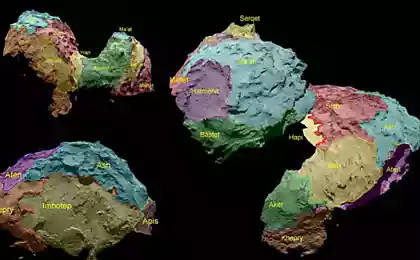
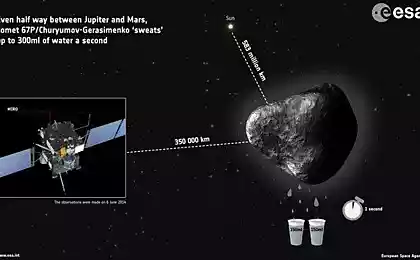
1590
Philae: detail of scientific equipment and the results to date
Now, when the probe Philae sleeping for the third day, it's time to draw a line under the performance of scientific researches.

Philae probe is equipped with ten scientific system with a total mass 26, 7 kg. Their main difference from the usual ground equipment - less weight, compactness, autonomy and no need for maintenance. Work carried out on miniaturization really titanic: since the establishment of the unit has been more than ten years, but there are still many devices Philae easier their earthly counterparts almost an order of magnitude, as things are, and with power. In addition, stringent requirements for operating temperatures - the equipment is functioning nominally probe in the range from -130 to +50 ° C.
The preliminary results of scientific work in a nutshell - a dizzying success! Aside from problems with the landing (or rather, fixation) lander, all systems worked perfectly. Despite the problems with energy, the probe had somehow perform all primary scientific objectives.
Under the cut - a detailed description of the equipment Philae, the results obtained, a lot of pictures, a few words about the problems and even real telemetry data. (Beware of traffic!)
All research Philae system can be divided into four groups:
Information about the results of SESAME until released.
Equipment for research across the core
CONSERT (Comet Nucleus Sounding Experiment by Radiowave Transmission) - radar for imaging the comet's nucleus. The experiment is to measure the delay and attenuation of electromagnetic waves on the way from the space station and back to Philae.
The study was carried out successfully, despite the nearly exhausted by the time the battery, but it is clear that a small duration of the measurement is not allowed to make the tomogram fully and accurately - the orbiter physically did not have time to do the required number of turns. A side effect of the experiment is to determine the location of the probe - maybe it will help him find the photographs with Rosetta.
ROMAP (Rosetta Lander Magnetometer and Plasma Monitor) - magnetometer and plasma detector for the study of the magnetic field of the nucleus of the comet and its interaction with the solar wind. Also allowed to monitor the process of landing.
So far only published data on the landing.
Use ROMAP precise time machine bounces
That (so far) failed to make
Shoot harpoons. The only really serious problem of the mission. The reason seems to use the nitrocellulose in the squib, which, according to recent studies, in vacuo unreliable. Problem hurtful as to replace part of something else you could without problems. The remaining shortcomings - hops investigation caused a lack of energy. Failed to analyze the core material with the help of Ptolemy - to drill a second time had neither the time nor the inclination (unattached probe could easily fly away somewhere). Do not have time to properly educate the core of the radar. Failed to enter the nucleus PEN - the surface was much harder than expected. In general, there is no one's fault, MUPUS worked according to specifications. Run pinch engines also failed, but hardly a problem harpoons time not worked. Despite the problems with locking and power, the probe coped brilliantly with the vast majority of priorities. When I heard that it was not possible to fix the probe and he went into an unscheduled flight, I did not expect that everything will end so well. Ten most complex scientific devices, flying more than ten years, flown more than six billion kilometers - and all ten worked like a Swiss watch. I am sincerely happy for ESA - great job, it was a delightful пятьдесят seven o'clock.
I would like to end the article with a poem:

Philae probe is equipped with ten scientific system with a total mass 26, 7 kg. Their main difference from the usual ground equipment - less weight, compactness, autonomy and no need for maintenance. Work carried out on miniaturization really titanic: since the establishment of the unit has been more than ten years, but there are still many devices Philae easier their earthly counterparts almost an order of magnitude, as things are, and with power. In addition, stringent requirements for operating temperatures - the equipment is functioning nominally probe in the range from -130 to +50 ° C.
The preliminary results of scientific work in a nutshell - a dizzying success! Aside from problems with the landing (or rather, fixation) lander, all systems worked perfectly. Despite the problems with energy, the probe had somehow perform all primary scientific objectives.
Under the cut - a detailed description of the equipment Philae, the results obtained, a lot of pictures, a few words about the problems and even real telemetry data. (Beware of traffic!)
All research Philae system can be divided into four groups:
- Observation equipment in the visible and infrared ranges - CIVA, ROLIS.
- The devices are being introduced into the kernel - SD2, MUPUS
- Devices for surface analysis or selected samples - COSAC, Ptolemy, AXPS, SESAME
- The equipment for research across the core - CONSERT, ROMAP.
Layout devices
Instruments for observation in the visible and infrared ranges

CIVA (Comet IR & Visible Analyser) - a system of seven cameras resolution of 1 megapixel each and IR spectrometer. Six cameras allow to get a full 360 ° panoramic image, the seventh and enables stereofotosemku.
IR spectrometer is used to analyze the samples withdrawn through SD2. Operating wavelength range - 1-4 micron spatial resolution - 40 microns.
Pictures CIVA have probably all seen, and that if there were withdrawn IR spectra, not yet reported. It depends on whether you are a high-temperature pyrolysis of the sample (see Section on SD2).
The total mass of CIVA - 4 kg.
Layout cameras on the machine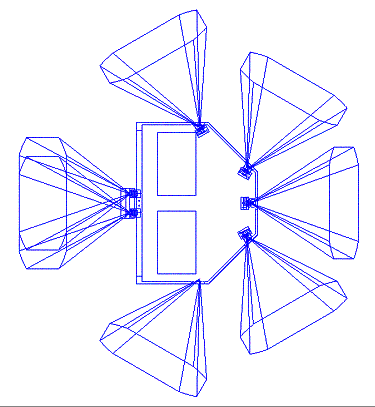

ROLIS ( Ro setta L ander I maging S ystem) - camera installed Bottom lander. Designed for shooting during planting and after it. Allows you to clean the drill SD2 to the right place. Resolution - 1 megapixel, field of view 75/50 ° (switches; after landing permission is obtained 0, 3 mm / pixels to) the camera in black and white, but is equipped with red, green, blue and IR LED illumination that produces color images. Minimum operating temperature - minus 150 ° C. Supports compression, the compression ratio can be different for different portions of the picture (Region-of-Interest coding). Weight of the device - 0, 4 kg.
The camera worked flawlessly. After landing, the camera photographed three different places, although it is not clear what - after landing, after the first "flight" and after the second or immediately after planting, after the second "flight" and then swing.
Incoming! B>
Devices are being introduced into the core
SD2 h4> SD2 - a tool for drilling, soil sampling and distribution. The length of the drill - 581, 6 mm diameter - 12 mm, the maximum drilling depth - 230 mm. Boer is made of aluminum alloy with diamond-coated, maximum tensile strength of rock - 50 MPa. Operating voltage - 28V
The device makes a hole in the ground a predetermined depth, selects a portion of the volume of rock 10-40 mm² with its bottom and placed in a heating cell (oven). Drilling is carried out through a hole in the bottom of the unit, the place can be selected using the camera ROLIS. The probe 26 has compartments for heating samples, sixteen of them maintain the temperature to 800 ° C (pyrolysis test), the remaining 10 - 180 ° C (for vaporization / mild decomposition). When heated in the latter it is possible to hold the IR spectrometry apparatus using CIVA due to the presence in them of transparent sapphire prism.
There is a risk that the unit will come off from the comet during drilling, but it was decided to hold it, because without excavation to a depth of scientific problems can not be considered as resolved. Drilling was made the day 14.11 and took two hours. Boer was lowered to a maximum depth and seems to have successfully taken samples of soil.
Was selected because only one sample, it was necessary to decide whether to send it for analysis to the device COSAC or Ptolemy. Mission team opted COSAC - mainly because the information from it better complements the data obtained using the tools orbital station (determination of inorganic compounds from orbit to carry out easier than organic). Ptolemy also had to settle for the analysis of dust, which is also very good.
The sample was treated with heat (temperature not yet specified) and sent for analysis. Seizure, handling, transport and analysis took place in normal mode, the problems have not been reported. Did get a micrograph of the sample and IR spectra with a device CIVA, have not yet specified.
A diagram and photos of the device Nominated tube for selection of soil:
Arrows indicate cells for stoves:
Furnace with a sapphire prism:
Being tested:
Telemetry first in the history of drilling comet nucleus! Enters and exits ... ... goes great! B> On a scale of ordinates - departures drill in mm (in red). It's a pity that there are no data from the ammeter could be seen when the drill went into the ground.
MUPUS h4> MUPUS (MUlti-PUrpose Sensors for Surface and Sub-Surface Science) - sensors for measuring temperature and the mechanical properties of the comet's nucleus at a depth of 0-32 cm.
On the shaft that failed were installed accelerometers to determine the strength and hardness of the surface of the nucleus and the thermometer to determine the temperature of the soil.
On the probe - infrared camera MUPUS TM for remote determination of the surface temperature of the core. (Sorry, could not find details on this device.)
By five-foot mechanical arm moves penetrator, scored in the nucleus of a comet mechanical hammer. The maximum penetration depth - 32 cm. Penetrator equipped with a thermometer and a thermal conductivity detector, allows you to build profiles of the respective kernel with the deepening of the device, and the speed of clogging can be seen on the hardness of the soil. Removing the probe is not provided (only in a natural way in the process of erosion of the comet's nucleus).
Drive a probe into the hard ground in space - not an easy task. A classic solution is to squib, but it does not allow to explore the ground layers in the process of hammering. The device is used MUPUS tridtsatigrammovy goods accelerated by a magnetic field up to 8 m / s. After impact, the spring, which is suspended from the load returns to its initial position.
A diagram and photos of the device
Results
IR Camera TM showed "very cold vertical wall before the probe." Analyzed daily fluctuations in temperature - the surface of the core heats up quickly in direct sunlight and cools quickly when they are not. Sensors located in the shadow of the probe harpoons also record daily fluctuations in temperature.
When vydviganii device temperature dropped penetrator and some changes were seen in the other instruments - apparently, with the Philae slightly shifted and / or rod that is stuck. Because based on the readings from the infrared camera is waiting for a loose surface layer ("probably small grains of minerals or organic dusts such as tobacco ash"), the hammer was included in the minimum power mode, but it did not bring success. Even after switching to a third maximum design mode, the rod did not begin to enter the nucleus. The team decided to activate an undocumented fourth mode, which they called "desperate." Unfortunately, after seven minutes of unsuccessful attempts to hammer out of order. Thus, the tensile strength of the core surface is clearly greater than 2 MPa (for comparison, the tensile strength of ice - 0 7-3 MPa concrete - 2.5 MPa, granite - 5-20 MPa). Granules designed for 8-10 MPa, so that it is unknown if they entered into the ground if the shot. If included, their sensors would give us enough valuable information.
Was it true solution "to the last score"? If the probe is no longer wake up, then of course. If you wake up, will be a little disappointing - suddenly penetrator just got on some solid plot.
Devices for surface analysis or selected samples
COSAC - one of the main instruments of the probe, gas chromatography-mass spectrometer (GC with katarometricheskim and mass spectrometric detectors). The carrier gas chromatograph - helium. The apparatus allows the identification of various organic compounds such as amines, carboxylic acids, amino acids and others. Chromatograph equipped with eight columns and two separate detectors - katarometricheskim simple (non-selective device for detecting a change in conductivity material gas was chosen because it does not alter the sample in the research process) and time of flight mass spectrometer with electron impact ionization, which allows to determine the composition of matter flowing. All of the gas sent to the speaker of the katharometer and then part of the columns (as required) - the mass spectrometer.
Analysis was performed using COSAC immediately after drilling and machining. Modes of processing and analysis has not yet made public, but reports of problems have been reported.
Ptolemy - gas chromatograph with a mass spectrometer to determine the isotopic composition. Detector - quadrupole ion-cyclotron (ion trap). Unlike COSAC, is intended primarily to determine the lightest elements - hydrogen, carbon, nitrogen and oxygen, and the ratio of their isotopes.
Since the resulting SD2 soil sample was sent to the COSAC, Ptolemy analyzed only collected dust («concentrated sniff»).
Weight of the device - 5 kg (for comparison, commercially available mass spectrometers ion trap weigh from 60 kg to a hundred or more).
APXS (Alpha Proton X-Ray Spectrometer) - alpha proton X-ray spectrometer for determining the elemental composition of the surface of the nucleus. Consists of an alpha radiation source (curium-244) and alpha-particle detectors and X-ray radiation. Spectroscopy alpha-particles based on the phenomenon of Rutherford backscattering and allows to determine the carbon, nitrogen, oxygen. X-ray detector allows to determine the heavier elements - from sodium to zinc.
APXS - must-have for the lander: low weight (just 640 grams!), Low power consumption (1, 5 W, t. To. In fact, the experiment provides energy radioactive decay) and versatility make it almost indispensable. The only notable drawback - study duration is measured in hours.
Philae produced surface analysis using APXS on the third and last landing site. Information on how well, not yet.
Driving device
SESAME (Surface Electric Sounding and Acoustic Monitoring Experiments) - 3 instrument for measuring the properties of the outer layers of the comet:
- CASSE (Cometary Acoustic Sounding Surface Experiment) - an experiment to study the acoustic surface of a comet,
Information about the results of SESAME until released.
Equipment for research across the core
CONSERT (Comet Nucleus Sounding Experiment by Radiowave Transmission) - radar for imaging the comet's nucleus. The experiment is to measure the delay and attenuation of electromagnetic waves on the way from the space station and back to Philae.
The study was carried out successfully, despite the nearly exhausted by the time the battery, but it is clear that a small duration of the measurement is not allowed to make the tomogram fully and accurately - the orbiter physically did not have time to do the required number of turns. A side effect of the experiment is to determine the location of the probe - maybe it will help him find the photographs with Rosetta.
ROMAP (Rosetta Lander Magnetometer and Plasma Monitor) - magnetometer and plasma detector for the study of the magnetic field of the nucleus of the comet and its interaction with the solar wind. Also allowed to monitor the process of landing.
So far only published data on the landing.
Use ROMAP precise time machine bounces
That (so far) failed to make
Shoot harpoons. The only really serious problem of the mission. The reason seems to use the nitrocellulose in the squib, which, according to recent studies, in vacuo unreliable. Problem hurtful as to replace part of something else you could without problems. The remaining shortcomings - hops investigation caused a lack of energy. Failed to analyze the core material with the help of Ptolemy - to drill a second time had neither the time nor the inclination (unattached probe could easily fly away somewhere). Do not have time to properly educate the core of the radar. Failed to enter the nucleus PEN - the surface was much harder than expected. In general, there is no one's fault, MUPUS worked according to specifications. Run pinch engines also failed, but hardly a problem harpoons time not worked. Despite the problems with locking and power, the probe coped brilliantly with the vast majority of priorities. When I heard that it was not possible to fix the probe and he went into an unscheduled flight, I did not expect that everything will end so well. Ten most complex scientific devices, flying more than ten years, flown more than six billion kilometers - and all ten worked like a Swiss watch. I am sincerely happy for ESA - great job, it was a delightful пятьдесят seven o'clock.
I would like to end the article with a poem:
Now Philae down to sleep
We pray a sunbeam soon to sweep
And if the hibernation break
We have more science yet to make- Exclamation Snark (BadPhysics) November 14, 2014 blockquote>
Source: geektimes.ru/post/241522/