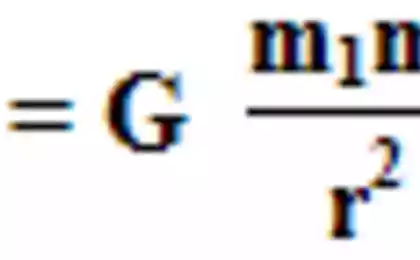1484
Great Pacific garbage patch: to prevent pollution of the planet

Probably very few people have heard about this phenomenon, but this is not surprising. Characteristic of the human race is easy to forget about their mistakes and sweep the dust under the carpet. So, on the debris - did you know that there is a Большое Pacific Garbage Patch , it is the same garbage Eastern continent, it is the Pacific "musorovorot"? This accumulation of debris in the North Pacific. Collection, created, of course, people. In ancient times, the ocean seemed endless, a few days it was not the way to overcome so far shore and the water is always inhabited by various monsters. Those days are gone, white spots left nothing but humanity still seems that their planet is so vast that can endure any treatment.
Many scientists have hit the alarm, calling for the reduction of emissions of CO 2 sub>, which, in their view, lead to the greenhouse effect and global warming that threatens to flood with water and melted poles are many coastal regions. Other reported problems launching satellites into orbit because there accumulated huge amount of debris and spent satellites of the old generation. But few pay attention to another danger - the world's oceans is almost unable to cope with millions of tons of plastic debris that kopilsya there last fifty years.
For the first time this problem had predicted as early as 1988, researchers from the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration in the United States. And the existence of Garbage Patch was published by Charles Moore, the captain of the Navy and Marine California, whose articles have described this phenomenon. Sailing North Pacific currents system after participating in the regatta, Moore found a huge cluster of debris on the surface of the ocean. He reported his finding oceanographer Curtis Ebbesmeyeru, who later called this area "East garbage continent».
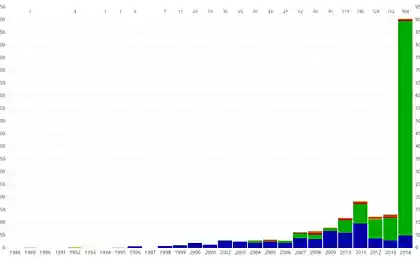
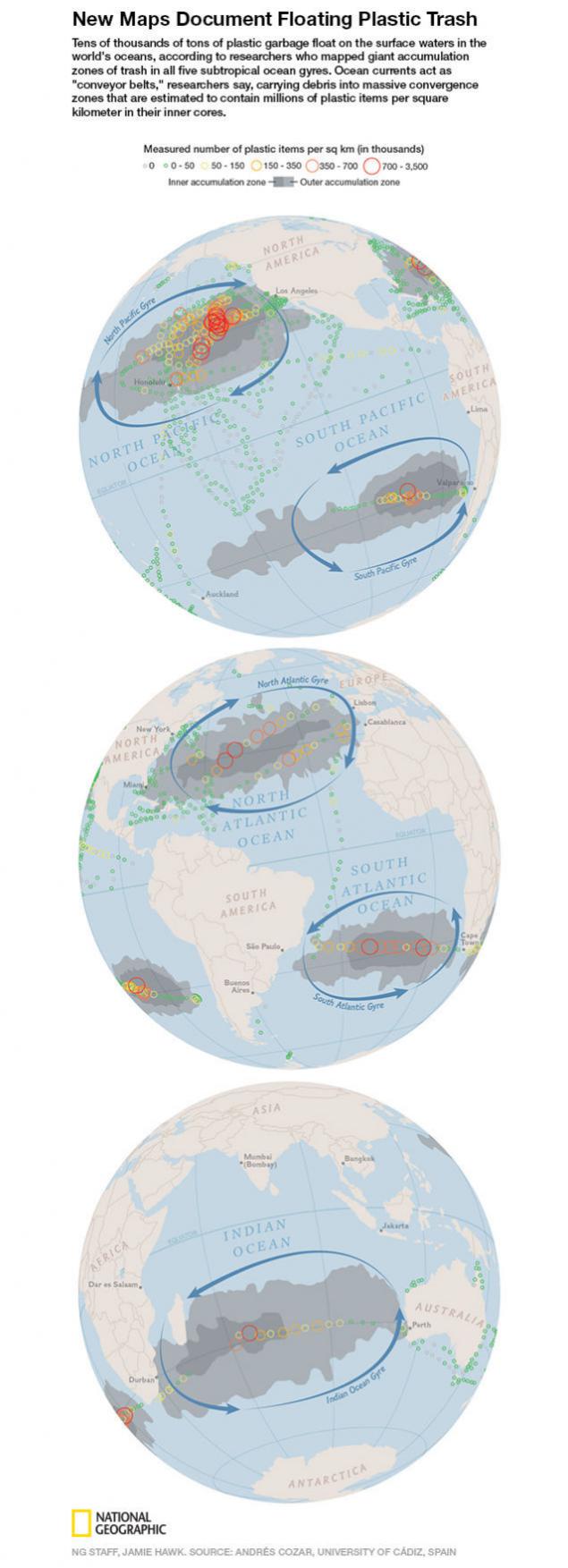
Spot formed prevailing currents, which are twisted around a particular area. Its exact size is unknown. Estimates vary from area of 700 thousand. Up to 15 million square kilometers or more, (0, 41% and 8, 1% of the total area of the Pacific Ocean). Probably at this site is over a hundred million tons of garbage. It is known that plastic is very badly decomposed, in the ocean, he just swims near the surface, gradually destroying physically and crushed into small fragments, but not chemically degrading.
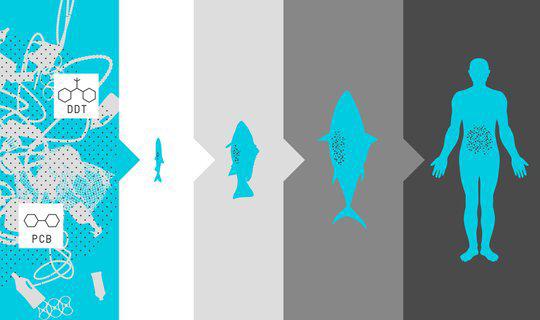
Ocean animals eat pieces of plastic, confusing it with the plankton, and thus it is included in the food chain - if the animals do not die from suffocation or starvation after eating plastic. In addition to direct harm to animals, floating waste from the water can absorb organic pollutants including PCBs, DDT and PAHs. Some of these substances are not only toxic - their structure is similar to the hormone эстрадиолом, resulting in failure to hormonal poisoned animal. The consequences of these phenomena, how they affect the ecosystem in general and men in particular, have not even fully understood.
Unfortunately, there is no international recognition of the problem (the same level as, for example, the agreement on the limitation of emissions of CO 2 sub> in the atmosphere), no proven technology to clean up the ocean from pollution. In 2008, Richard Owen, instructor-diver, organized by the Coalition to clean up the environment (Environmental Cleanup Coalition, ECC), is engaged in the problems of pollution of the North Pacific. The organization calls on the ECC to form a fleet of ships to clear the waters and the open laboratory Gyre Island for processing of rubbish.
In 2009, the scientist-oceanographer Dr. Marcus Eriksen and his wife Anna Cummins was established "Institute of five whirlpools" (5 Gyres Institute). The Institute explores the problem of pollution of the oceans, have found garbage spots, as well as seeking new.
In 2014, a group of scientists with the support of National Geographic nine months furrows oceans, collecting information about the pollution of the ocean and making "plastic" card Ocean.
In 2014, 19-year-old Bojan Slet, a student from Delft University of Technology, The Netherlands introduced system cleaning debris from the ocean autonomous platforms that float freely in the ocean and catch debris with flooded the barriers. For three years before that Slet diving on the coast of Greece, and his very excited by the fact that in the Mediterranean swims more packages than jellyfish. He decided to devote his life to solving the problem with the cleaning of the ocean, and together with his team conducted a comprehensive study and collected on the continuation of work through Crowdfunding more than $ 2 million.
Their method uses the natural ocean currents and winds, which are passive garbage collection to the platform. Then used solid floating barriers to trap and concentrate debris from the ocean, eliminating the risk of entanglement of fish and other living things that have happened in the collection of garbage by other methods such as networks. Although the method is not cheap (for its implementation requires about 32 million. Per year), it is many times cheaper than other proposed methods of treatment.
Organization The Ocean Cleanup regularly takes donations and volunteer help. In November, the organization arranged a second объёмный report on the feasibility of the ocean clean proposed method. Conclusion of the report is not changed - it was recognized that a realistic method, and that it can possibly clean half of the ocean for 10 years. Well, time will tell. In the meantime, try less trash and not to use plastic bags.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/242324/