1089
Jellyfish Lake (14 photos)
In the eastern part of the densely forested island ESD-Malki, part of the archipelago of rocky islands (the state of Palau) is amazing saltwater lake in which he lives a huge number of jellyfish. And live here only two species of jellyfish - gold and lunar.
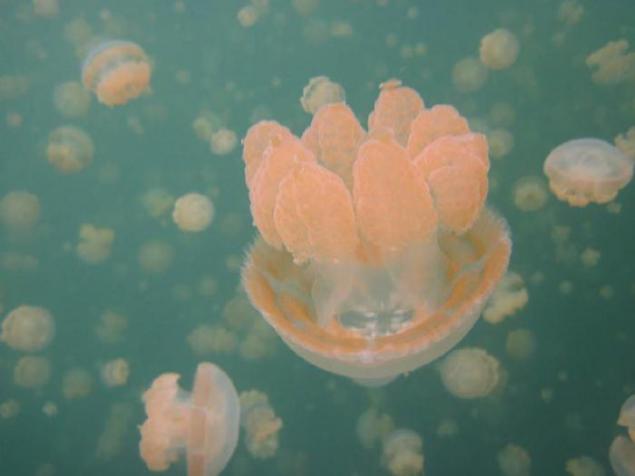

1. Water Jellyfish Lake salty lake itself is associated with the Pacific Ocean by a network of cracks and three small tunnels that permeate the surrounding limestone. Nevertheless, the inhabitants of the lake is completely isolated from the ocean, and the living conditions in the lake are quite unlike ocean.
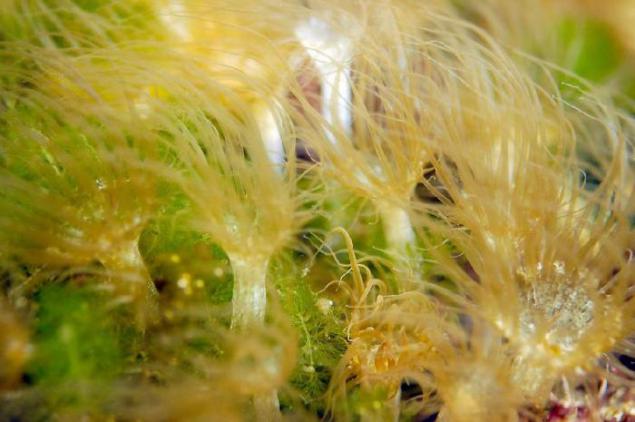

2. Therefore, gold and moon jellyfish that inhabit the lake, are very different from their relatives that live in the lagoon ocean just 200 meters away from them.
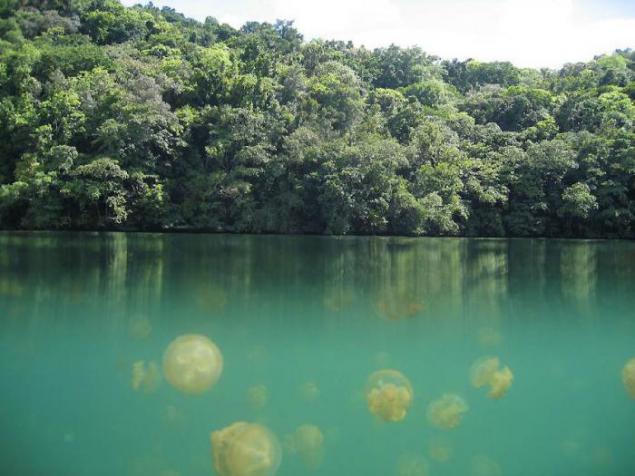

3. Jellyfish Lake in the absence of their natural enemies of jellyfish have multiplied to an incredible amount. Now the lake, with an area of only 0, 057 square kilometers and a depth of about 50 m, inhabited almost 2 million jellyfish. Number of jellyfish is so great that their weight can be easily seen, even on an airplane. These jellyfish almost completely lost the ability to defend themselves, because eventually they disappeared stinging cells. Diving enthusiasts can safely swim in the lake and enjoy the jellyfish without fear get a nasty burn.
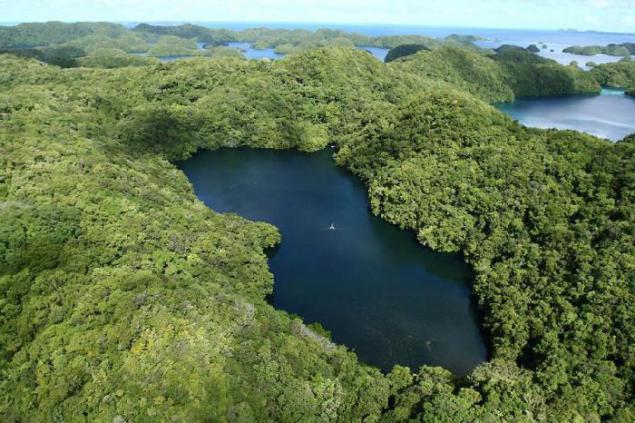

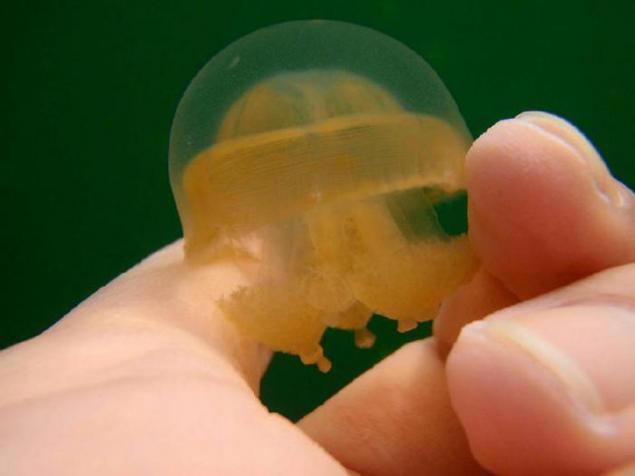
4. The most numerous inhabitants of the lake - it's golden jellyfish. Unlike their closest relatives that live in the ocean, lake golden jellyfish lishis and age spots, and almost completely lost the ability to sting. There are also other differences in the structure of the body, so even offer some biologists distinguish gold jellyfish living in the lake, a separate subspecies.
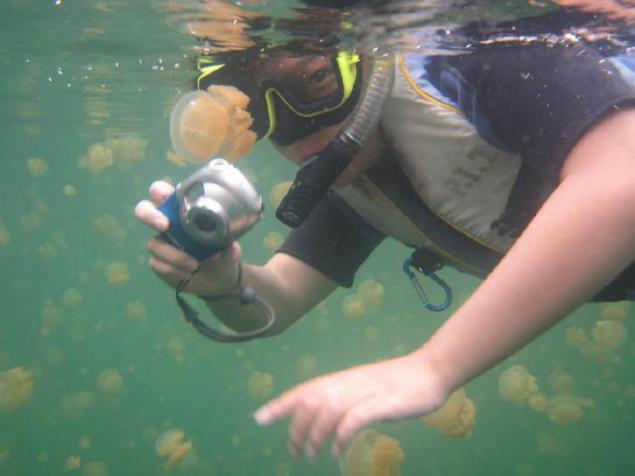

5. Water in Jellyfish Lake is clearly divided into two layers - top and bottom. The oxygen content in the top layer is significantly greater than in the lower. At a depth of 15m the content of oxygen in water decreases to zero. The upper and lower layers of the lake never mixed. Tunnel, which connects the lake to the ocean, provides a flow of a small amount of fresh water used in the upper layer of the lake.
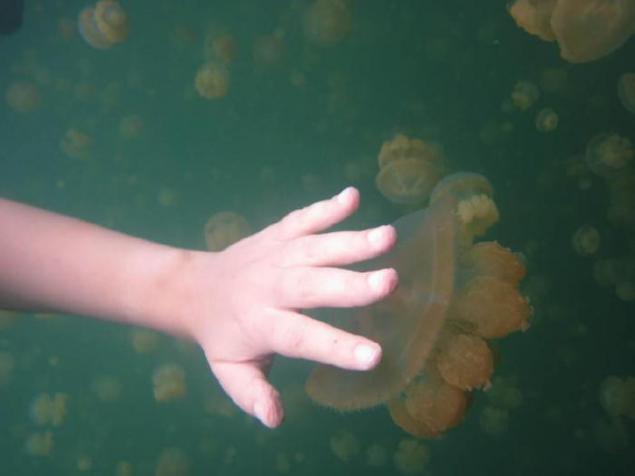

6. Thus, all the jellyfish and other animals that live in the lake, have to live only in the upper layer of water. In anoxic bottom water layer can survive only a few types of bacteria. The lower layer of water so heavily saturated with hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and phosphate, which represents a danger to divers, as the man is in a similar solution can get serious poisoning directly through the skin.
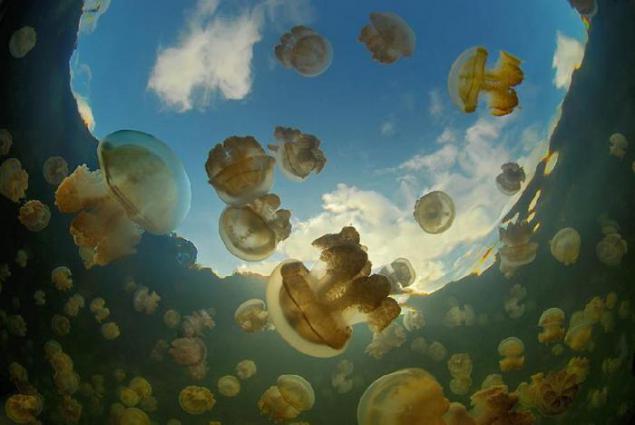

7. Medusa need oxygen, so they can live only in the upper layer of water Jellyfish Lake. Nevertheless, jellyfish daily rhythmic perform migration, in both the horizontal and vertical direction, falling to near the border of the oxygen-containing layer. Migration golden jellyfish are particularly organized. All night until two o'clock in the afternoon jellyfish rhythmically raised and lowered in the surface layer of water. With the arrival of jellyfish in the morning leaving the western part of the lake and going on the east side. In the middle of the day, they again returned to the western part of the lake. When the jellyfish floating at the water surface, they rotate counterclockwise. Suggestions have been made that the way jellyfish provides uniform illumination of their symbiotic algae that live in her body and provide it with an additional power supply.
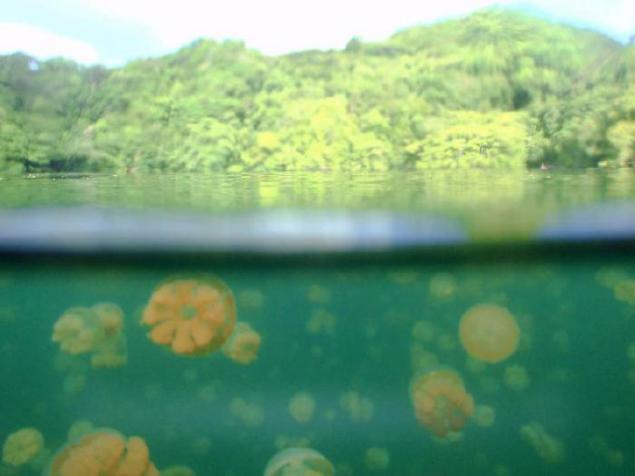

8. Moon jellyfish move not so organized and orderly, like gold, but the migration also are massive. Night moon jellyfish spend at the water surface, where they catch copepods.
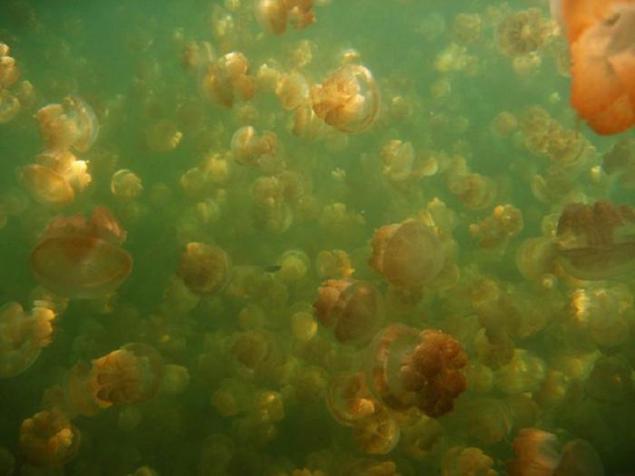

9. Some biologists have suggested that migration jellyfish between the eastern and western parts of the lake is associated with actin Entacmaea medusivora, which feed on jellyfish. These anemones live on the eastern shore of the lake. Medusa try to avoid shadows and kept in the light. Following the maximum illuminated area, they are able to better avoid encounters with dangerous for them to actin.
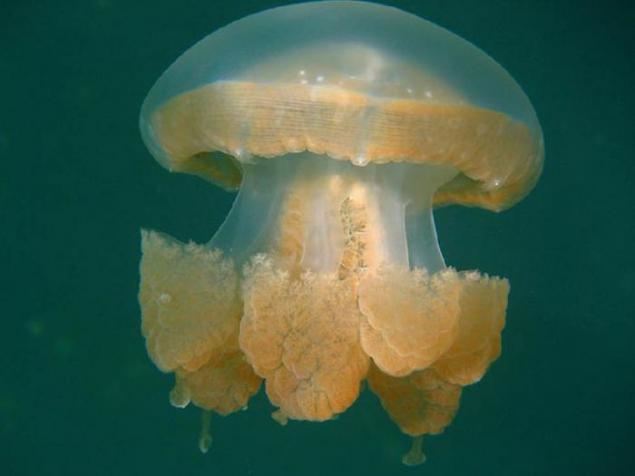

10. In 1998, Jellyfish Lake was almost completely lost its main inhabitants - golden jellyfish. By December 1998, their numbers in the lake dropped to almost zero. It is believed that such a drastic reduction in population was due to the influence of the powerful phase of El Niño, during which there is a redistribution of huge masses of warm water in the surface layer of the ocean.
11. As a result of the El Niño temperature of the water in the lake has risen strongly that killed symbiotic algae, without which it can not survive jellyfish. In 1999, the lake could not find any golden jellyfish, but in January 2000 they again began to appear, and today their number has fully recovered.
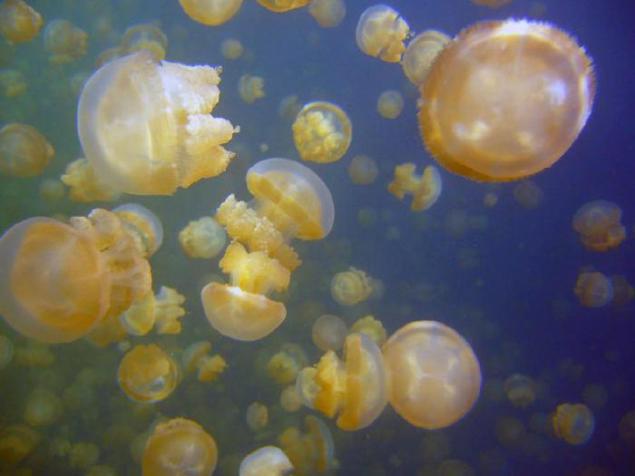

12. The picturesque cluster of jellyfish lake to attract a lot of tourists and diving. Swimming among the jellyfish lake is quite safe, as they are almost completely lost the ability to "bite". Yet people with sensitive skin or allergies it is recommended to use the immersion protective suit. Dive in Jellyfish Lake is permitted only with a mask and snorkel and enjoy the diving is prohibited.
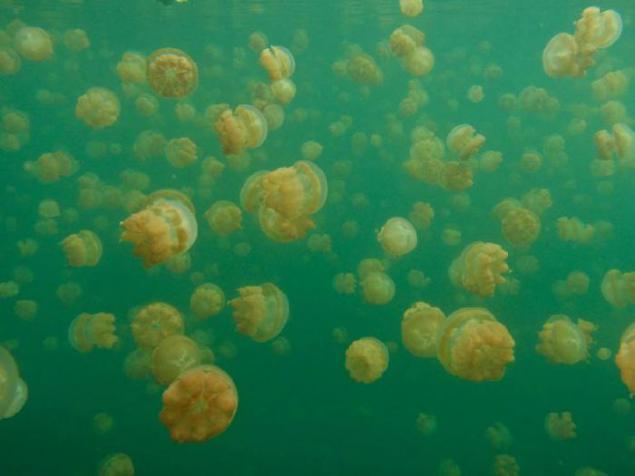

13. Scuba banned for two reasons: firstly, the air bubbles from scuba fall under the dome of the jellyfish, why they may die; secondly, allows a person to scuba dive at depth over 15 meters, which is oxygen free layer.
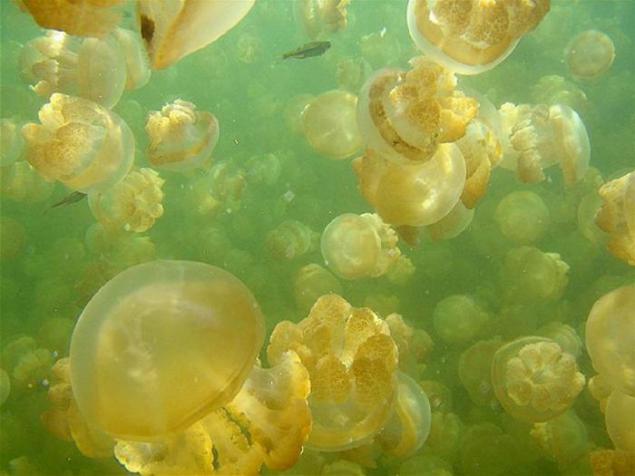

14. Mass dive to the bottom layer of the lake is bound to cause mixing of the upper and lower layers of water (which naturally never happens), all of the lake's ecosystem will be irretrievably broken, that lead to the death of all its inhabitants. In addition, the unwary diver can get himself fatal poisoning through the skin, while in the lower layer of water saturated with hydrogen sulphide and ammonia.

1. Water Jellyfish Lake salty lake itself is associated with the Pacific Ocean by a network of cracks and three small tunnels that permeate the surrounding limestone. Nevertheless, the inhabitants of the lake is completely isolated from the ocean, and the living conditions in the lake are quite unlike ocean.

2. Therefore, gold and moon jellyfish that inhabit the lake, are very different from their relatives that live in the lagoon ocean just 200 meters away from them.

3. Jellyfish Lake in the absence of their natural enemies of jellyfish have multiplied to an incredible amount. Now the lake, with an area of only 0, 057 square kilometers and a depth of about 50 m, inhabited almost 2 million jellyfish. Number of jellyfish is so great that their weight can be easily seen, even on an airplane. These jellyfish almost completely lost the ability to defend themselves, because eventually they disappeared stinging cells. Diving enthusiasts can safely swim in the lake and enjoy the jellyfish without fear get a nasty burn.

4. The most numerous inhabitants of the lake - it's golden jellyfish. Unlike their closest relatives that live in the ocean, lake golden jellyfish lishis and age spots, and almost completely lost the ability to sting. There are also other differences in the structure of the body, so even offer some biologists distinguish gold jellyfish living in the lake, a separate subspecies.

5. Water in Jellyfish Lake is clearly divided into two layers - top and bottom. The oxygen content in the top layer is significantly greater than in the lower. At a depth of 15m the content of oxygen in water decreases to zero. The upper and lower layers of the lake never mixed. Tunnel, which connects the lake to the ocean, provides a flow of a small amount of fresh water used in the upper layer of the lake.

6. Thus, all the jellyfish and other animals that live in the lake, have to live only in the upper layer of water. In anoxic bottom water layer can survive only a few types of bacteria. The lower layer of water so heavily saturated with hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and phosphate, which represents a danger to divers, as the man is in a similar solution can get serious poisoning directly through the skin.

7. Medusa need oxygen, so they can live only in the upper layer of water Jellyfish Lake. Nevertheless, jellyfish daily rhythmic perform migration, in both the horizontal and vertical direction, falling to near the border of the oxygen-containing layer. Migration golden jellyfish are particularly organized. All night until two o'clock in the afternoon jellyfish rhythmically raised and lowered in the surface layer of water. With the arrival of jellyfish in the morning leaving the western part of the lake and going on the east side. In the middle of the day, they again returned to the western part of the lake. When the jellyfish floating at the water surface, they rotate counterclockwise. Suggestions have been made that the way jellyfish provides uniform illumination of their symbiotic algae that live in her body and provide it with an additional power supply.

8. Moon jellyfish move not so organized and orderly, like gold, but the migration also are massive. Night moon jellyfish spend at the water surface, where they catch copepods.

9. Some biologists have suggested that migration jellyfish between the eastern and western parts of the lake is associated with actin Entacmaea medusivora, which feed on jellyfish. These anemones live on the eastern shore of the lake. Medusa try to avoid shadows and kept in the light. Following the maximum illuminated area, they are able to better avoid encounters with dangerous for them to actin.

10. In 1998, Jellyfish Lake was almost completely lost its main inhabitants - golden jellyfish. By December 1998, their numbers in the lake dropped to almost zero. It is believed that such a drastic reduction in population was due to the influence of the powerful phase of El Niño, during which there is a redistribution of huge masses of warm water in the surface layer of the ocean.

11. As a result of the El Niño temperature of the water in the lake has risen strongly that killed symbiotic algae, without which it can not survive jellyfish. In 1999, the lake could not find any golden jellyfish, but in January 2000 they again began to appear, and today their number has fully recovered.

12. The picturesque cluster of jellyfish lake to attract a lot of tourists and diving. Swimming among the jellyfish lake is quite safe, as they are almost completely lost the ability to "bite". Yet people with sensitive skin or allergies it is recommended to use the immersion protective suit. Dive in Jellyfish Lake is permitted only with a mask and snorkel and enjoy the diving is prohibited.

13. Scuba banned for two reasons: firstly, the air bubbles from scuba fall under the dome of the jellyfish, why they may die; secondly, allows a person to scuba dive at depth over 15 meters, which is oxygen free layer.

14. Mass dive to the bottom layer of the lake is bound to cause mixing of the upper and lower layers of water (which naturally never happens), all of the lake's ecosystem will be irretrievably broken, that lead to the death of all its inhabitants. In addition, the unwary diver can get himself fatal poisoning through the skin, while in the lower layer of water saturated with hydrogen sulphide and ammonia.























