1575
Almost forgotten giant: radio telescope TNA-1500

Source photo
Some unique engineering objects of the past are preserved almost in its original form (Shukhov Tower), although it has been losing value, while others gradually lose its former luster, and then completely destroyed. Many unique facilities built during the Soviet era, now look just like the scenery for a horror film - pile of gray concrete, broken bricks and rusty iron constructions. One of its kind, they evoke sadness. And once you count the cost of the project and grief is magnified - literally billions of rubles are lying under the feet of debris piles
. But there is construction, which was lucky to survive a period of decline, continue and be further developed. On the title picture you see an object in the past called the Space Communication Center of the Special Design Bureau of MEI "Kalyazin". Now the name is more concise - Kalyazin Radio Astronomy Observatory. It is located 200 kilometers north of Moscow, and its territory is a unique radio telescope TNA-1500, also known as PT-64 (RT - radio telescope, and 64 - the antenna diameter)
.
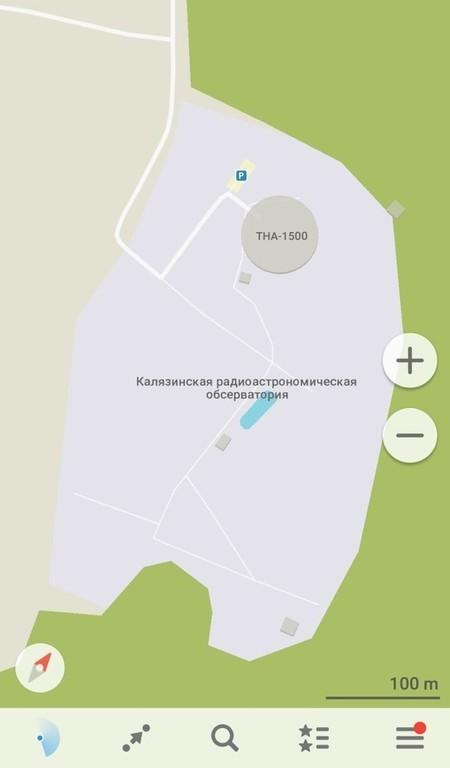
On campus you will not let go, but it is possible to drive close enough to estimate the scale of the construction
Together with MAPS.ME we prepared an overview of exciting developments in space during 2015-2016, where for the first time mentioned the PT-64. It is time to tell you more. The object attracts attention sizes: diameter of the telescope intended for basic space research, is 64 meters. Total weight is approximately 3800 tons, the weight of the mirror - 800 m
.
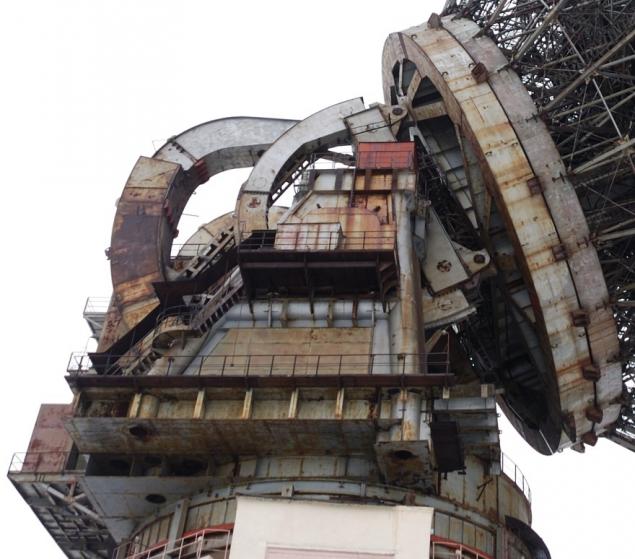

Photo source
Until 2010, the objects of the external look does not matter, a large amount of rust literally absorb radio telescope. However, after an extensive renovation of the RT-64 has become like new.
Kalyazin Observatory is engaged in the radio-astronomical studies, studies of pulsars, and a search of galactic, extragalactic objects and receiving data from remote cosmic satellites. The observatory on a regular basis working 10 employees.

The pipe, which rotates together with a plate - this elevator shaft with a ladder to attach to it
.
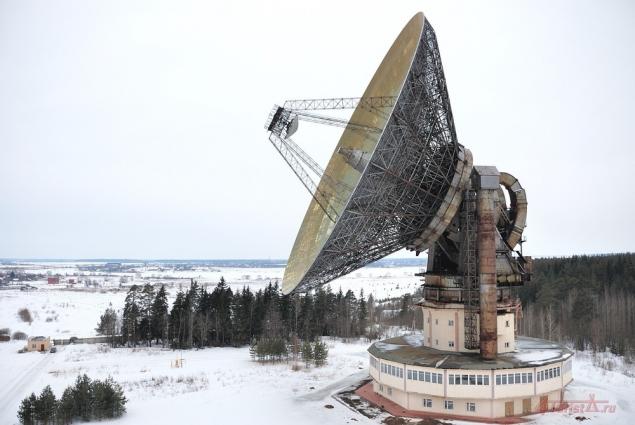

Photo source
But why Kalyazin? After all, this radio telescope does not exist in single copy (in Russia and the CIS are only seven, and in Yalta and Ussuriisk were set even more impressive 70-meter antenna), but in the network for the most part you will find pictures of the object. The answer, it seems, lies in the picturesque surrounding landscapes: near the river Volga, around tens of kilometers of forest are located only. However, there is a purely technical factor recognition: Kalyazinsky telescope is characterized in that its mirror can be rotated horizontally through 360 degrees, and vertically - more than 90 degrees. When the whole stadium, raised to the sky starts turning - a fascinating spectacle
.
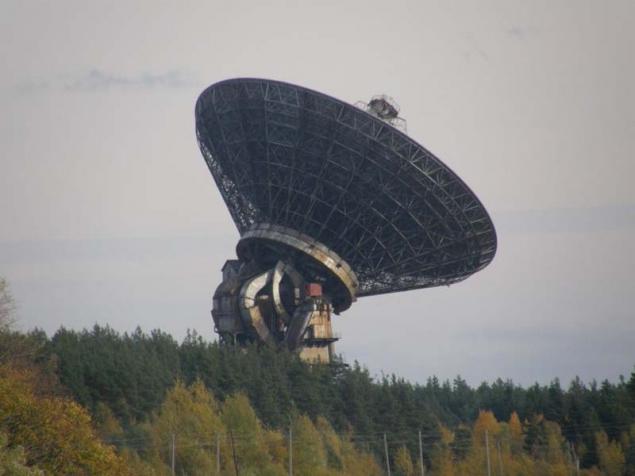

Photo source
It is worth mention that the history of the radio telescope in Kalyazin began after the collapse of the Soviet Union. He was commissioned in 1992, and regular observations of pulsars for timekeeping in Kalyazin program began in 1995. However, its construction began in 1974 and lasted 18 years.
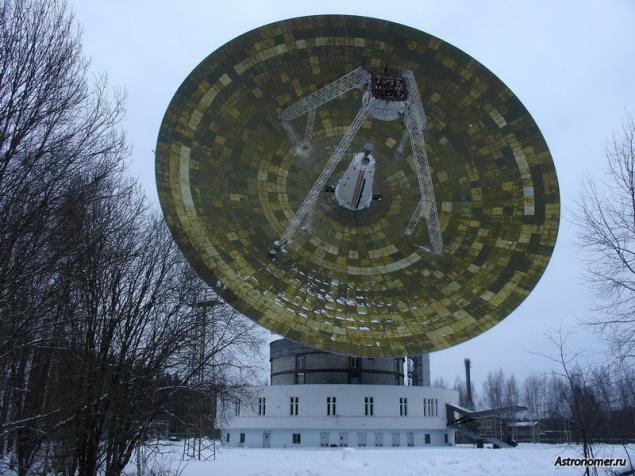

Photo by Igor Molotov
Center in Kalyazin - a branch of the Space Communication Center "Bear Lake." In the 17 km from Moscow, in a place called Bear Lake, located an identical radio telescope. Construction of the telescope began in 1969, and the work he joined in 1979. Both the radio telescope of information related to each other and may be considered as a single complex. The center itself appeared much earlier, it was founded in 1958 on the 26-kilometer Schelkovskogo highway, in the village of Long Ledovo, and was used as a testing ground, which were tested and the testing of airborne and ground-based antenna device.

According to eyewitnesses, next to the telescope in Bear Lake dug a trench 6 meters deep. In this pit in the bottom of the receivers installed, to check how the submarines will catch a signal.
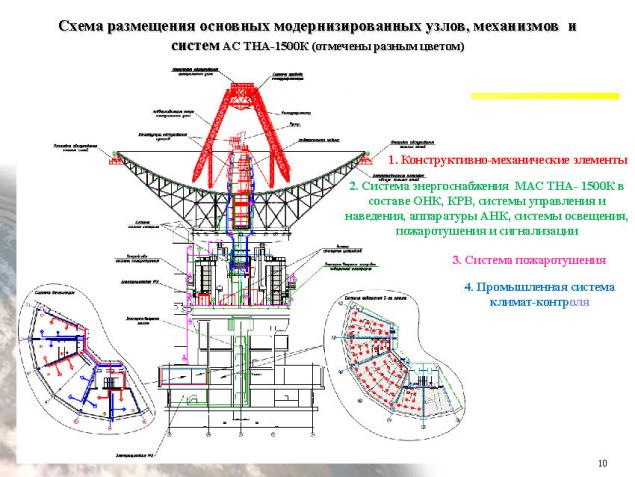
Steerable parabolic antenna TNA-1500 was built a special design bureau of the Moscow Energy Institute (MEI OKB) and used for a long time for the problems of distant space communications and satellite navigation. Construction began with the foundation in the form of 800 equally spaced ten-meter reinforced concrete piles driven into the ground and connected by monolithic reinforced concrete plate, on which was built the reference building.
In 1983-84 the RT-64 radar imagery received data and heat map of the planet Venus, then participated in the programs Vega (1986), when the image of Halley's Comet had been taken, and Phobos (1988-89.).
< br> Initially receive data automatic interplanetary station "Venera-15" and "Venera-16" with locators "Pole-In" on board was 70-meter telescope in Evpatoria, but due to a number of organizational and technical problems of the reserve item in the "Bear Lake" based on the TNA-1500 performed the bulk of the work.
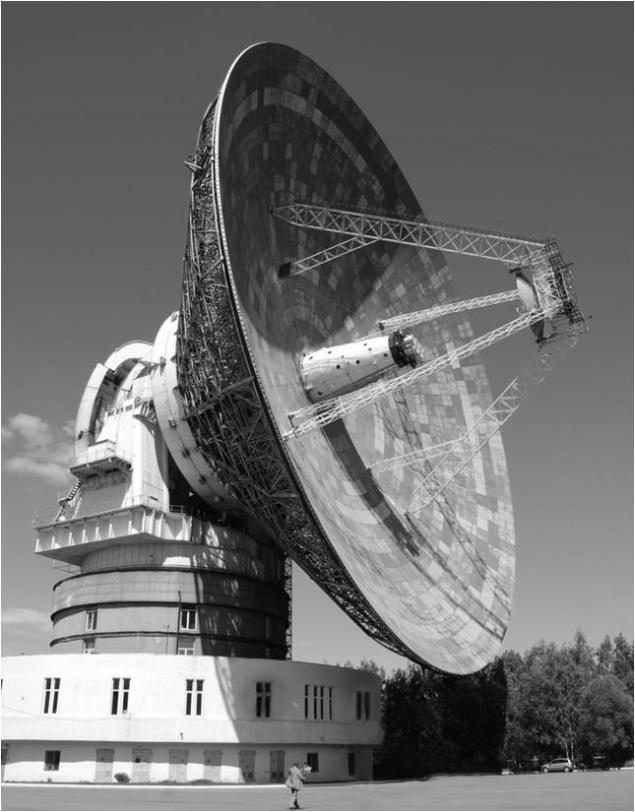

Photo source
In 1967, at the landfill site, the first test session with the satellite communication Vladivostok.

"Father" of the telescope can be regarded as Academician Alexei Bogomolov, who became the founder of the whole Soviet electronics. You name may not be familiar, but almost all of the electronics that worked in Soviet times in the space and rockets, was set up a team, headed by Bogomolov. He was a powerful expert in the development of radio astronomy and radio physical systems. Alex Bogomolov graduated from the Moscow Power Engineering Institute with honors in 1937 with a degree in "Electric power transmission and integration of electrical systems." In 1955 he was elected head of the department of radio engineering devices.
When I started developing the first operational missiles, it became necessary to provide continuous control of the flight path and obtain current information about the work of the engine and systems control rocket flight. In 1954 began the development of the missile R-7, which seven years later led to Gagarin's orbit. The development of telemetry and trajectory of funds for the new rocket instructed staff Bogomolov and telemetry system "Tral" was set up as soon as possible.
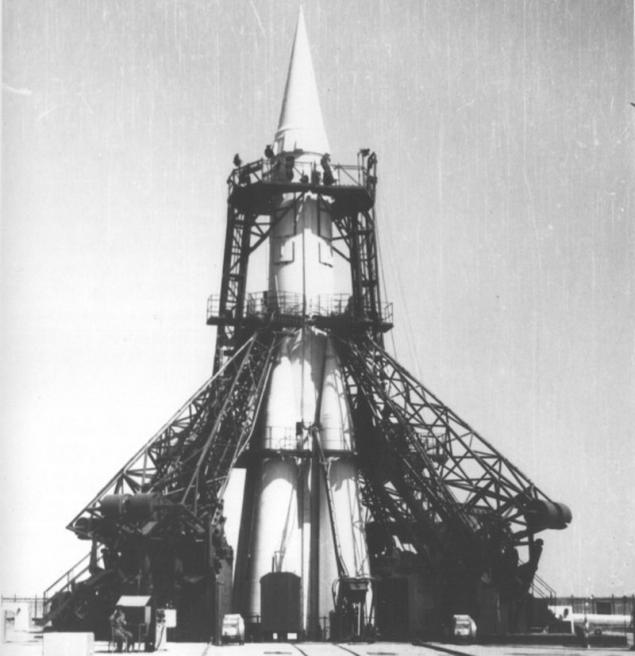

In the years 1960-65 under the direction of Bogomolov were built antenna first with a mirror diameter of 32 meters, and then with a diameter of 64 meters for communication with interplanetary research devices that run to the planets of the solar system. The first high-performance reflector antenna system, which appeared in the Space Communication Center, was a multi-purpose antenna TNA-200, used in a number of deep space operations.
Why was it necessary to build two identical radio telescope, located not so far from each other? In fact, the presence of two THA-1500 makes it possible to obtain high-precision signals, the equivalent received data from the radio telescope with an antenna of about 80 m. Today it is only available in Russian complex of this class, which is in working order and solve a wide range of tasks in astronomy.
Conclusion
Of the 11 that existed at the time in the world of radio telescopes with a diameter of more than 60 m were three in Russia and two of them were created in OKB MEI. OKB MEI received a unique base for research and ensure long-range space communication. In severe 90 years on the RT-64 radio astronomy research conducted with virtually no funding, the efforts of several scientific institutions and employees of the Moscow Energy Institute. The main thing is that these unique and beautiful global structures have survived and continue space exploration.
Source: geektimes.ru/company/mailru/blog/278954/
Negotiations on salary: 4 errors that allow for even intelligent people
When a woman has a strong man