1710
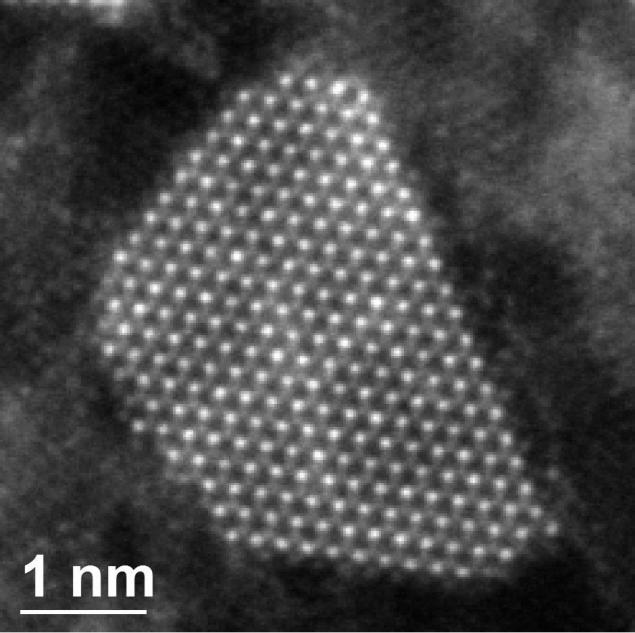
Electron microscope to distinguish between individual atoms, appeared in the British National Laboratory SuperSTEM
Nion Hermes Scanning Transmission Electron Microscope worth 3, 7 million pounds sterling ($ 5, 5 million) and allows you to see objects a million times smaller than a human hair. The main focus of the electron microscope is that, instead of the photon beam as a conventional light microscope, it uses a beam of electrons. Electron wavelength is smaller and that allows to obtain a greater increase with better resolution.
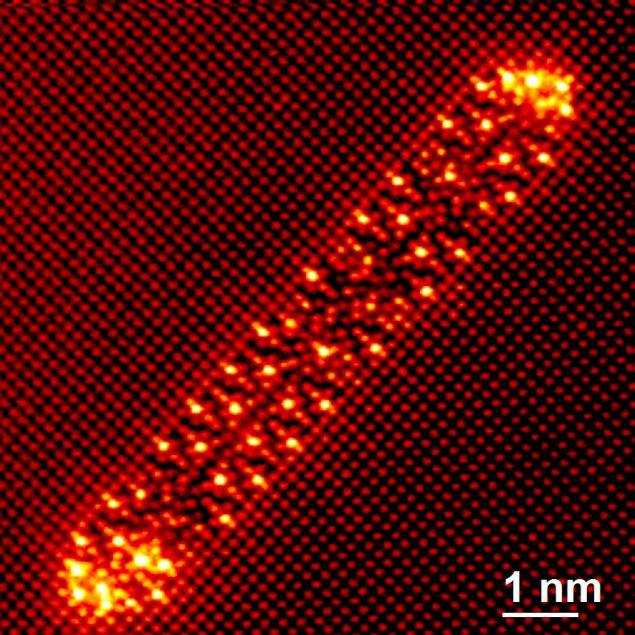
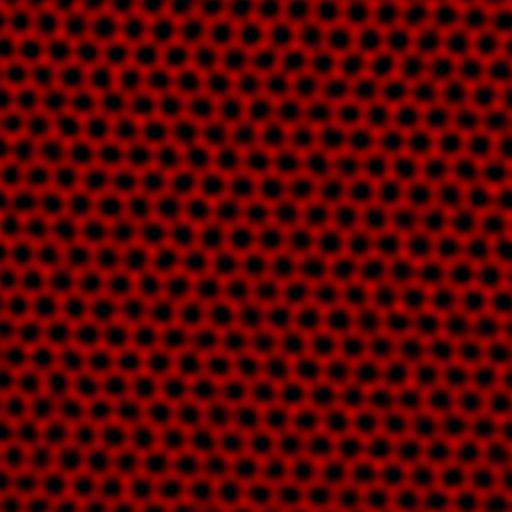
As to the application of such a device, it is vast. Take, for starters, electrical engineering. All prefer compact portable devices. Our gadgets are getting smaller by the day. To create these necessary transistors, semiconductors, and so on. The details, but to create these miniature products must be able to manipulate materials at the atomic level. After all, if the structure, for example, graphene, a two-dimensional sheet of carbon atoms to add extra atom to change the material itself! Therefore, you need a special atomic control, preserving the integrity of the material.
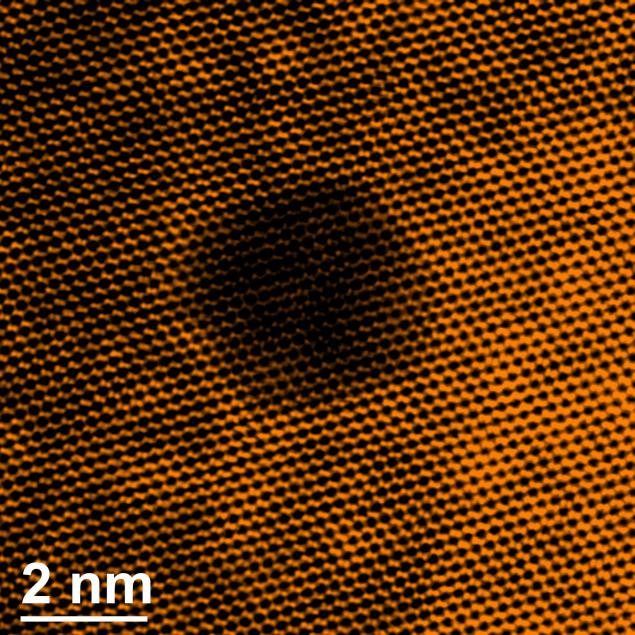
Scientists in the laboratory SuperSTEM develop your project with molybdenum disulfide. This is another 2D material such as graphene. It is used as an industrial catalyst, e.g., to remove sulfur from fossil fuels. Danish chemical company Haldor Topsoe uses electron microscopes to study how rearranging atoms molybdenum disulfide, can affect its catalytic properties.
Super microscope and demand in nanomedicine. With it, you can check how reliable the drug molecule is attached to the nanoparticle serving as the transport of drugs.
And yet, it can be considered the crystal structure of the particles of meteoric dust. While all this is still just a good foundation for the future.

Source: geektimes.ru/post/247452/

As to the application of such a device, it is vast. Take, for starters, electrical engineering. All prefer compact portable devices. Our gadgets are getting smaller by the day. To create these necessary transistors, semiconductors, and so on. The details, but to create these miniature products must be able to manipulate materials at the atomic level. After all, if the structure, for example, graphene, a two-dimensional sheet of carbon atoms to add extra atom to change the material itself! Therefore, you need a special atomic control, preserving the integrity of the material.
Scientists in the laboratory SuperSTEM develop your project with molybdenum disulfide. This is another 2D material such as graphene. It is used as an industrial catalyst, e.g., to remove sulfur from fossil fuels. Danish chemical company Haldor Topsoe uses electron microscopes to study how rearranging atoms molybdenum disulfide, can affect its catalytic properties.
Super microscope and demand in nanomedicine. With it, you can check how reliable the drug molecule is attached to the nanoparticle serving as the transport of drugs.
And yet, it can be considered the crystal structure of the particles of meteoric dust. While all this is still just a good foundation for the future.



Source: geektimes.ru/post/247452/
Compact and agile robotic arm helps to make copies of itself
Acoustic Detection System shots earned in New York in test mode