711
Flying dvuhstvolka
What do you think, could this be the reality of the plane and fly?
Now we know more ...
9 photo.
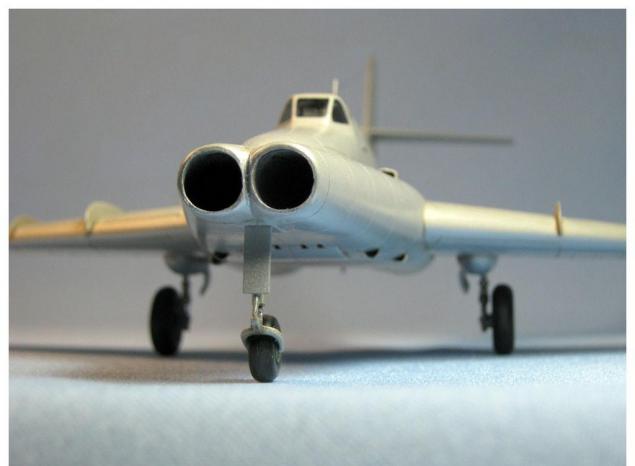

At the end of 1951 we developed a technical proposal for the creation of two-seat armored attack aircraft IL-40 with two engines AM-5F, with powerful artillery, missile and bomb armament. In preparing the materials were actively involved S.N.Chernikov, V.M.Germanov, N.P.Stolbovoy, V.M.Sheynin and other specialists. This proposal to the government in January 1952, very quickly examined, and on February 1 issued a decree of the Council of Ministers on the design and manufacture of prototype IL-40.
Under the scheme of IL-40 is a twin-engine nizkoplan with swept wings and tail surfaces (sweep angle anywhere along the line 0 35╟ 25 chords). The chassis was retractable, tricycle, with the nose wheel. The crew consisted of two people - a pilot and radio operator-gunner. The main part of the power structure of the aircraft was the hull of which bears the load of the engine is attached to it, the nose and tail of the fuselage, wings. It placed unsealed cockpit, six fuselage fuel tanks with total capacity of 4285 liters and units of the electrical and radio equipment. Performs hull of steel sheets with thickness from 3 to 8 mm (depending on the probable destruction of protected parts of the machine guns of ground troops or fighter planes).
To protect the pilot from the fire in the front cockpit was placed 10 mm bronestenka and 124 mm in a stationary windshield visor lamp. The side window visor had a thickness of 68 mm. From the fire from above and behind the pilot protected 8-mm armor plates on the sliding canopy and a 16-mm bronezagolovnik seat. The cabin also had a strong hand is armor-plated steel sheets with thickness of 4-10 mm. Installed in the cockpit ejection seat: the pilot catapulted back upwards at an angle of 16 degrees, and the arrow - up and down at an angle of 9 degrees. Canopy have two independent emergency opening system - air (acting on the shutter ejection seats) and electrical (triggered by pressing a button on the side of the cabin). On the creation of the fuselage structure, hulls, cockpit crew, setting ejection seats worked V.A.Borog, Yu.V.Komm, E.A.Shushpanov, M.K.Tsimbalyuk, A.A.Belov, A.S.Artamonov , G.V.Novozhilov, I.Ya.Katyrev.A.A. Shakhnovich, S.I.Dmitriev.
On the sides of the hulls between the spars of center, close to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft mounted engines AM-5F with afterburner, each of which had a takeoff thrust without afterburner 2150 kg, and with afterburner - 2700 kg. This arrangement simplifies the management of aircraft engines in the event of failure of one of them. Air intakes were in favor of a few leading edge of the wing and the air intake channels extend through the front spar of center. Through the rear spar were skipped engine exhaust. In these places, the front and rear spars of center have an annular shape. On the outer side and below the engine protected armor thickness of 4 mm. The development of the power plant of IL-40 was led by G.M.Litvinovicha. The total weight of the metal and transparent armor on the plane with the fixings was equal to 1918 kg.
The forward fuselage was attached to the front bronestenke hulls. It housed six cannons NR-23 23 mm design A.E.Nudelmana and A.A.Rihtera and nose landing gear in the retracted position and a piece of equipment. Guns were firing rate of 800 rounds per minute and sets of three on each side. The ends of their trunks were out of ammunition consisted of 900 rounds - 150 per gun.
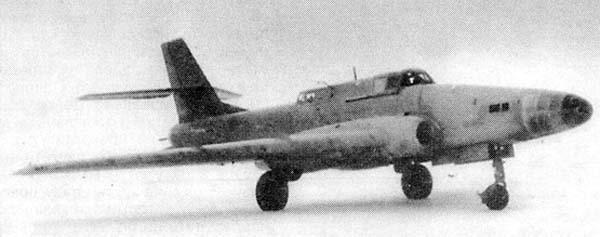
Aft fuselage is attached to the rear bronestenke hulls, carried vertical tail, at half height which establishes a fixed horizontal tail. Furthermore, aggregates are housed the special equipment of the aircraft. Along the sides and bottom of the tail part had three large brake plate with perforated surface, which could be opened in flight to an angle of 50 degrees. Side shields made traditionally - against the flow and the bottom had a feature - it opens the flow. Brake pads improved maneuverability characteristics of the aircraft over the battlefield, making it easier to attack ground targets with a dive.
Rounding out the aft fuselage aft movable gun mount Il-K10, remote-controlled from the cab arrow. It was designed to protect the rear hemisphere of the aircraft from enemy air attack and ground attack after attack aircraft from attack. Installation was a gun HP-23 with ammunition 200 rounds, which by means of electro-hydraulic servo drive could deviate by up 55╟, 40╟ 60╟ down and right and left. The maximum angular velocity of rotation arms were 42 deg. / S (horizontal) and 38 ° C / sec (vertical). The bow and stern gun installation created in the subdivision V.A.Fedorova. Technical documentation on the remote control aft installation let A.P.Zhuravlenko.
The trapezoid wing in terms of 52, 3 m2 was aerodynamic configuration of the profiles TsAGI: CP-10c-12 with relative thickness of 18, 44% at the root and CP 11-12 with a relative thickness of 12, 86% at the end. It consisted of a center section integrally connected to the hulls and two detachable parts. In the center section there was a tiltable landing flap, and detachable parts installed retractable flaps type TsAGI. The design of the wing and the landing mechanization was developed under the leadership of E.I.Sankova.
Most of the relative thickness of the wing has allowed not only to remove the main landing gear legs, but also to create there four small bomb bay - for internal suspension in each of bombs weighing up to 100 kg. In addition, under the center wing and detachable parts installed four of the beam, which could be suspended or two bombs weighing up to 500 kg, or jet gun type ODP with unguided missiles TPC 132 and TPC-82, or the external fuel tanks on holders under center total capacity of 1,100 liters. The normal bomb load of IL-40 in accordance with the government and TTT customer was 400 kg, and accelerated version plane could carry 1,000 kg of bombs. It was possible to establish by overloading jet guns with eight TRS-132 and twelve TRS-82. Over Bombings armament specialists worked under the direction of D.I.Koklina. The stabilizer and fin of the aircraft - two-spar, rudder had a weight balance and aerodynamic axial compensation and trimmers. Lead designer plumage was N.I.Maksimov.

Work on the creation of the IL-40 were a very fast pace. Here it affects both Ilyushin organizational skills and extensive experience and highly qualified design team. In just three and a half months after the publication of the decision of the government commission headed by Air Force combat pilot of attack aircraft, Major General Aviation A.D.Reyno acquainted with the layout of the IL-40 and gave positive feedback. In February 1953 we completed the construction of experimental aircraft IL-40. After a short airfield mining-board systems and equipment 7 March 1953 by test pilot VK Kokkinaki raised IL-40 into the air. With him in the test program was APVinogradov engineer who, during flight in the cockpit was a radio operator-gunner. Lead engineer for the factory flight tests of IL-40 was appointed A.I.Zhukovskogo. The first test flights were evaluated and received ╚dobro╩ pilot aircraft performance data of the aircraft, its characteristics of stability and controllability. At the end of March 1953 Kokkinaki flew to the landfill ╚Faustovo╩ test firing front gun mount on the ground targets.
An experienced pilot approached the polygon at an altitude of 5000 meters, the aircraft entered into a shallow dive, pulled the trigger and the guns ... immediately stopped to see the goal - to pull out of the trunks of guns flame blinded him. At the same time spontaneously sharply slowed down and then shut off the engine. Kokkinaki stopped shooting, was able to restart the engines (thanks to clearance) and returned to base. The incident was immediately reported Ilyushin, who ordered an urgent to develop a program of research unstable mode of the engine is fired from the gun mount the front of the aircraft IL-40. Then was released technical documentation for installation on the trunks of two types of muzzle guns, and eight types of different kinds of nozzles, removal of powder gases in the side of the air intakes.
Tests for this program began April 1, 1953 Lead engineer appointed an experienced specialist vooruzhentsa M.G.Ovchinnikova. Shooting at the shooting range with power (with simultaneous high-speed filming processes occurring on the muzzle of guns) and flight showed that the use of muzzle and tips does not give positive results - the engine resets momentum already at shooting only one gun burst in 5 - 10 shells . Research in this direction ceased. In addition, during the tests it revealed that in addition to the propellant gases erratic motor drives changes in pressure and temperature non-uniformity in the flow at the inlet of the air intakes.
We decided to replace the six cannons NR-23 with four more powerful and quick-firing gun TKB-495A, which at the same caliber (23 mm), the rate of fire was half times higher - 1300 rounds per minute. The weight TCB-495A compared to the weight of HP-23 increased by only 4 kg. Guns TKB-495A designed under the guidance and N.M.Afanaseva N.F.Makarova in the Tula Design Bureau. Later they were taken to the Soviet Air Force under the designation AM-23. IL-40, each gun had 225 rounds ammo. The power of fire four TKB-495A was the equivalent firepower of six HP-23. Gun TKB-495A equipped and aft gun mount plane.
For the front guns TKB-495A constructed the vapor chamber, which is simultaneously the bow of a stormtrooper. The camera was designed to tap into the external flow of gases from the fire. It is an isolated from the fuselage removable compartment, made of heat-resistant steel sheet, the bottom of which there was a hatch with two doors. Their discovery was blocked with fire control guns. When firing the powder gases have been through the hatch out of the chamber to the outside, passing the engine air intakes.
Guns TKB-495A and the gas chambers were installed on the first prototype. Immediately there were problems. When shooting guns in the front compartment of the vapor chamber, where the assembled cartridge cases and units began to occur flare gases accumulating there - sometimes even the deformation occurred chamber design. Quickly find a way to remedy the defect: an effective blowing compartment liners and installed on the trunks of guns muzzle ensure stable operation of the engines at the front of the firing gun mount.
During test flights demonstrated volley of cannon fire from long lines without disrupting the normal operation of the engines. In support of the document will bring along the following lines: ╚Poslednyaya bow design installation with the gas chamber to ensure the reliability and operation of the engine fire, regardless of altitude and airspeed, power setting and duration of fire. Besides eliminated blinding the pilot at the time of the shooting. During firing at different dive angles as with brake flaps and without the normal behavior of the aircraft, no singularities. Targeting an easy, confident in the dive plane is stable. Using the convenient sight ... In continuous release 320 pieces of shells from the nasal installation, the smell of powder gases in the cockpit felt slightly. Lead Pilot Air Force Major General VK Kokkinaki. December 29 1953g.╩.
On the results of factory tests immediately reported to the Minister of Aviation Industry P.V.Dementevu who, knowing that the matter is interested in leadership of the country, directs the Presidium of the USSR Council of Ministers addressed G.M.Malenkova memo. He reports, including, and the difficulties encountered during the test was the reason for failure of terms of presentation of the IL-40 on state tests in July 1953 Reaction was immediate. Already 31 December 1953 Deputy Minister of Defense Marshal of the Soviet Union AM Vasilevsky his order appoints a special committee to carry out the state tests. It was led by Hero of the Soviet Union, Air Force Major General M.G.Sklyarov, during the Great Patriotic War, commanded the Guards Attack Aviation Regiment.
In early 1954, a pilot plant has eliminated the IL-40 deficiencies identified in the factory tests and has made a replacement engine. The plane arrived in January 21 GK NII VVS. State tests did not last long, and already March 15 ended. The lead pilot was Major V.S.Kipelkin, pilots flying by - Heroes of the Soviet Union Colonel Yu.A.Antipov, I.M.Dzyuba, VA Ivanov, V.G.Ivanov. Senior lieutenant A.A.Yablonsky served as a leading radio operator-gunner. Leading engineers - A.S.Rozanov, S.G.Frolov. During state testing IL-40 with a normal gross weight 16200 kg, carrying a gun full of ammunition and bomb payload of 400 kg, at the ground showed a top speed of 910 km / h and at an altitude of 1,000 meters - 950 km / h. Tactical aircraft with a range of reloading flight weight 17275 kg with external fuel tanks was 270 km.
Military experts noted that the attack on the flight technique is simple. Aircrew familiar with jet aircraft MiG-17 and IL-28, easily mastered flying on the IL-40 - day and night, in all weather conditions. The behavior of the aircraft at high airspeed and Mach numbers (up to Mkrit = 0, 89) had no negative features. IL-40 can perform a simple aerobatics figures. When exiting at large angles of attack occurred warning shaking - as fighter aircraft with swept wings. The installation of two engines flying is not complicated, but improve safety.
They were evaluated and tactical features of IL-40 compared to a piston Il-10M, which consisted at the time in the Air Force. Comparative analysis showed that IL-40 is significantly superior to IL-10M at the maximum level flight speed, speed range, rate of climb, the heights of the practical application, on the bomb load and the power of artillery weapons. It was noted that the range of tactical aircraft and equipment allow you to use it without rebasing for direct support of ground troops to a depth of 250 km. IL-40 could also maintain a strategic visual and photographic reconnaissance in the interests of aviation and Combined Arms Command. Official tests conducted Dogfight Il-40 MiG-15bis and MiG-17. It has been established that the conduct of the aiming gun shooting attack aircraft maneuvering is complicated because of the large horizontal and vertical velocities of IL-40, and their wide range and availability of the aircraft at the effective air brakes.
In carrying out attacks on ground targets IL-40 proved to be more resilient to manage than the Il-10M. He created a high density of fire, with a higher shooting accuracy. The simultaneous use of all four guns had no effect on the piloting of the aircraft, the impact was small with the shooting. The aircraft was tested in dive-bombing at an angle of 30 to 50 degrees, and from horizontal flight at an altitude of 300 meters at a speed of 700 km / h. The destructive effects of weapons of IL-40 has been very strong. However, during the execution of operations with sliding and simultaneous maintenance of multiple rocket launchers from the front gun mount (for factory tests volley fire was the rectilinear motion of the aircraft toward the goal) were cases of spontaneous shutdown or significant reduction in turnover with a simultaneous increase in emissions above the allowable temperature - the engine located on the side opposite to the sliding direction.

More testers noticed over the rear of the aircraft operational alignment of 36 - 38% MAC. In conjunction with the small base of the chassis, this led to the aircraft pitching when driving on uneven ground airfields, complicated the implementation of the taxi, takeoff and landing. In general, military pilots praised the tactical flight characteristics of the IL-40, recommended it for serial production and adoption of the Air Force after the elimination of the identified deficiencies. Air Force Commander Air Marshal P.F.Zhigarev approved April 22, 1954 act on the results of the state tests.
Now we know more ...
9 photo.

At the end of 1951 we developed a technical proposal for the creation of two-seat armored attack aircraft IL-40 with two engines AM-5F, with powerful artillery, missile and bomb armament. In preparing the materials were actively involved S.N.Chernikov, V.M.Germanov, N.P.Stolbovoy, V.M.Sheynin and other specialists. This proposal to the government in January 1952, very quickly examined, and on February 1 issued a decree of the Council of Ministers on the design and manufacture of prototype IL-40.
Under the scheme of IL-40 is a twin-engine nizkoplan with swept wings and tail surfaces (sweep angle anywhere along the line 0 35╟ 25 chords). The chassis was retractable, tricycle, with the nose wheel. The crew consisted of two people - a pilot and radio operator-gunner. The main part of the power structure of the aircraft was the hull of which bears the load of the engine is attached to it, the nose and tail of the fuselage, wings. It placed unsealed cockpit, six fuselage fuel tanks with total capacity of 4285 liters and units of the electrical and radio equipment. Performs hull of steel sheets with thickness from 3 to 8 mm (depending on the probable destruction of protected parts of the machine guns of ground troops or fighter planes).
To protect the pilot from the fire in the front cockpit was placed 10 mm bronestenka and 124 mm in a stationary windshield visor lamp. The side window visor had a thickness of 68 mm. From the fire from above and behind the pilot protected 8-mm armor plates on the sliding canopy and a 16-mm bronezagolovnik seat. The cabin also had a strong hand is armor-plated steel sheets with thickness of 4-10 mm. Installed in the cockpit ejection seat: the pilot catapulted back upwards at an angle of 16 degrees, and the arrow - up and down at an angle of 9 degrees. Canopy have two independent emergency opening system - air (acting on the shutter ejection seats) and electrical (triggered by pressing a button on the side of the cabin). On the creation of the fuselage structure, hulls, cockpit crew, setting ejection seats worked V.A.Borog, Yu.V.Komm, E.A.Shushpanov, M.K.Tsimbalyuk, A.A.Belov, A.S.Artamonov , G.V.Novozhilov, I.Ya.Katyrev.A.A. Shakhnovich, S.I.Dmitriev.
On the sides of the hulls between the spars of center, close to the longitudinal axis of the aircraft mounted engines AM-5F with afterburner, each of which had a takeoff thrust without afterburner 2150 kg, and with afterburner - 2700 kg. This arrangement simplifies the management of aircraft engines in the event of failure of one of them. Air intakes were in favor of a few leading edge of the wing and the air intake channels extend through the front spar of center. Through the rear spar were skipped engine exhaust. In these places, the front and rear spars of center have an annular shape. On the outer side and below the engine protected armor thickness of 4 mm. The development of the power plant of IL-40 was led by G.M.Litvinovicha. The total weight of the metal and transparent armor on the plane with the fixings was equal to 1918 kg.
The forward fuselage was attached to the front bronestenke hulls. It housed six cannons NR-23 23 mm design A.E.Nudelmana and A.A.Rihtera and nose landing gear in the retracted position and a piece of equipment. Guns were firing rate of 800 rounds per minute and sets of three on each side. The ends of their trunks were out of ammunition consisted of 900 rounds - 150 per gun.

Aft fuselage is attached to the rear bronestenke hulls, carried vertical tail, at half height which establishes a fixed horizontal tail. Furthermore, aggregates are housed the special equipment of the aircraft. Along the sides and bottom of the tail part had three large brake plate with perforated surface, which could be opened in flight to an angle of 50 degrees. Side shields made traditionally - against the flow and the bottom had a feature - it opens the flow. Brake pads improved maneuverability characteristics of the aircraft over the battlefield, making it easier to attack ground targets with a dive.
Rounding out the aft fuselage aft movable gun mount Il-K10, remote-controlled from the cab arrow. It was designed to protect the rear hemisphere of the aircraft from enemy air attack and ground attack after attack aircraft from attack. Installation was a gun HP-23 with ammunition 200 rounds, which by means of electro-hydraulic servo drive could deviate by up 55╟, 40╟ 60╟ down and right and left. The maximum angular velocity of rotation arms were 42 deg. / S (horizontal) and 38 ° C / sec (vertical). The bow and stern gun installation created in the subdivision V.A.Fedorova. Technical documentation on the remote control aft installation let A.P.Zhuravlenko.
The trapezoid wing in terms of 52, 3 m2 was aerodynamic configuration of the profiles TsAGI: CP-10c-12 with relative thickness of 18, 44% at the root and CP 11-12 with a relative thickness of 12, 86% at the end. It consisted of a center section integrally connected to the hulls and two detachable parts. In the center section there was a tiltable landing flap, and detachable parts installed retractable flaps type TsAGI. The design of the wing and the landing mechanization was developed under the leadership of E.I.Sankova.
Most of the relative thickness of the wing has allowed not only to remove the main landing gear legs, but also to create there four small bomb bay - for internal suspension in each of bombs weighing up to 100 kg. In addition, under the center wing and detachable parts installed four of the beam, which could be suspended or two bombs weighing up to 500 kg, or jet gun type ODP with unguided missiles TPC 132 and TPC-82, or the external fuel tanks on holders under center total capacity of 1,100 liters. The normal bomb load of IL-40 in accordance with the government and TTT customer was 400 kg, and accelerated version plane could carry 1,000 kg of bombs. It was possible to establish by overloading jet guns with eight TRS-132 and twelve TRS-82. Over Bombings armament specialists worked under the direction of D.I.Koklina. The stabilizer and fin of the aircraft - two-spar, rudder had a weight balance and aerodynamic axial compensation and trimmers. Lead designer plumage was N.I.Maksimov.

Work on the creation of the IL-40 were a very fast pace. Here it affects both Ilyushin organizational skills and extensive experience and highly qualified design team. In just three and a half months after the publication of the decision of the government commission headed by Air Force combat pilot of attack aircraft, Major General Aviation A.D.Reyno acquainted with the layout of the IL-40 and gave positive feedback. In February 1953 we completed the construction of experimental aircraft IL-40. After a short airfield mining-board systems and equipment 7 March 1953 by test pilot VK Kokkinaki raised IL-40 into the air. With him in the test program was APVinogradov engineer who, during flight in the cockpit was a radio operator-gunner. Lead engineer for the factory flight tests of IL-40 was appointed A.I.Zhukovskogo. The first test flights were evaluated and received ╚dobro╩ pilot aircraft performance data of the aircraft, its characteristics of stability and controllability. At the end of March 1953 Kokkinaki flew to the landfill ╚Faustovo╩ test firing front gun mount on the ground targets.
An experienced pilot approached the polygon at an altitude of 5000 meters, the aircraft entered into a shallow dive, pulled the trigger and the guns ... immediately stopped to see the goal - to pull out of the trunks of guns flame blinded him. At the same time spontaneously sharply slowed down and then shut off the engine. Kokkinaki stopped shooting, was able to restart the engines (thanks to clearance) and returned to base. The incident was immediately reported Ilyushin, who ordered an urgent to develop a program of research unstable mode of the engine is fired from the gun mount the front of the aircraft IL-40. Then was released technical documentation for installation on the trunks of two types of muzzle guns, and eight types of different kinds of nozzles, removal of powder gases in the side of the air intakes.
Tests for this program began April 1, 1953 Lead engineer appointed an experienced specialist vooruzhentsa M.G.Ovchinnikova. Shooting at the shooting range with power (with simultaneous high-speed filming processes occurring on the muzzle of guns) and flight showed that the use of muzzle and tips does not give positive results - the engine resets momentum already at shooting only one gun burst in 5 - 10 shells . Research in this direction ceased. In addition, during the tests it revealed that in addition to the propellant gases erratic motor drives changes in pressure and temperature non-uniformity in the flow at the inlet of the air intakes.
We decided to replace the six cannons NR-23 with four more powerful and quick-firing gun TKB-495A, which at the same caliber (23 mm), the rate of fire was half times higher - 1300 rounds per minute. The weight TCB-495A compared to the weight of HP-23 increased by only 4 kg. Guns TKB-495A designed under the guidance and N.M.Afanaseva N.F.Makarova in the Tula Design Bureau. Later they were taken to the Soviet Air Force under the designation AM-23. IL-40, each gun had 225 rounds ammo. The power of fire four TKB-495A was the equivalent firepower of six HP-23. Gun TKB-495A equipped and aft gun mount plane.
For the front guns TKB-495A constructed the vapor chamber, which is simultaneously the bow of a stormtrooper. The camera was designed to tap into the external flow of gases from the fire. It is an isolated from the fuselage removable compartment, made of heat-resistant steel sheet, the bottom of which there was a hatch with two doors. Their discovery was blocked with fire control guns. When firing the powder gases have been through the hatch out of the chamber to the outside, passing the engine air intakes.
Guns TKB-495A and the gas chambers were installed on the first prototype. Immediately there were problems. When shooting guns in the front compartment of the vapor chamber, where the assembled cartridge cases and units began to occur flare gases accumulating there - sometimes even the deformation occurred chamber design. Quickly find a way to remedy the defect: an effective blowing compartment liners and installed on the trunks of guns muzzle ensure stable operation of the engines at the front of the firing gun mount.
During test flights demonstrated volley of cannon fire from long lines without disrupting the normal operation of the engines. In support of the document will bring along the following lines: ╚Poslednyaya bow design installation with the gas chamber to ensure the reliability and operation of the engine fire, regardless of altitude and airspeed, power setting and duration of fire. Besides eliminated blinding the pilot at the time of the shooting. During firing at different dive angles as with brake flaps and without the normal behavior of the aircraft, no singularities. Targeting an easy, confident in the dive plane is stable. Using the convenient sight ... In continuous release 320 pieces of shells from the nasal installation, the smell of powder gases in the cockpit felt slightly. Lead Pilot Air Force Major General VK Kokkinaki. December 29 1953g.╩.
On the results of factory tests immediately reported to the Minister of Aviation Industry P.V.Dementevu who, knowing that the matter is interested in leadership of the country, directs the Presidium of the USSR Council of Ministers addressed G.M.Malenkova memo. He reports, including, and the difficulties encountered during the test was the reason for failure of terms of presentation of the IL-40 on state tests in July 1953 Reaction was immediate. Already 31 December 1953 Deputy Minister of Defense Marshal of the Soviet Union AM Vasilevsky his order appoints a special committee to carry out the state tests. It was led by Hero of the Soviet Union, Air Force Major General M.G.Sklyarov, during the Great Patriotic War, commanded the Guards Attack Aviation Regiment.
In early 1954, a pilot plant has eliminated the IL-40 deficiencies identified in the factory tests and has made a replacement engine. The plane arrived in January 21 GK NII VVS. State tests did not last long, and already March 15 ended. The lead pilot was Major V.S.Kipelkin, pilots flying by - Heroes of the Soviet Union Colonel Yu.A.Antipov, I.M.Dzyuba, VA Ivanov, V.G.Ivanov. Senior lieutenant A.A.Yablonsky served as a leading radio operator-gunner. Leading engineers - A.S.Rozanov, S.G.Frolov. During state testing IL-40 with a normal gross weight 16200 kg, carrying a gun full of ammunition and bomb payload of 400 kg, at the ground showed a top speed of 910 km / h and at an altitude of 1,000 meters - 950 km / h. Tactical aircraft with a range of reloading flight weight 17275 kg with external fuel tanks was 270 km.
Military experts noted that the attack on the flight technique is simple. Aircrew familiar with jet aircraft MiG-17 and IL-28, easily mastered flying on the IL-40 - day and night, in all weather conditions. The behavior of the aircraft at high airspeed and Mach numbers (up to Mkrit = 0, 89) had no negative features. IL-40 can perform a simple aerobatics figures. When exiting at large angles of attack occurred warning shaking - as fighter aircraft with swept wings. The installation of two engines flying is not complicated, but improve safety.
They were evaluated and tactical features of IL-40 compared to a piston Il-10M, which consisted at the time in the Air Force. Comparative analysis showed that IL-40 is significantly superior to IL-10M at the maximum level flight speed, speed range, rate of climb, the heights of the practical application, on the bomb load and the power of artillery weapons. It was noted that the range of tactical aircraft and equipment allow you to use it without rebasing for direct support of ground troops to a depth of 250 km. IL-40 could also maintain a strategic visual and photographic reconnaissance in the interests of aviation and Combined Arms Command. Official tests conducted Dogfight Il-40 MiG-15bis and MiG-17. It has been established that the conduct of the aiming gun shooting attack aircraft maneuvering is complicated because of the large horizontal and vertical velocities of IL-40, and their wide range and availability of the aircraft at the effective air brakes.
In carrying out attacks on ground targets IL-40 proved to be more resilient to manage than the Il-10M. He created a high density of fire, with a higher shooting accuracy. The simultaneous use of all four guns had no effect on the piloting of the aircraft, the impact was small with the shooting. The aircraft was tested in dive-bombing at an angle of 30 to 50 degrees, and from horizontal flight at an altitude of 300 meters at a speed of 700 km / h. The destructive effects of weapons of IL-40 has been very strong. However, during the execution of operations with sliding and simultaneous maintenance of multiple rocket launchers from the front gun mount (for factory tests volley fire was the rectilinear motion of the aircraft toward the goal) were cases of spontaneous shutdown or significant reduction in turnover with a simultaneous increase in emissions above the allowable temperature - the engine located on the side opposite to the sliding direction.

More testers noticed over the rear of the aircraft operational alignment of 36 - 38% MAC. In conjunction with the small base of the chassis, this led to the aircraft pitching when driving on uneven ground airfields, complicated the implementation of the taxi, takeoff and landing. In general, military pilots praised the tactical flight characteristics of the IL-40, recommended it for serial production and adoption of the Air Force after the elimination of the identified deficiencies. Air Force Commander Air Marshal P.F.Zhigarev approved April 22, 1954 act on the results of the state tests.






















