644
Hugelkultur - the culture high bulk beds
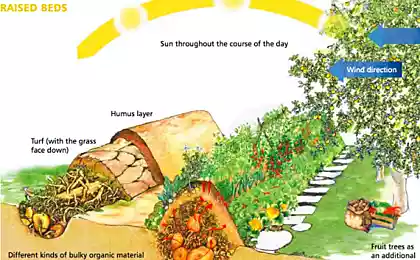
Instead of having to burn branches, leaves and grass clippings after cleaning your backyard and garden you could build a Hügel bed, known as high ridge Holzer. Simply put it is a large (about 1.5 m) the bulk of the mound, where dropping branches, leaves, grass clippings, straw, cardboard, paper, manure, compost or any other biomass that is at hand, and the top covered with soil and planted vegetables.
The gradual decay of the tree will become a consistent source of long-term nutrients for the plants. A large ridge can give a constant supply of nutrients for 20 years (or even longer if you use only hardwoods). The composting wood also generates heat which prolongs the vegetative period of plants.
The soil in this bed is well cultivated, has high aeration, and there is no need to dig for a long time.
The logs and branches act like a sponge. They akkumuliruya rainwater and then releasing it during dry days. In fact, after the first year you can never water your high bed (with the exception of long-term drought).
Absorbs carbon in the soil.
Sepp Holzer (expert on high beds) recommends to choose a small lawn and cut sod, dig a trench 30 cm deep and fill it with logs and branches. Then cover the logs are turned upside down turf. The top cover of cut grass, seaweed, compost, old manure, straw, green leaves, mulch, etc...
From the book permaculture by Sepp Holzer.

Comparison of traditional and high beds. Plants taken from one package of seeds. on a high bed plants were planted two weeks later than the left bed.
Marcella: saponaria-wortsandall.blogspot.com

High bed in Ontario, Canada. The branches are of height 30 cm.
greenshireecofarms.com

On branches and logs covered with a thick 12-15 cm of hay mixed with manure.

Here is a high garden beds planted with lettuce
www.richsoil.com/hugelkultur

Here is a beautiful high ridge lined with pallets. www.permies.com

A steep high ridge, convenient because no need to bend over to plant seeds or to harvest. the more bareven and branches inside the better it will hold moisture longer and will keep shape.

Sepp Holzer also recommends making high beds for better ventilation.
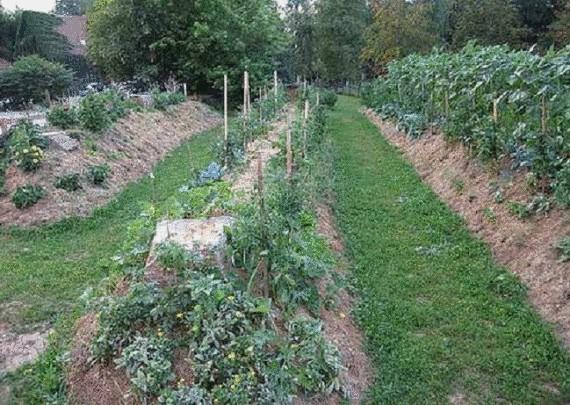

The land Sepp Holzer high beds.
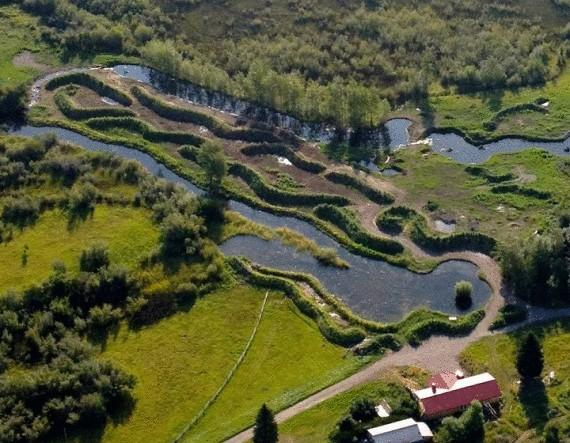

High beds, Holzer's farm in Montana. Here the most used the terrain for the organization of permaculture. The ponds and ridges near the water, a constant source of moisture. www.holzeragroecology.com
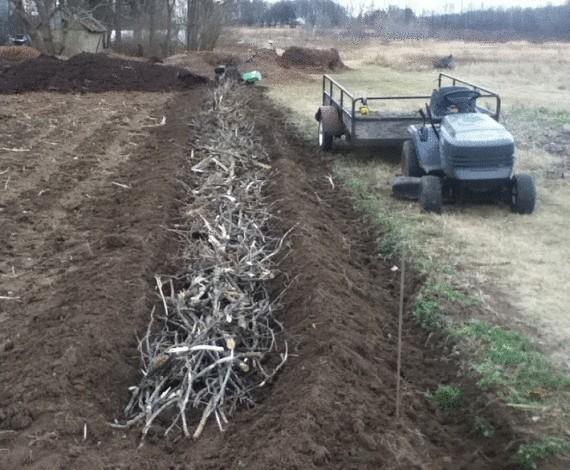

This bed is prepared for planting potatoes. Partially dug into the ground to reduce the height. The final height will be about 1 meter. Rob hopes that this bed will last 10 years.
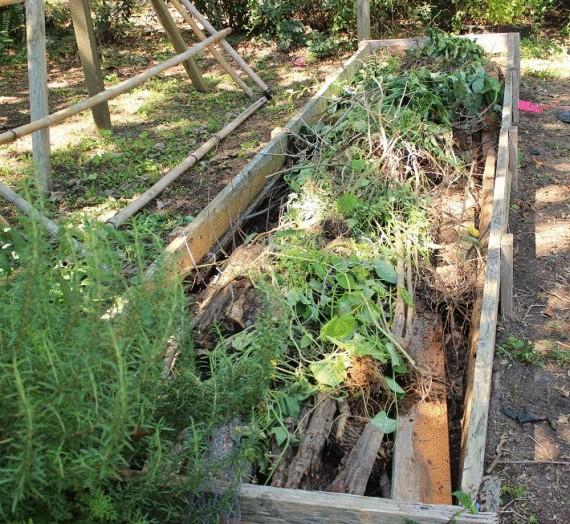

High bed frame
newwavegardeningexperiment.wordpress.com

The basis for this row will serve as a vertically installed logs. They will nourish the garden and to keep moisture in for many years.
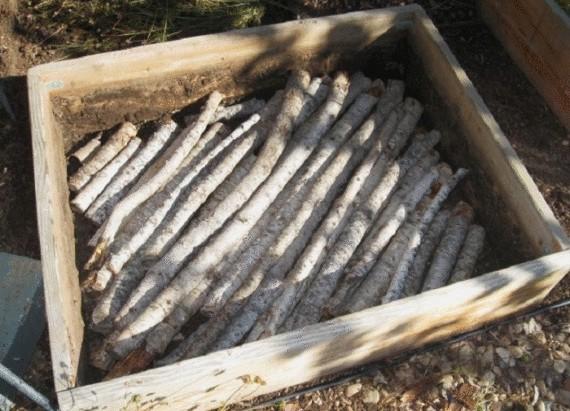

The basis for the beds in the arid climate homesteadingdownsized.com

The drier you climate the more need of firewood. Bed Caleb Larson, MT.
www.permies.com
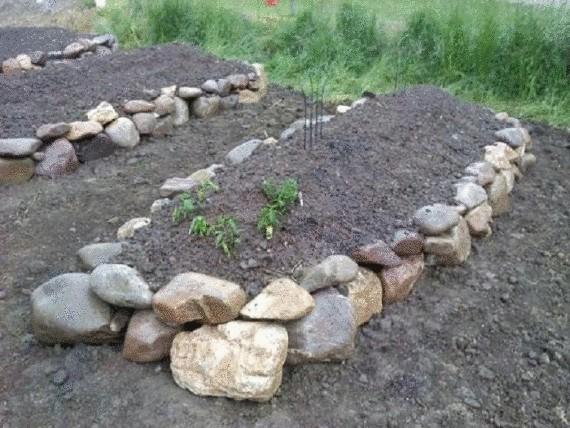

High beds John from Idaho
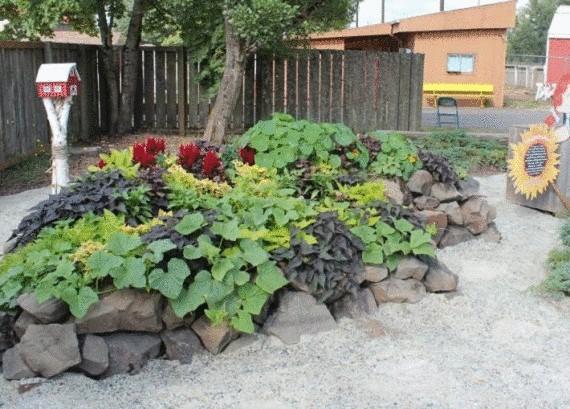

The stones retain heat longer. lewiscountyrecycles.org

Gralka from straw bales require less soil, less water and keep warm. When the straw decomposes, it provides nutrients to plants. The beds of straw bale use in regions with poor soil quality. naturespilgrim.com
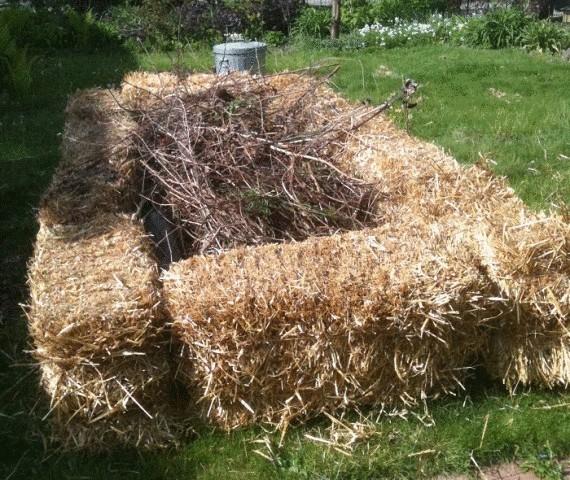

Bales can impose a bed smalltowngardens.blogspot.com

If you do not have at hand a lot of wood, you can put the bales as the base. But such a garden will quickly sink.
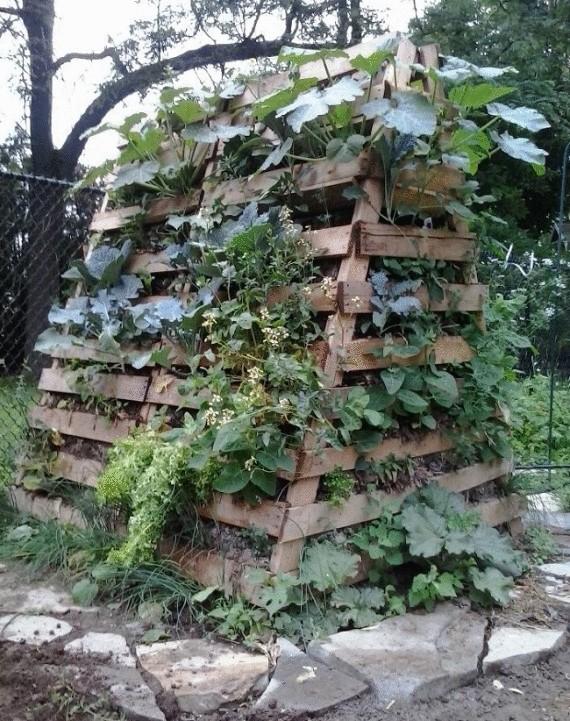

Here is a high ridge Tim barrow from Canada. He made it very narrow and high, due to the wooden frame.

Multimania patch looks like a layer cake. In order to give her enough food, a bed you want to fertilize a material rich in nitrogen to allow the active composting process. Suitable leaves and grass cuttings, straw.
To saturate the bed with nitrogen is possible by means of organic foods, especially in the first year to launch the necessary processes of fermentation inside.
The basis high the beds are always laid solid hardwoods (oak, beech, ash, acacia). It will help to keep the structure of your garden beds and the moisture inside it. Conifers will be humus faster and the bed will sink.
Trees that work best are: Apple, aspen, birch, poplar, maple, oak, poplar, willow (make sure it is dry).
published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©

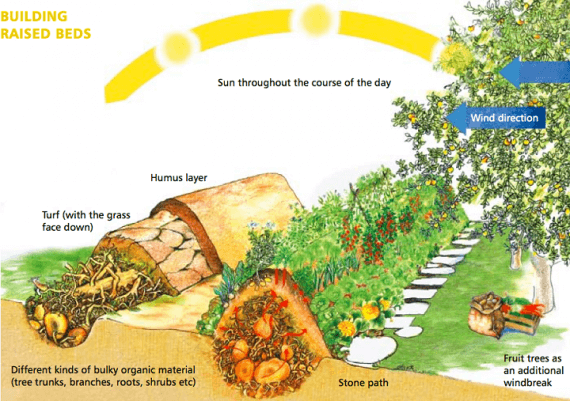
The gradual decay of the tree will become a consistent source of long-term nutrients for the plants. A large ridge can give a constant supply of nutrients for 20 years (or even longer if you use only hardwoods). The composting wood also generates heat which prolongs the vegetative period of plants.
The soil in this bed is well cultivated, has high aeration, and there is no need to dig for a long time.
The logs and branches act like a sponge. They akkumuliruya rainwater and then releasing it during dry days. In fact, after the first year you can never water your high bed (with the exception of long-term drought).
Absorbs carbon in the soil.
Sepp Holzer (expert on high beds) recommends to choose a small lawn and cut sod, dig a trench 30 cm deep and fill it with logs and branches. Then cover the logs are turned upside down turf. The top cover of cut grass, seaweed, compost, old manure, straw, green leaves, mulch, etc...
From the book permaculture by Sepp Holzer.

Comparison of traditional and high beds. Plants taken from one package of seeds. on a high bed plants were planted two weeks later than the left bed.
Marcella: saponaria-wortsandall.blogspot.com

High bed in Ontario, Canada. The branches are of height 30 cm.
greenshireecofarms.com

On branches and logs covered with a thick 12-15 cm of hay mixed with manure.

Here is a high garden beds planted with lettuce
www.richsoil.com/hugelkultur

Here is a beautiful high ridge lined with pallets. www.permies.com

A steep high ridge, convenient because no need to bend over to plant seeds or to harvest. the more bareven and branches inside the better it will hold moisture longer and will keep shape.

Sepp Holzer also recommends making high beds for better ventilation.

The land Sepp Holzer high beds.

High beds, Holzer's farm in Montana. Here the most used the terrain for the organization of permaculture. The ponds and ridges near the water, a constant source of moisture. www.holzeragroecology.com

This bed is prepared for planting potatoes. Partially dug into the ground to reduce the height. The final height will be about 1 meter. Rob hopes that this bed will last 10 years.

High bed frame
newwavegardeningexperiment.wordpress.com

The basis for this row will serve as a vertically installed logs. They will nourish the garden and to keep moisture in for many years.

The basis for the beds in the arid climate homesteadingdownsized.com

The drier you climate the more need of firewood. Bed Caleb Larson, MT.
www.permies.com

High beds John from Idaho

The stones retain heat longer. lewiscountyrecycles.org

Gralka from straw bales require less soil, less water and keep warm. When the straw decomposes, it provides nutrients to plants. The beds of straw bale use in regions with poor soil quality. naturespilgrim.com

Bales can impose a bed smalltowngardens.blogspot.com

If you do not have at hand a lot of wood, you can put the bales as the base. But such a garden will quickly sink.

Here is a high ridge Tim barrow from Canada. He made it very narrow and high, due to the wooden frame.

Multimania patch looks like a layer cake. In order to give her enough food, a bed you want to fertilize a material rich in nitrogen to allow the active composting process. Suitable leaves and grass cuttings, straw.
To saturate the bed with nitrogen is possible by means of organic foods, especially in the first year to launch the necessary processes of fermentation inside.
The basis high the beds are always laid solid hardwoods (oak, beech, ash, acacia). It will help to keep the structure of your garden beds and the moisture inside it. Conifers will be humus faster and the bed will sink.
Trees that work best are: Apple, aspen, birch, poplar, maple, oak, poplar, willow (make sure it is dry).
published
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Sadness is the longest living emotion.
The largest of the volcanoes that shook the Earth the last 200 years