666
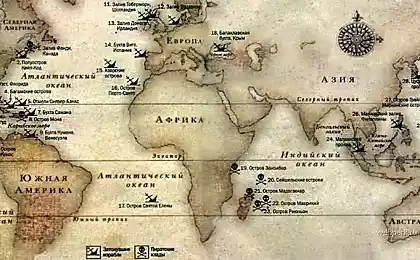
At the bottom of the ocean at rest over 3 million shipwrecks
"Titanic" - the most famous shipwreck, but not edinstvennyy
According to United Nations estimates, at the bottom of the ocean buried more than three million shipwrecks. Marine archaeologists use these vehicles as a museum - studying them, we can learn a lot about navigation, intelligence, military, technology and culture of the past. The reasons why the ship sank, and that what the cargo is on board, helping to draw conclusions about how people lived.
Despite the value of such information, the passengers and crew of these ships would give all the treasures that are safe to swim to the destination, in this no doubt. The most common causes of shipwrecks are design flaws, navigational errors, bad weather, fire, improper positioning of cargo on board, and, of course, war.

Depending on what the cargo is on board, the wrecks are divided into two categories: wreccum maris (debris washed ashore) and adventurae maris (the debris left on the seabed). Historically valuable fragments are often protected from looting by the laws on the protection of cultural heritage as well as marine archaeologists are unlikely to know something, if the ships will roam the crowd of greedy looters.
via factroom.ru

According to United Nations estimates, at the bottom of the ocean buried more than three million shipwrecks. Marine archaeologists use these vehicles as a museum - studying them, we can learn a lot about navigation, intelligence, military, technology and culture of the past. The reasons why the ship sank, and that what the cargo is on board, helping to draw conclusions about how people lived.
Despite the value of such information, the passengers and crew of these ships would give all the treasures that are safe to swim to the destination, in this no doubt. The most common causes of shipwrecks are design flaws, navigational errors, bad weather, fire, improper positioning of cargo on board, and, of course, war.

Depending on what the cargo is on board, the wrecks are divided into two categories: wreccum maris (debris washed ashore) and adventurae maris (the debris left on the seabed). Historically valuable fragments are often protected from looting by the laws on the protection of cultural heritage as well as marine archaeologists are unlikely to know something, if the ships will roam the crowd of greedy looters.
via factroom.ru
The most expensive honey in the world is like a small car
In Switzerland, it is illegal to keep the house only one guinea pig