603
Scientists have found a giant black hole in an ordinary galaxy
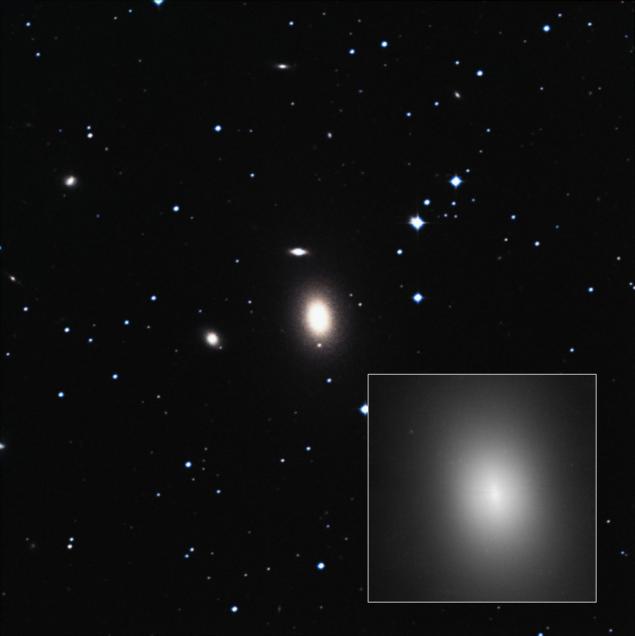

elliptical galaxy NGC 1600 bigger and brighter than the neighbors. But no one expected to find in the center of such a large object (Photo: ESA)
Astronomers have found a black hole whose mass of 17 billion solar masses at the center of a nondescript galaxy NGC 1600. This object is only slightly inferior to the weight of the most massive objects known to man - another black hole with a mass of 21 billion solar masses, but this supergiant located in a cluster of galaxies, rather than in the center of a small galaxy, located at a considerable distance from its neighbors. For scientists detect a supermassive black hole in NGC 1600, located at a distance of 200 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Eridanus, was a big surprise.
Until now, massive black holes with masses of billions of solar masses found in dense clusters of galaxies. Until now, in the middle of ordinary galaxies so massive objects, scientists have not observed. Perhaps, the new discovery is an indication that supermassive black holes are not so uncommon.
Scientists have compared the find to the largest skyscraper, which is located in the center of the small town. Discover the supermassive black hole was possible thanks to the project MASSIVE Survey, started in the 2014. The purpose of the project - the largest discovery and cataloging of galaxies and black holes. The first discovery of a new black hole occurred in the McDonald Observatory in Texas. Initially, astronomers could determine the extent of the findings, although it was clear that this place is pretty big. After additional resources and other observatories to observe the galaxy NGC 1600, it became clear that the object found a giant.
Larger black hole that only object in the Coma Cluster. This cluster brings together around 1,000 identified galaxies. The mass of a black hole in this region is about 21 billion solar masses (for comparison, the black hole, located in the center of the Milky Way, is heavier than the Sun only 4 million times).

Image: ESA
The mass of the object in the center of the galaxy NGC 1600 is about 2% of the mass of the galaxy. This is 10 times greater than would be expected, scientists. Typically, large galaxies are formed from several smaller ones. It may well be that NGC 1600 simply "ate" their neighbors. This hypothesis may explain the relative isolation of the galaxy - next to it there is simply no more neighbors, other galaxies are located at a considerable distance
. In addition, there is one more opportunity - for example, at the beginning of the formation of NGC 1600 in the region was a large amount of gas, from which emerged the galaxy itself with its enormous black hole at the center. In this case, no one is absorbed - the neighbors just did not have originally.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/273974/
Samsung has filed a patent application smart contact lenses
New record: transplanted baboon heart pigs has been working for more than two years