1240
Rosetta - 2 days before the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko
After 10 years, the spacecraft Rosetta at the finish line and is going to do something that no one previously could not - get into orbit of the comet. On Wednesday, August 6, it is expected that Rosetta will orbit the comet, completing its journey in 6, 4 billion miles.
About Rosetta mission already wrote Habré, I'll try to post the data supplement. After two canceled attempts (engine failure), the unit Rosetta was launched from Kourou (French Guiana) March 2, 2004 with the help of the carrier rocket Ariane-5G +.
Using the gravitational field of the Earth and Mars, the machine must be able to set the speed, and then headed for the Rosetta comet, having on the way to make a lot of beautiful pictures . Rosetta then loaded into hibernation, and successfully "wake up" in January 2014. At the same time it was the largest spacecraft hibernation period - 957 days.
At a distance of 350 km of Rosetta recorded the evaporation of water in the amount of 300ml per second and is at a distance of 583 million kilometers from the Sun, with the approach to the Sun, the figure begins to increase sharply.
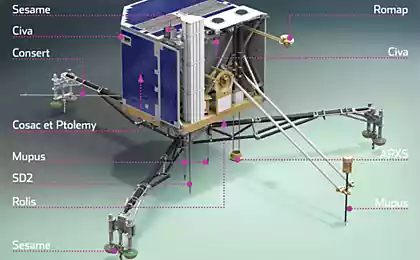
On board Rosetta is 11 scientific instruments (on the name of each is a link to the specification to angl.yaz not consider for advertising, just pdf it easier to back):
ALICE . Ultraviolet Spectrometer - defines the characteristics of the comet's nucleus and coma. Analyzes the gases in the coma and tail, measures the rate of discharge of water and oxide / carbon dioxide.
CONSERT (Comet Nucleus Sounding Experiment by Radio wave Transmission) - studies the internal structure of the comet with the Philae lander .
COSIMA (Cometary Secondary Ion Mass Analyser) - examines the composition of the dust in the coma of the comet. Makes test for organics.
GIADA (Grain Impact Analyser and Dust Accumulator) - measures the amount of mass, momentum and velocity of the dust particles in Environment comet.
MIDAS (Micro-Imaging Dust Analysis System) - is studying dust in the environment of the comet.
MIRO (Microwave Instrument for the Rosetta Orbiter) - explores the nature of the comet's nucleus, the nucleus of the degassing and Development coma. Determines the temperature of the nucleus.
OSIRIS (Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System Camera) - dual photo devices consisting of cameras narrow and wide viewing angles, which operates in the visible, infrared and ultraviolet ranges.
ROSINA (Rosetta Orbiter Spectrometer for Ion and Neutral Analysis) - is responsible for determining the composition of the comet's atmosphere and ionosphere , temperature, density and velocity of gas flow. Consists of 2 spectrometers and sensors: DFMS (Double-focusing mass spectrometer), RTOF (Reflectron Time-Of-Flight mass spectrometer) and COPS (Comet Pressure Sensor).
RPC (Rosetta Plasma Consortium) - studies the plasma environment of the comet. Consists of ICA (Ion Composition Analyser), IES (Ion and Electron Sensor), LAP (Langmuir Probe), MAG (Fluxgate Magnetometer), MIP (Mutual Impedance Probe), PIU (Plasma Interface Unit).
RSI (Radio Science Investigation) - examines the mass, density and gravity of the nucleus of the comet, the definition of the orbit of a comet. The study of the solar corona on the way to the target comet.
VIRTIS (Visible and Infrared Thermal Imaging Spectrometer) - examines the nature of the comet's nucleus and the gases in the coma. Maps and explores the nature of hardwood, determines the temperature on the surface of the nucleus. Also determines the comet gases, characterizes the physical conditions in the coma, and helps determine the best landing sites.
Since May 2014 the machine slows down. By successive complex maneuvers he should go into orbit of the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, moving at 1m / s faster. Comet currently traveling at 55'000km / hour.
In November 2014 the unit must be reset Philae, which will research the soil and the environment on a comet.
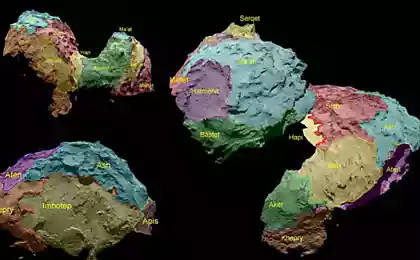
In the period from 13 th to July 21 with the help of Rosetta VIRTIS measured temperature on the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, and it amounted to -70 ° C, which was 20-30 degrees higher than expected. August 3rd was published the latest pictures of the comet from a distance of 300km:
Above 3D-visualization in ESA tried their best, very cool happened, cluck and look all the way Rosetta. And subscribe to twitter Rosetta (which, incidentally, funny in the first person), there will soon be followed by a lot of interesting news.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/232221/
About Rosetta mission already wrote Habré, I'll try to post the data supplement. After two canceled attempts (engine failure), the unit Rosetta was launched from Kourou (French Guiana) March 2, 2004 with the help of the carrier rocket Ariane-5G +.
Using the gravitational field of the Earth and Mars, the machine must be able to set the speed, and then headed for the Rosetta comet, having on the way to make a lot of beautiful pictures . Rosetta then loaded into hibernation, and successfully "wake up" in January 2014. At the same time it was the largest spacecraft hibernation period - 957 days.
At a distance of 350 km of Rosetta recorded the evaporation of water in the amount of 300ml per second and is at a distance of 583 million kilometers from the Sun, with the approach to the Sun, the figure begins to increase sharply.
On board Rosetta is 11 scientific instruments (on the name of each is a link to the specification to angl.yaz not consider for advertising, just pdf it easier to back):
ALICE . Ultraviolet Spectrometer - defines the characteristics of the comet's nucleus and coma. Analyzes the gases in the coma and tail, measures the rate of discharge of water and oxide / carbon dioxide.
CONSERT (Comet Nucleus Sounding Experiment by Radio wave Transmission) - studies the internal structure of the comet with the Philae lander .
COSIMA (Cometary Secondary Ion Mass Analyser) - examines the composition of the dust in the coma of the comet. Makes test for organics.
GIADA (Grain Impact Analyser and Dust Accumulator) - measures the amount of mass, momentum and velocity of the dust particles in Environment comet.
MIDAS (Micro-Imaging Dust Analysis System) - is studying dust in the environment of the comet.
MIRO (Microwave Instrument for the Rosetta Orbiter) - explores the nature of the comet's nucleus, the nucleus of the degassing and Development coma. Determines the temperature of the nucleus.
OSIRIS (Optical, Spectroscopic, and Infrared Remote Imaging System Camera) - dual photo devices consisting of cameras narrow and wide viewing angles, which operates in the visible, infrared and ultraviolet ranges.
ROSINA (Rosetta Orbiter Spectrometer for Ion and Neutral Analysis) - is responsible for determining the composition of the comet's atmosphere and ionosphere , temperature, density and velocity of gas flow. Consists of 2 spectrometers and sensors: DFMS (Double-focusing mass spectrometer), RTOF (Reflectron Time-Of-Flight mass spectrometer) and COPS (Comet Pressure Sensor).
RPC (Rosetta Plasma Consortium) - studies the plasma environment of the comet. Consists of ICA (Ion Composition Analyser), IES (Ion and Electron Sensor), LAP (Langmuir Probe), MAG (Fluxgate Magnetometer), MIP (Mutual Impedance Probe), PIU (Plasma Interface Unit).
RSI (Radio Science Investigation) - examines the mass, density and gravity of the nucleus of the comet, the definition of the orbit of a comet. The study of the solar corona on the way to the target comet.
VIRTIS (Visible and Infrared Thermal Imaging Spectrometer) - examines the nature of the comet's nucleus and the gases in the coma. Maps and explores the nature of hardwood, determines the temperature on the surface of the nucleus. Also determines the comet gases, characterizes the physical conditions in the coma, and helps determine the best landing sites.
Since May 2014 the machine slows down. By successive complex maneuvers he should go into orbit of the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, moving at 1m / s faster. Comet currently traveling at 55'000km / hour.
In November 2014 the unit must be reset Philae, which will research the soil and the environment on a comet.
In the period from 13 th to July 21 with the help of Rosetta VIRTIS measured temperature on the comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko, and it amounted to -70 ° C, which was 20-30 degrees higher than expected. August 3rd was published the latest pictures of the comet from a distance of 300km:
Above 3D-visualization in ESA tried their best, very cool happened, cluck and look all the way Rosetta. And subscribe to twitter Rosetta (which, incidentally, funny in the first person), there will soon be followed by a lot of interesting news.
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/232221/
Carrier rocket Falcon 9 successfully launched commercial satellite
Sony will no longer offer e-books. End of another era