998
Astronomers have recorded at one of the galaxies record power gamma-ray bursts
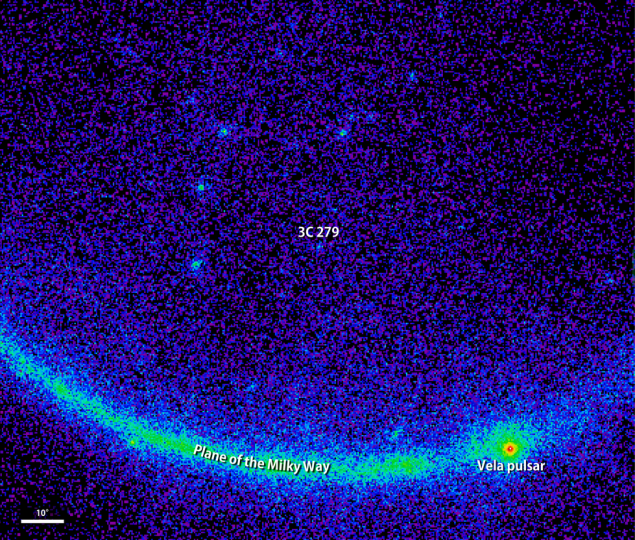
The galaxy 3C 279 "at rest" in the gamma-ray spectrum / NASA i>
Five billion years ago, a major cataclysm shook the region near the giant black hole at the center of the galaxy 3C 279, сообщает Sience Daily . June 14 powerful boost of energy that accompanies the event, finally reached Earth and has been fixed with the help of NASA гамма-телескопа Fermi , as well as satellites and other devices. Astronomers around the world have sent "eyes" of tools available to them in the direction of the galaxy, to further consider this brief but spectacular event record.
"A couple of days ago, 3C 279 had a normal active galaxy, which we constantly observe. But now it has become a bright gamma-ray source, "says Sarah Kutin, scientists working with the Fermi telescope from the Italian Space Agency in Rome.
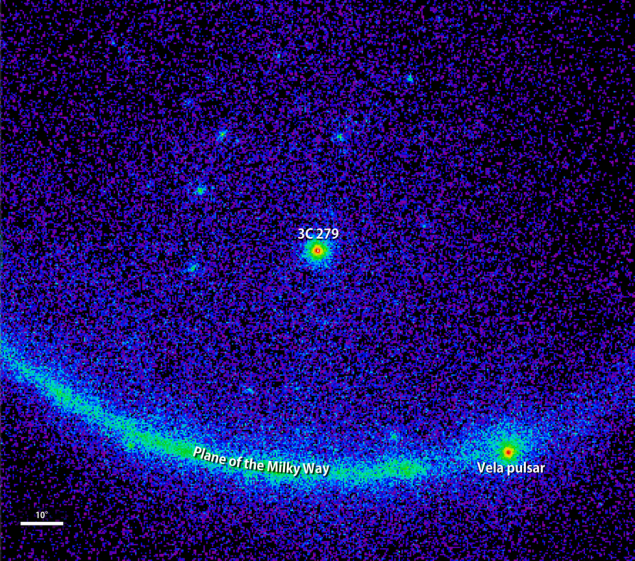
The galaxy 3C 279 at the time of the explosion recorded by scientists in the gamma spectrum / NASA i>
The galaxy 3C 279 - known blazar, whose high energy activity due to the presence of a supermassive black hole at its center, the size of about a planetary system of our star. As the black hole consumes matter around itself and has a powerful gravitational field, some light photons change their motion path, going in the "beams". This makes blazar so bright for us.
"This outbreak - the most active, that the Fermi telescope observed for all seven years of its operation. For one night 3C 279 has become ten times brighter, "says Elizabeth Hayes, deputy project manager Fermi Control Center at Goddard Space Flight , NASA . Astronomers believe that a change in the light emitted by the galaxy associated with the change in direction of light beams, formed under the influence of the black hole, but why these changes are taking place - a mystery.
Another bright gamma-ray source in the night sky is a Vela pulsar , neutron star, formed after the explosion of a different light. Distance from Vela is about 1,000 light-years.
3C 279 is a million times farther away from us, but at the time she was a flash in 4 (!) Times brighter Vela. This indicates that five billion years ago in a galaxy 3C 279 was a massive, unstable burst of energy. Galactica has returned to its original state (in terms of the observed gamma-ray) for 18 of June.
Why such a hurry astronomers to collect data on emerging Blazar? "The priority of our research is to collect information until blazar bright" shared Masaaki Hayashida, Fermi team member of the Research Institute of Cosmic radiation (Institute for Cosmic Ray Research) at the University of Tokyo. "After all the stops, we can begin to analyze the information to gain insight into the mechanisms of what happened."
Italian research satellite AGILE gamma-ray spotted the first outbreak, and after information was confirmed by Fermi. Reacting to the findings, NASA urgently refocused satellite Swift, and the European Space Agency has sent a galaxy gaze spacecraft INTEGRAL. He was also involved a number of optical and radio telescopes located on the ground.
3C 279 has a special place in the history of astronomy, studying gamma-ray objects. The first outbreak was registered in 1991. It found svezhezapuschennaya at the moment Гамма-обсерватория Compton , which was in service until 2000. The galaxy 3C 279 then set the record for the most distant and at the same time the brightest gamma-ray source known at the time. "Although we do not expect to find such a bright galaxy, we expect another big surprise," recalls Robert Hartmann, the head of the first study of gamma radiation 3C 279 is still in the project Compton Observatory, and now a member of the project team "Fermi" in the Mission Control Center at Goddard. "The brightness of the observable galaxy 3C 279 then quadrupled in ten days." New explosion began June 14 and reached its peak on the 16th day. The new gamma-ray burst was 10 times brighter than that observed by scientists in 1991.
Mid-June has been a busy time for the team of the "Fermi". Ever since the start of the mission system, last month was the busiest of all time operation. In addition to observing the explosion in the galaxy 3C 279, Fermi has photographed a series of eruptions on the sun's surface, which is unusual in itself, and also recorded several outbreaks in a binary system V404 in the constellation Cygnus, containing a black hole, which makes itself felt every few decades.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/253398/
3D-technology in cooking: where and how are already being applied
In the US, charging systems for electric vehicles become more affordable for ordinary consumers