 varieties, rare and little known group. Name the most common species is also referred to iris spuria. Durable plants with original and unusual flowers, different color. The flowers of these irises to confuse with other species is almost impossible, they have the most narrow petals. Tolerates drought and frost. A characteristic feature of Spurrier irises – they do not like transplanting and bloom for a long time in one place. Height are divided into short, medium and tall. Iris spuria

Landing
Can be planted from spring to autumn. The best time for dividing and transplanting in a few weeks after flowering. Land for planting it must be light and a good drainage. The soil is loamy with neutral or slightly acid reaction. It is desirable to transplant irises every 3 to 5 years. Siberian irises should be transplanted every 10 years so that they are not degenerated. Bearded irises to plant better-lit areas with good drainage. Bog irises grow best in moist soils. Before planting, very long roots should be shortened and remove the decaying parts of the rhizome. For disinfection can be soaked in solution of potassium permanganate 20-25 minutes after dry. Bearded irises are planted in a shallow hole in a pile of sand, straighten the roots and fall asleep earthy blend, not buried rhizome. Beardless irises same when landing needs a little bury and mulch with pine needles. Land is at a distance of 30-40 cm between the dwarf irises to 80 cm between the high irises. Planting irises telenok Care mainly due to timely weeding and hoeing, watering and fertilizing. Weeding is best done manually, as the root system of the plant is close to the soil surface and it can be a damage hoe. Watering. Irises – plants drought-resistant and long time without water. But to increase the flowering period requires regular watering, particularly during budding and flowering. After flowering, watering should be reduced.
Feeding.
Periodically irises should be fertilized. Nitrogen-phosphorus fertilizer feed during the growing season and after flowering. A comprehensive — period of laying the flower buds. During flowering it is not recommended to fertilize. You can use compost and humus, but not the manure. Before the cold weather rhizome irises opening to the soil surface must be covered with earth or peat.

Reproduction
Reproduction of irises is carried out by dividing the Bush. It is best to divide in the spring before active growth or after flowering. It must be pre-watered to be broken from all sides with a fork and remove. Rhizomes are washed and divided into 1-2 year links with a fan of leaves, called "spatula". The rhizome should be cut with a sharp disinfected knife on a hard surface. The roots to shorten, the leaves to cut by 2/3. Put "spatula" in a tilted position, not buried below the rhizome with the Bud was on the surface. It is possible to hold the division without disturbing the entire hive, and Podkopaev on the one hand, to cut off part of the rhizome. The separated part of the roots are also divided into "spatula". And the land part are disinfected the ashes and sprinkled the ground. In this way it is possible not only to propagate the plant, but also to rejuvenate. When the reproduction of irises separates year links

Diseases and pests
One of the most dangerous diseases – bacterial blight or rot of the rhizomes. The leaves turn brown and wither, the fan is easily pulled out, fall off. The rot covers the rhizome, it collapses and becomes a white mass, covered with skin. The plant dies. Bacteriosis affected irises discarded. The damaged areas of the rhizome should be cut out down to healthy tissue, sprinkle with charcoal... Gray mold is a fungal disease. At high humidity the leaves become brown and rot, there is a gray patina. Rot spreading to the rhizome. When symptoms occur, it is necessary to use fungicides. Heterosporous. Can be recognized by brown spots with yellow edging on the leaves. Diseased leaves should be cut off and burned. The plant should be treated with a solution of copper sulfate or other fungicide drug. Iris, stricken heterosporium Of pests are the most annoying – winter shovels. In winter, gray caterpillars burrow into the soil and crawl out in the spring, pupate and turn into butterflies that lay eggs on the iris. After 1-2 weeks the eggs appear again and the caterpillars eat up the stems and leaves. To prevent these invasions should in early may, spray the plant with Uktelecom, according to instructions, and when there are caterpillars Cinecom. In recent years, plants often suffer from iris flies. Winters in the ground, leaves in the spring and lay eggs in unopened buds. The eggs hatch into larvae and eat the Bud. Spraying can be carried out by the medicines recommended to control the Colorado potato beetle. For irises dangerous mole crickets, podgryzayuschie rhizomes. Bronze beetle loves regales unopened buds. Gladiolus caused great damage in hot weather.

Composition with irises Use in landscape design In our country are very much lovers of irises, probably, in every second section you can see them. Slides are suitable for dwarf varieties, on the banks of artificial reservoirs often planted swamp iris. Very impressive look irises of different heights and colors, planted close together. Irises appropriate in any composition, can play as main role and secondary. published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! © Join us at Facebook , Vkontakte, Odnoklassniki
Source: 101dizain.ru/rasteniya/cveti/klumb/iris.html
Ecologist Artyom Akshentsev about the secret algae-extremophiles and expeditions to Kamchatka
How to raise children in other countries




















