2705
Interesting about the stars.
1. What is the closest star to the earth? This sun. It is located just 150 million. Km from the Earth, and space standards is an average star. Classified as a yellow dwarf main sequence G2. It converts hydrogen into helium has been 4, 5 billion years, and will probably continue to do so for another 7 billion years. When the sun runs out of fuel, it will become a red giant star, the size of the star will increase many times over. When it expands, it will swallow Mercury, Venus, Earth, and possibly even.
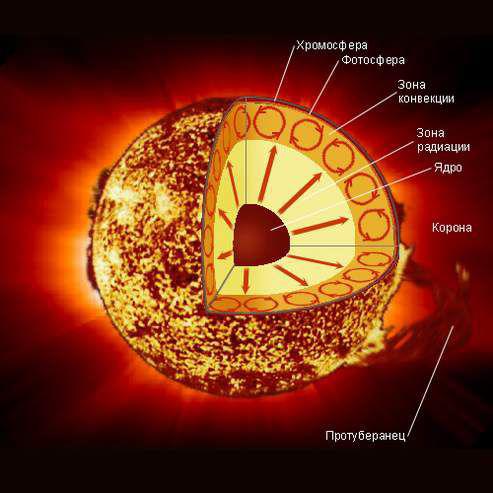
2. All the stars have the same composition. A star is born begins in the cloud of cold molecular hydrogen, which begins to gravitationally contract. When the cloud of molecular hydrogen is compressed fragmented, then the set of these parts will form a separate stars. The material is collected in a ball that continues to contract under its own gravity, until the center reaches the temperature capable of igniting nuclear fusion. The feed gas was formed back in the Big Bang and is composed of 74% hydrogen and 25% helium. Over time, it converts part of the hydrogen in helium. That's why part of our Sun 70% hydrogen and 29% helium. But initially they consist of 3/4 hydrogen and 1/4 helium doped with other micronutrients.
3. The stars are in perfect balance. Any star as it is in constant conflict with itself. On the one hand, the whole mass of the star by gravity squeezes her constantly. But the red-hot gas, has a lot of pressure from within, breaking its gravitational collapse. Fusion kernel generates a huge amount of energy. Photons before get out, make a journey from the center to the surface, about 100,000 years. When the star becomes brighter, it expands and becomes a red giant. When nuclear fusion stops in the center, then nothing can hold back the growing pressure of the overlying layers and turning it collapses into a white dwarf, neutron star or black hole. It is possible that the stars in the sky that we see, is no longer there, because they are very far away and their light takes billions of years to reach the earth.
4. Most of the stars are red dwarfs. Comparing all the known stars, it can be argued that the most red dwarfs. They have less than 50% of the mass of the Sun and red dwarfs can weigh even 7, 5%. Below this weight, gravitational pressure will compress the gas in the center to start nuclear fusion. They are called brown dwarfs. Red dwarfs emit less than 1/10, 000 solar energy, and can burn tens of billions of years.
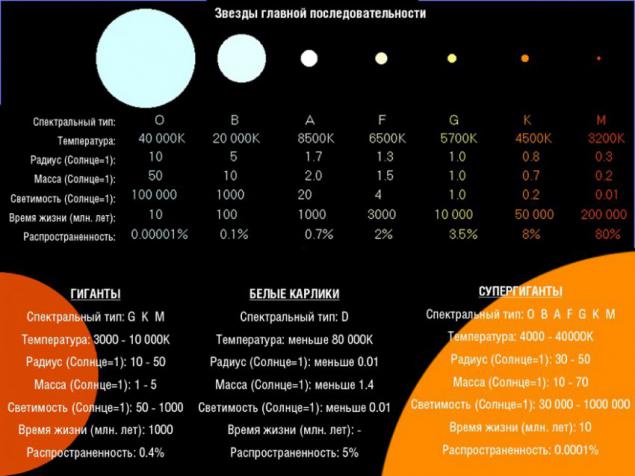
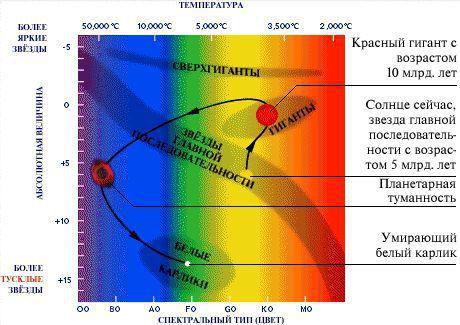
5. The mass equal to its temperature and color. Stars color can vary from red to white or blue. The red color corresponds to the coldest temperatures are less than 3500 degrees Kelvin. Our light is yellowish-white, with an average temperature of about 6000 Kelvin. Hottest - blue, with surface temperatures above 12,000 degrees Kelvin. Thus, the color temperature and interconnected. Weight determines the temperature. The greater the mass, the greater will be the nucleus and the more active nuclear fusion will occur. This means that more energy reaches the surface and raises its temperature. But there is an exception, it is red giants. A typical red giant may have a mass of our sun, and be white star on lifelong learning. But as we approach the end of his life, and it increases the luminosity increases in 1000 and seems unnaturally bright. Big Blue - it's just a big, massive and hot light.

6. Most of the stars are double. Many stars are born in pairs. This double star, where two luminaries orbiting around their common center of gravity. There are other systems with 3, 4 or even more participants. Just think how beautiful sunrises can be seen on the planet in four-star system.
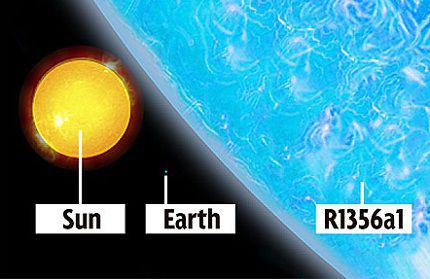
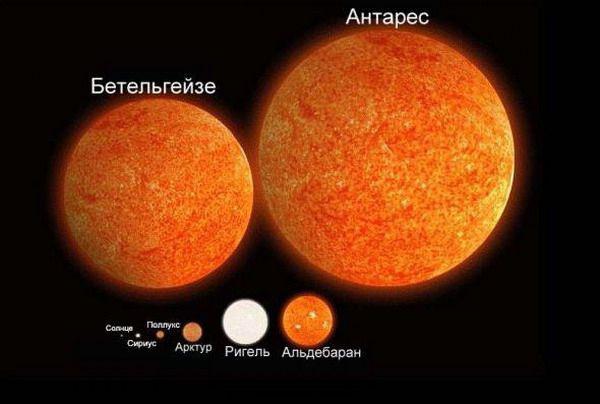
7. The size of the biggest suns, is orbiting Saturn. Let's talk about red giants, or to be more precise, a red supergiant, against which our star looks quite small. Betelgeuse is a red supergiant in the constellation of Orion. It is 20 times the mass of the sun and still 1000 times greater. The largest known star is VY Canis Majoris. It is 1800 times larger than our Sun and would fit into the orbit of Saturn!
However, our time is the biggest star in the universe has already lost more than half its mass. That is, the star is aging and its fuel from hydrogen is running out. The outer part VY become more due to the fact that gravity can not prevent weight loss. Scientists say that when the fuel runs out the star, it is likely to explode supernova and become a neutron star or a black hole. According to observations, the star loses its brightness, since 1850.
Nowadays, the study of the universe, scientists do not leave for a minute. Therefore, this record was broken. Astronomers have found in the vastness of space is still a big star. The discovery of a group of British scientists made, led by Paul Crowther in late summer 2010. The researchers studied the Large Magellanic Cloud and found star R136a1. Incredible discovery helped make NASA space telescope "Hubble».

8. In the most massive stars are very short life. As mentioned above, low mass red dwarf star may be enough for tens of billions of years of burning before, run out of fuel. The opposite is true, for the most massive that we know. Giant luminaries can 150 times the mass of the Sun and to allocate huge amounts of energy. For example, one of the most massive stars, which we know is Eta Carinae, located approximately 8,000 light years from Earth. It allocates 4 million times more energy than the sun. At that time, like our Sun can easily burn fuel for billions of years, Eta Carinae, can shine only a few million years. And astronomers expect that Eta Carinae may explode at any time. When she goes out, it will be the brightest object in the sky.
9. The number of stars is overwhelming. How many stars are in the Milky Way? You may be surprised to learn that there are about 200-400 billion pieces in our galaxy. Each may have planets, and some, life is possible. In the universe of about 500 billion galaxies, each of which can have as much or even more than the Milky Way. Multiply these two numbers together, and you'll see how many of them there are about.

10. They are very, very far away. The closest to the Earth (other than the Sun) is Proxima Centauri, is located in 4, 2 light-years from Earth. In other words, it takes the light itself more than 4 years to complete the journey from Earth. If we run the fastest spacecraft ever previously launched from Earth, he will fly to her more than 70,000 years. To date, travel between the stars is simply not possible.
--img9--

2. All the stars have the same composition. A star is born begins in the cloud of cold molecular hydrogen, which begins to gravitationally contract. When the cloud of molecular hydrogen is compressed fragmented, then the set of these parts will form a separate stars. The material is collected in a ball that continues to contract under its own gravity, until the center reaches the temperature capable of igniting nuclear fusion. The feed gas was formed back in the Big Bang and is composed of 74% hydrogen and 25% helium. Over time, it converts part of the hydrogen in helium. That's why part of our Sun 70% hydrogen and 29% helium. But initially they consist of 3/4 hydrogen and 1/4 helium doped with other micronutrients.

3. The stars are in perfect balance. Any star as it is in constant conflict with itself. On the one hand, the whole mass of the star by gravity squeezes her constantly. But the red-hot gas, has a lot of pressure from within, breaking its gravitational collapse. Fusion kernel generates a huge amount of energy. Photons before get out, make a journey from the center to the surface, about 100,000 years. When the star becomes brighter, it expands and becomes a red giant. When nuclear fusion stops in the center, then nothing can hold back the growing pressure of the overlying layers and turning it collapses into a white dwarf, neutron star or black hole. It is possible that the stars in the sky that we see, is no longer there, because they are very far away and their light takes billions of years to reach the earth.

4. Most of the stars are red dwarfs. Comparing all the known stars, it can be argued that the most red dwarfs. They have less than 50% of the mass of the Sun and red dwarfs can weigh even 7, 5%. Below this weight, gravitational pressure will compress the gas in the center to start nuclear fusion. They are called brown dwarfs. Red dwarfs emit less than 1/10, 000 solar energy, and can burn tens of billions of years.

5. The mass equal to its temperature and color. Stars color can vary from red to white or blue. The red color corresponds to the coldest temperatures are less than 3500 degrees Kelvin. Our light is yellowish-white, with an average temperature of about 6000 Kelvin. Hottest - blue, with surface temperatures above 12,000 degrees Kelvin. Thus, the color temperature and interconnected. Weight determines the temperature. The greater the mass, the greater will be the nucleus and the more active nuclear fusion will occur. This means that more energy reaches the surface and raises its temperature. But there is an exception, it is red giants. A typical red giant may have a mass of our sun, and be white star on lifelong learning. But as we approach the end of his life, and it increases the luminosity increases in 1000 and seems unnaturally bright. Big Blue - it's just a big, massive and hot light.

6. Most of the stars are double. Many stars are born in pairs. This double star, where two luminaries orbiting around their common center of gravity. There are other systems with 3, 4 or even more participants. Just think how beautiful sunrises can be seen on the planet in four-star system.

7. The size of the biggest suns, is orbiting Saturn. Let's talk about red giants, or to be more precise, a red supergiant, against which our star looks quite small. Betelgeuse is a red supergiant in the constellation of Orion. It is 20 times the mass of the sun and still 1000 times greater. The largest known star is VY Canis Majoris. It is 1800 times larger than our Sun and would fit into the orbit of Saturn!
However, our time is the biggest star in the universe has already lost more than half its mass. That is, the star is aging and its fuel from hydrogen is running out. The outer part VY become more due to the fact that gravity can not prevent weight loss. Scientists say that when the fuel runs out the star, it is likely to explode supernova and become a neutron star or a black hole. According to observations, the star loses its brightness, since 1850.
Nowadays, the study of the universe, scientists do not leave for a minute. Therefore, this record was broken. Astronomers have found in the vastness of space is still a big star. The discovery of a group of British scientists made, led by Paul Crowther in late summer 2010. The researchers studied the Large Magellanic Cloud and found star R136a1. Incredible discovery helped make NASA space telescope "Hubble».

8. In the most massive stars are very short life. As mentioned above, low mass red dwarf star may be enough for tens of billions of years of burning before, run out of fuel. The opposite is true, for the most massive that we know. Giant luminaries can 150 times the mass of the Sun and to allocate huge amounts of energy. For example, one of the most massive stars, which we know is Eta Carinae, located approximately 8,000 light years from Earth. It allocates 4 million times more energy than the sun. At that time, like our Sun can easily burn fuel for billions of years, Eta Carinae, can shine only a few million years. And astronomers expect that Eta Carinae may explode at any time. When she goes out, it will be the brightest object in the sky.
9. The number of stars is overwhelming. How many stars are in the Milky Way? You may be surprised to learn that there are about 200-400 billion pieces in our galaxy. Each may have planets, and some, life is possible. In the universe of about 500 billion galaxies, each of which can have as much or even more than the Milky Way. Multiply these two numbers together, and you'll see how many of them there are about.

10. They are very, very far away. The closest to the Earth (other than the Sun) is Proxima Centauri, is located in 4, 2 light-years from Earth. In other words, it takes the light itself more than 4 years to complete the journey from Earth. If we run the fastest spacecraft ever previously launched from Earth, he will fly to her more than 70,000 years. To date, travel between the stars is simply not possible.
--img9--