1253
The method of "twin stars" will more accurately calculate the distance to distant stars
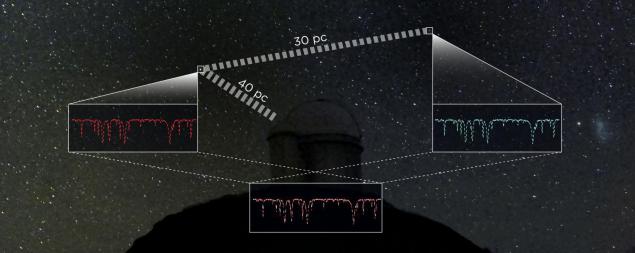
The two stars with similar spectra with a known distance to one of them i>
Astronomers from the University of Cambridge come up with a new, more accurate way to measure the distances to remote stars, using zvёzdy- "twins". The difference in brightness of the two stars with the same range, one of which is close enough to us, and allows you to accurately measure the difference in distance between them.
Measuring the distance to objects in the universe - the key task of astronomy. Without this it is impossible to draw any scientific conclusions about the size of objects and their properties. Each new accurate measurement of distance - another step in the study of the universe.
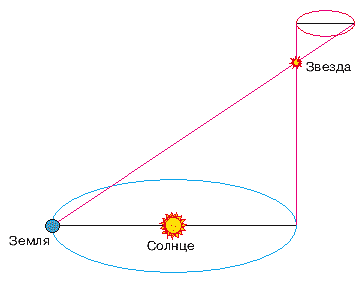
The best way to measure the distance to remote sites using the parallax, or apparent shift of celestial body when you change the angle. To do this, measure the two angles from different places of observation (the larger the database, the distance between the two places of observation - the better), and by simple trigonometry to calculate the height of a triangle.
The largest database available to us - the diameter of Earth's orbit, so the measured displacement of stars called the annual parallax. The first attempts to measure stellar parallax to test the Copernican theory of the Earth's rotation around the sun has made more Tycho Brahe in the 16th century, but then it just was not enough precision tools - for the parallax of stars is less than 1 arcsecond.
The first person who was able to accurately measure the parallax of stars began in 1837. Friedrich Georg Wilhelm von Struve (at that time director of the Dorpat Observatory, and later - Pulkovo). He measured the parallax of Vega, and found it to be 0, 12 arcsec.
Since then, the instruments are constantly improved, and, until recently, the best tool for measuring the parallax was satellite Hipparcos (acronym for High Precision Parallax Collecting Satellite - «precision satellite to collect parallax"). It was launched in 1989 and for 37 months of work, collected information about more than a million stars. It was the first and only complete its work space astrometric project. The success of the program will increase the accuracy of astrometric measurements on the order.
But this wonderful device is only suited for measuring distances to stars, distant from us no more than 1,600 light-years. In our galaxy is about 100,000 stars. For all other measured angles are too small.
The recently launched to replace him satellite Gaia improved and allows to measure distances up to 30,000 light-years, which will affect billions of stars of the Milky Way - the order of 1% of all stars galaxy.
But the distance to very distant stars to be measured indirectly - from the temperature, chemical composition, spectrogram, and data on the evolution of the brightness of the star of stars calculated, and compared with the apparent brightness. However, this method has an accuracy of up to 30%.
Astronomers from the Cambridge hit upon a rather simple solution. We need to find two identical spectra of stars, one of which will be located close enough to us to be able to accurately measure the distance to it through parallax. Then the difference in the apparent brightness of the two stars will directly reflect the difference in the distance between them. Accuracy of the method is not more than 8% when tested by measuring its parallax and does not increase with increasing distance.
"It's a remarkably simple idea - so simple that it is strange that no one before her had not guessed, - says Dr. Paula Joffre Pfeil (Paula Jofre Pfeil), the project manager. - The further the star, the dimmer it is in heaven, and if the two stars is identical to the spectrum, we can use the difference in brightness to calculate distances ».
Of all the stars of the spectrum, which is measured at 280,000 pixels, 400 lines are selected that best describe the properties of stars. In this line you can be armed with the existing catalog of stars, which measure the distance to look for distant stars with identical spectra, and add to the catalog distances. This method will be a powerful complement the work performed within the framework of Gaia.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/261944/