1494
At Stanford created a new type of pacemaker with a wireless power supply
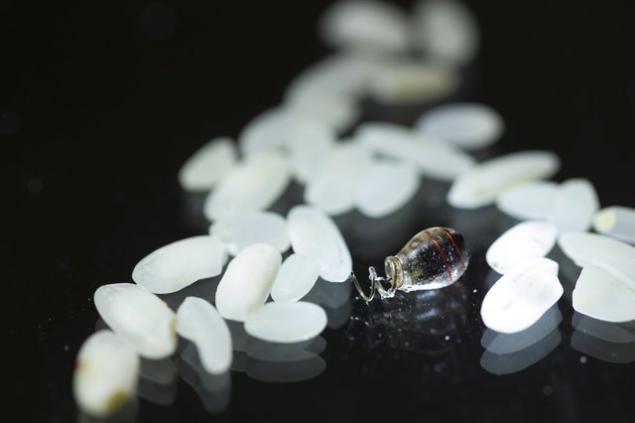
What you see in the picture - a miniature pacemaker, the size of a grain of rice. Power is transmitted to the chip "in the air", and such a device may be deep in the human body to recharge energy devices used electromagnetic waves of a certain type. The charging device has small dimensions comparable with the dimensions.
The author of a new method of wireless charging implanted chips and the chips stands Stanford team, led by Professor Ada Poon a >. The method was called "wireless transmission of the mean-field» (mid-field wireless transfer). The principle of wireless transmission of energy used in the case of changing the properties of electromagnetic waves when the wave passes through the various materials.
Poon notes that some medical devices, such as hearing aids, wireless power transmission using the "near field". But there is a condition - the transmission can be performed only on a very small distance in the body. In conventional devices, without being charged, used waves "far-field", which are not suitable for charging the chip inside the human body, such as waves or reflected or absorbed by the human body.
Well, charger Stanford team generates waves "mean-field", which are transmitted through the air, changing its characteristics in the human body, and reaching the "address" of the device. The system has already been successfully tested on a rabbit and pig.
The developers believe that their project will be very useful for creating miniature medical chips, pacemakers, various sensors and miniaturized systems injection drugs. All of this will work without the need to replace batteries or power wire that is used today.
Among other things, the miniature device can be used as a stimulant of the brain that affect the weak current to the various lobes of the brain. In this sense similar medical Soup may replace some kinds of therapy where medical uses. The device can act dot and medicine acts on the whole brain and the effectiveness of such exposure is lower than it could be.
The main thing - do not forget the source of electromagnetic radiation somewhere in the cafe, as a mobile phone, for example.
Via stanford
Source: habrahabr.ru/company/medgadgets/blog/223613/