1640
Planting probe Philae / Rosetta: what will happen when landing a probe on a comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko?

November 11, the date of the landing of a probe on the surface of Philae comet Churyumov-Gerasimenko ( landing pad J ) closer. But how will the landing, and that will make the probe during the various stages of its mission?
Recently, the European Space Agency ESA has announced a detailed plan that I think will be of interest to many. Incidentally, in the continuation and video model of landing a probe on a comet.
So, the researchers divided the core mission of the probe into three stages: separation from Rosetta, the approach to the comet, landing on the surface of the comet. Philae is equipped with a number of scientific instruments, and during all these stages include the following tasks.
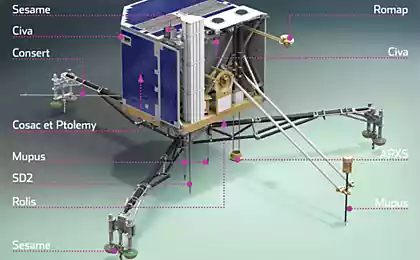
Separation from the parent plant and the approach to the comet:
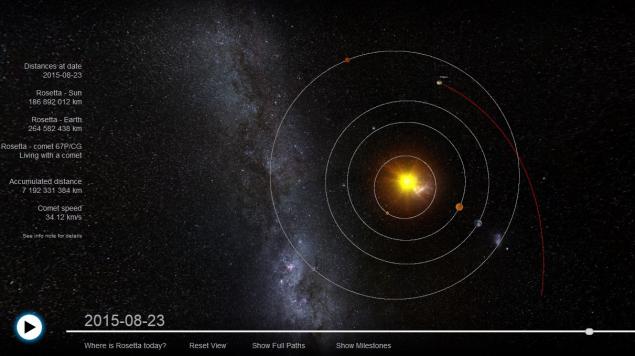
- CIVA make "farewell" photo station Rosetta (by the way, August 23, 2015 Rosetta will pass by Earth at a minimum distance - 264 million kilometers, track path here ).
- ROLIS will take photos during descent;
- COSAC and PTOLEMY will select a sample of" atmosphere "of the comet, during landing; < /
- ROMAP measure the level of the solar wind interaction with the substance of the comet, "Plasma»;
- SESAME / DIM and SESAME / PP conduct additional measurements, dust and plasma;
- CONSERT together with other tools, measure the vertical velocity, and explore the upper layers of the cometary nucleus.
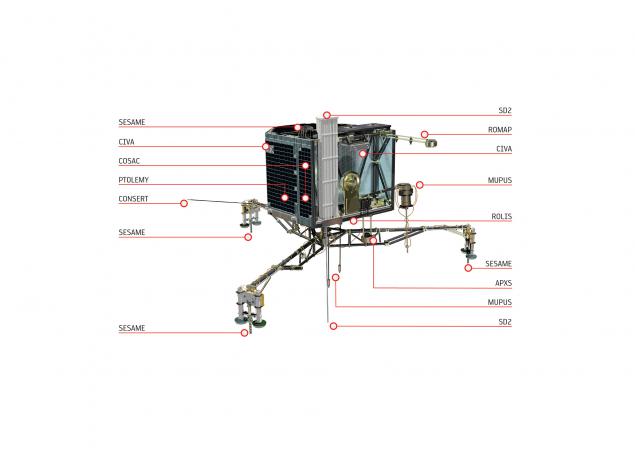
Planting:
- CIVA a panoramic picture the place of landing, the picture will evaluate the landing module;
- MUPUS measure inhibition of harpoons, which are used to attach the probe to the surface of the comet;
- SESAME / CASSE measure the physical parameters of the surface.
Branch, descent and landing will take about 10-11 hours. During this process will depend upon the particular landing pad and, accordingly, the trajectory of the probe.
In case of a successful landing and perform the first three tasks already on the comet, Philae will begin work on the next steps, which will take about 54 hours. The task - to perform all of the most important scientific work, then you can begin to perform tasks that can be called less important (although, to study the comet all tasks are extremely important to science).
- ROLIS make pictures of the surface with micron resolution;
- ROMAP measure the properties of the magnetic field and plasma;
- MUPUS measure the physical parameters of the surface and the temperature of the surface layers in the landing zone;
- CONSERT will select a sample of the substance of the nucleus of the comet.
Simultaneously, the probe will examine its own location and orientation in space, to find the optimum position in which the solar panels will receive the maximum amount of solar energy.
The next stage of research - the study of the subsurface layers of the comet, with drilling conducted tool SD2. COSAC and PTOLEMY during drilling will assess the level of concentration of gaseous substances. SD2 will drill twice during this phase, the selected samples are heated in an oven, to release the related chemical compounds without heating will be in a solid state.
When analyzing the first sample to be measured the concentration of carbon, oxygen, hydrogen and nitrogen, with determination of the content of isotopes. The second specimen is used to determine the presence and concentration of chemical compounds. The study of dust in the ambient environment probe will be conducted by means of SESAME.
Among other things, will be studied and the surface of the comet. "Hammer» MUPUS immerse themselves into the ground to measure the temperature of various surface layers. Acoustic signals and vibration of the hammer will be analyzed acoustic sensors, and the data will serve to clarify the properties of the deeper layers of the comet's nucleus. APXS will study the elemental composition of the surface material of the comet. With the help of SESAME / DIM scientists can study the effect of the dust particles, and the SESAME / PP will get data on the dielectric properties of the soil, which in turn will enable to understand whether frozen water / ice under the surface of the comet.
A little later, SD2 drill again the comet's surface, to obtain samples that will be photographed CIVA-M with a large increase in the visible and infrared spectra. These samples will be studied tool COSAC.
Scientists probe Philae operations will be performed on approximately March 2015. Thereafter, the core temperature of the comet will rise to a level where the operation of the probe would be impossible, and the mission duration of ten years gets its logical conclusion.
Via esa
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/237239/
Municipality of Turin goes on Linux - five years is planned savings of € 6 million
Social network "for the rich"