844
In the craters of Mars found glass, which could capture a ancient microorganisms
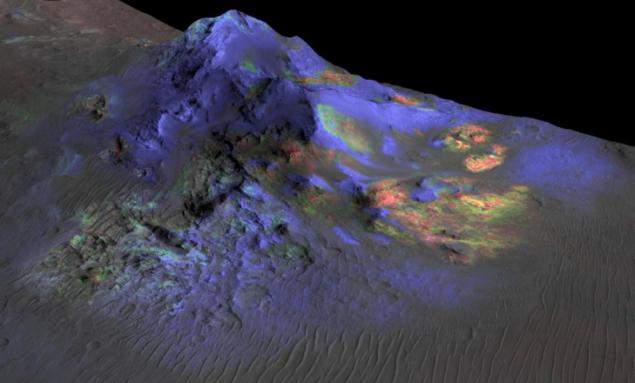
Исследователи found on Mars signs , that impact craters from meteorites glass is formed of sand under high pressure and temperatures. This glass, as it was already proven in studies on the Earth's surface, can save a existed at the time of the fall of the meteorite microscopic life forms.
The presence of water on Mars has proven science . Is there and parched river bed, and the ice caps of ice (which freezes periodically carbon). But evidence of life on the red planet, we still can not find any way. Only indirect evidence, such as the availability of favorable conditions or the presence of local hydrocarbon . Is that live there are bacteria that brought with him Curiosity .
Who in the world of life can not be at all, but it could be earlier - when there was more water, for example. Planetary scientist Peter Schultz, who recently explained the presence of turbulence on the moon , made the assumption that Mars does not interfere with form the same glass which It was found in the Earth craters. As such, it is in it may, like flies in amber, kept the ancient Martian bacteria, or at least traces of microorganisms.
Researchers from Brown University, inspired by this suggestion, began an active search window on Mars - and before them, no one has ever reached this success. Careful spectral analysis of the reflected light from the surface areas to help them find a few craters, which formed the said glass. The work led by Kevin Cannon, a university student. He assisted Professor Jack Masted.
"Glass Education emphasizes not provide spectrograms, so they are usually muted range of minerals that are on them - says Masted. - But Kevin came up with a way to vytsepit their signal from the general noise. "
Scientists in the laboratory of "baked" similar in composition glass, figured out what he should be spectrogram and transferred the data algorithm is specifically designed for disassembly spectra obtained device Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars (CRISM), which is on board the orbital station Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter .
This technique made it possible to detect traces of glass, formed as a result of meteorite impacts, few craters of Mars. One of the craters - Hargraves, located in a depression Nili Fossae , stretching for 600 km of the planet's surface. It will just be one of the possible places to sit next rover from NASA, the mission of which is scheduled for 2020. This rover will need to obtain soil samples that the scientists are planning to bring back to Earth.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/251744/