896
Technologies that help to survive on Mars
Last time in one form or another appear frequently news about Mars. Aerospace fluid agency NASA has found water on the Red Planet. Cinemas released film "Martian", created in consultation with scientists and allows to see the Martian expanses eyed actor Matt Damon. At this wave, we have accumulated a lot of questions about the mysteries of this cold world. For example, does the presence of liquid water on Mars, the possible existence of life there? Will they grow plants? Is it possible to recycle there the water into oxygen for breathing and to make Mars ever new tourist destination?

If one person really meet live on this planet, you have to solve at least some of the critical problems. Firstly, the climate is very unstable. The temperature ranges from -140 to +20 degrees Celsius. Therefore, we will either have to get used to it, or try to change the climate. That's for sure thought Elon Musk, when expressed their assumptions about the carrying out of nuclear explosions at the poles of the planet. After that, we need shelter, food and oxygen. And although no one knows exactly when it will start the first manned mission to Mars, engineers and scientists are working on technologies to solve all these issues.
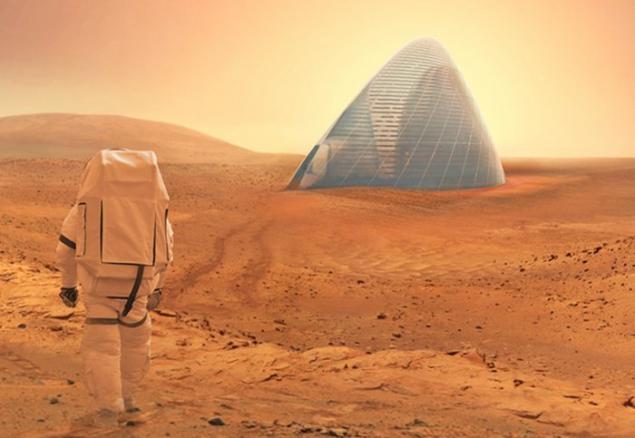
3D-printing house

NASA likes to spend all sorts of competitions, inspiring designers and engineers to develop new approaches conquest of outer space. Most recently, the agency conducted a competition for the development of 3D-printed home on Mars. The winner of the contest was the concept of 3D-printed Space needle ICE HOUSE, which developed the New York studio SEArch (Space Exploration Architecture) and Clouds AO (Clouds Architecture Office). The aim of the competition was to develop a concept of Martian home for four people by using 3D-printing technologies and material available on Mars. The winners took the prize of 25 000 dollars.
Space vegetables

The experiment on the ISS has shown that in space you can grow fresh salad and mikrozelen and without any fear of eating them. Last year, the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket delivered to the ISS the first portable greenhouse, in which each type of plant grown in his individual cell. Most recently, the team has collected ISS grew romaine lettuce crop and with great pleasure it was used for its intended purpose.
Of course, if people are going to live on Mars, even with temporary conditions, they need access to fresh food and vegetables in particular. Fortunately, for their own health, even in 55 million kilometers from Earth, to give up fresh greens on your plate does not work anymore.
Artificial greens, producing oxygen
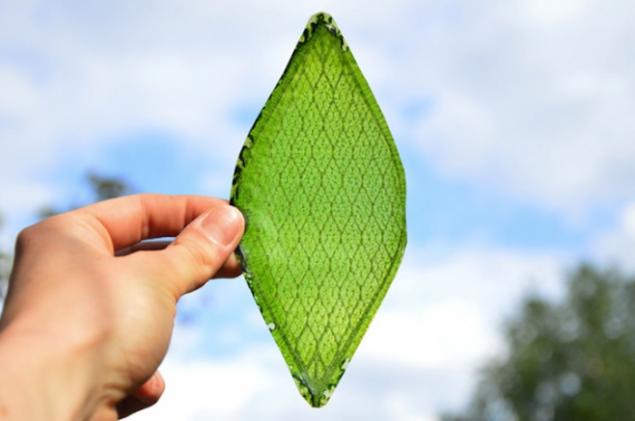

One of the biggest and most obvious obstacles between man and his travel to Mars, the planet is a lack of oxygen to breathe. Oxygen, of course, it is possible to deliver in special containers from the Earth. However, in the case of long-term stay on the planet where reasonable and practical is to create oxygen on the spot, instead of dragging it through the solar system. To do this, perfectly suited plants, which, for example, in the world are its main source. But on Mars, because of the very harsh conditions, they can not survive. The logical solution is to create an "artificial green," which, using the same principles and consisting of the same components as that of natural grass, will be able to produce pure oxygen for respiration, using only water and light as a source of growth.
Tools for
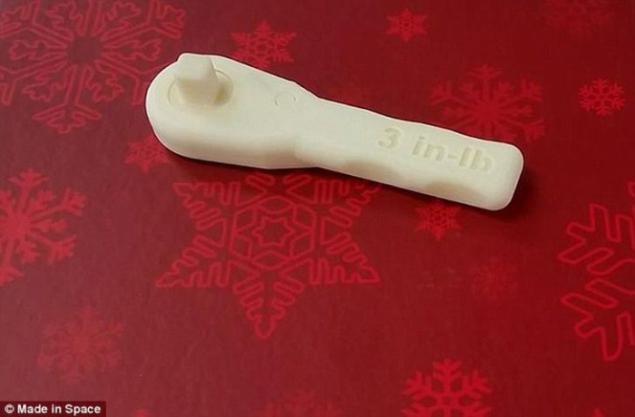

Here again come to the aid of 3D-printing technology that allows to produce any tools needed for work and home arrangement Martian colonists. Possibility of using conventional materials and 3D-printer to create any tool that may be required will be truly invaluable. After waiting another parcel from Earth would be extremely impractical - to take months. In the best case - a minimum of 280 days.
What fly?
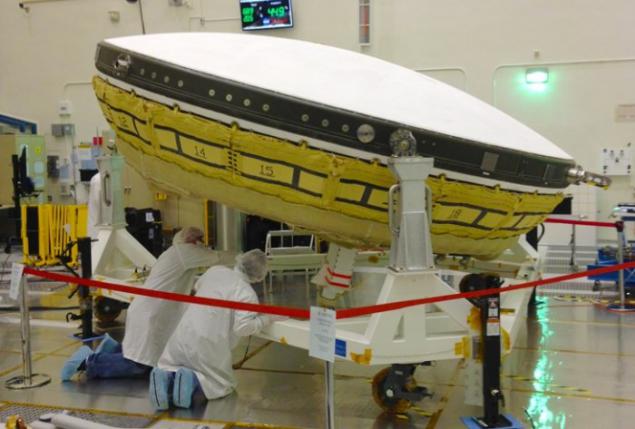

On a flying saucer, of course! No kidding. In NASA develop and test new lander, which resembles a flying saucer from many science fiction movies. The device has a new system of inflatable soft landing Low Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD). Interestingly, the design of the new descent module was inspired by technologies that have been used for landing on Mars in 1976. In addition, similar to the device used to deliver the rover "Kyuriositi" on the surface of the Red Planet in 2012.
Food from the 3D-printer
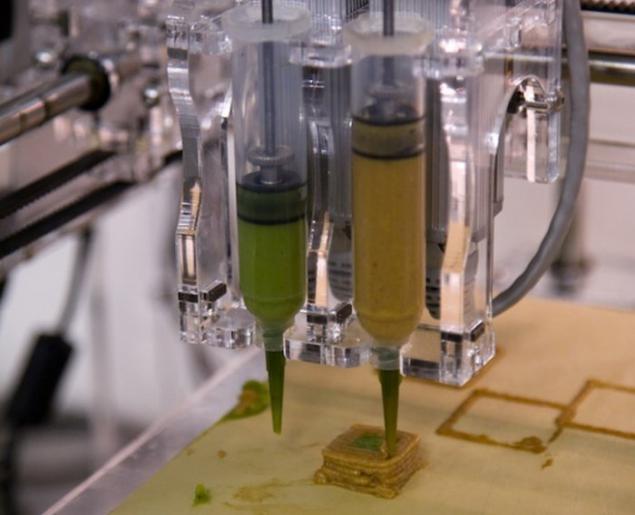

So, the problem of shelter, oxygen, organic vegetables and even the correct size wrenches we've already covered, and now it's the most important aspect that must be addressed, and then double-double-check before we go to Mars. Unfortunately, on the Red Planet is no supermarket where we could purchase the necessary food. However, there is another way to provide themselves with the right amount of daily calories. The food we print the 3D-printer.
Despite the fact that some of the vegetables we have learned to grow in microgravity, a large part of the diet of astronauts still consists of prepackaged food, designed primarily for convenience and long-term storage rather than to maintain nutritional balance. Talk about some culinary delights here is not necessary. 3D-printed food could diversify the diet, providing people with additional vital nutrients and amino acids.

If one person really meet live on this planet, you have to solve at least some of the critical problems. Firstly, the climate is very unstable. The temperature ranges from -140 to +20 degrees Celsius. Therefore, we will either have to get used to it, or try to change the climate. That's for sure thought Elon Musk, when expressed their assumptions about the carrying out of nuclear explosions at the poles of the planet. After that, we need shelter, food and oxygen. And although no one knows exactly when it will start the first manned mission to Mars, engineers and scientists are working on technologies to solve all these issues.
3D-printing house

NASA likes to spend all sorts of competitions, inspiring designers and engineers to develop new approaches conquest of outer space. Most recently, the agency conducted a competition for the development of 3D-printed home on Mars. The winner of the contest was the concept of 3D-printed Space needle ICE HOUSE, which developed the New York studio SEArch (Space Exploration Architecture) and Clouds AO (Clouds Architecture Office). The aim of the competition was to develop a concept of Martian home for four people by using 3D-printing technologies and material available on Mars. The winners took the prize of 25 000 dollars.
Space vegetables

The experiment on the ISS has shown that in space you can grow fresh salad and mikrozelen and without any fear of eating them. Last year, the SpaceX Falcon 9 rocket delivered to the ISS the first portable greenhouse, in which each type of plant grown in his individual cell. Most recently, the team has collected ISS grew romaine lettuce crop and with great pleasure it was used for its intended purpose.
Of course, if people are going to live on Mars, even with temporary conditions, they need access to fresh food and vegetables in particular. Fortunately, for their own health, even in 55 million kilometers from Earth, to give up fresh greens on your plate does not work anymore.
Artificial greens, producing oxygen

One of the biggest and most obvious obstacles between man and his travel to Mars, the planet is a lack of oxygen to breathe. Oxygen, of course, it is possible to deliver in special containers from the Earth. However, in the case of long-term stay on the planet where reasonable and practical is to create oxygen on the spot, instead of dragging it through the solar system. To do this, perfectly suited plants, which, for example, in the world are its main source. But on Mars, because of the very harsh conditions, they can not survive. The logical solution is to create an "artificial green," which, using the same principles and consisting of the same components as that of natural grass, will be able to produce pure oxygen for respiration, using only water and light as a source of growth.
Tools for

Here again come to the aid of 3D-printing technology that allows to produce any tools needed for work and home arrangement Martian colonists. Possibility of using conventional materials and 3D-printer to create any tool that may be required will be truly invaluable. After waiting another parcel from Earth would be extremely impractical - to take months. In the best case - a minimum of 280 days.
What fly?

On a flying saucer, of course! No kidding. In NASA develop and test new lander, which resembles a flying saucer from many science fiction movies. The device has a new system of inflatable soft landing Low Density Supersonic Decelerator (LDSD). Interestingly, the design of the new descent module was inspired by technologies that have been used for landing on Mars in 1976. In addition, similar to the device used to deliver the rover "Kyuriositi" on the surface of the Red Planet in 2012.
Food from the 3D-printer

So, the problem of shelter, oxygen, organic vegetables and even the correct size wrenches we've already covered, and now it's the most important aspect that must be addressed, and then double-double-check before we go to Mars. Unfortunately, on the Red Planet is no supermarket where we could purchase the necessary food. However, there is another way to provide themselves with the right amount of daily calories. The food we print the 3D-printer.
Despite the fact that some of the vegetables we have learned to grow in microgravity, a large part of the diet of astronauts still consists of prepackaged food, designed primarily for convenience and long-term storage rather than to maintain nutritional balance. Talk about some culinary delights here is not necessary. 3D-printed food could diversify the diet, providing people with additional vital nutrients and amino acids.