673
Plants for vertical landscaping of Your home
Eighty six million one hundred forty two thousand two hundred sixty seven
Wisteria
The advantage of using climbing plants for landscaping is that with a relatively small depth of the green wall to green up significant space in height and width. Plants used in vertical gardening, grow quickly and therefore in a short time they can green up a variety of objects.
Use vertical gardening in the decoration of different buildings, stone walls and steep slopes, arbors, pergolas, etc. With landscaping of buildings climbing plants are placed along the walls, attaching directly to the wall or set on special supports. Greening the building also provides for the placing of plants on balconies and in window openings.
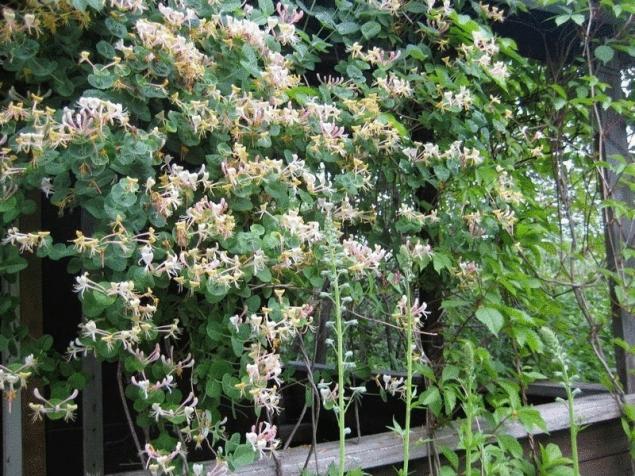

Perfoliate honeysuckle
You should consider the possibility of destruction of the powerful vines of the roof and other parts of buildings. Thus, a powerful Wisteria stems can sprawl to damage the roof. When landscaping balconies and Windows, you cannot create a solid green wall of climbing plants, as the room receives less light and air.
With vertical landscaping, retaining walls and steep slopes, you can use plants that rise up, attaching directly to plant surfaces or special devices, and also plants that hang down or fall down.

Japanese honeysuckle
Landscaping arbors, pergolas, trellis climbing plants, which twine around supports or attached to her antennae, hooks, etc., and are fixed on the support by tying stems, allows you to to create shade and coolness to plant the object, to close a variety of items and divide the territory into individual plots.
If vertical gardening use plants attached directly to the wall of buildings or to the supports using the "suckers" or adventitious roots, the walls should have a slightly rough surface. Such plants can include certain types and forms of girlish grapes, ivy, campsis and rooting.

Celastrus
When you use plants that do not have devices that allow them to attach to the bare walls, you must create a special support on which the plants climb upward, secured to her by tendrils (grape), petioles (clematis), or being twisted around (honeysuckle, kirkazon).
Some plants have to be tied up to supports. Support structures may be different, but they all must be durable and strong enough to withstand the weight of plants and, of course, not to reduce the ornamental plant facilities. Support made of wood or metal. In the first case, you need all parts in contact with the soil, treated with antiseptic (creosote).

Lemongrass
All supports are vertical posts or rails, which are connected by horizontal bars or bands. Design can be hard or soft. Most recent at the top attached to the walls of houses or other structures.
Types of plants for landscaping are selected depending on the climatic conditions of the area. On the North side planted shade-tolerant and moisture-loving species, and the southern light and is drought resistant. You must also consider the decorative quality of the vines and the intensity of their growth and capacity development.
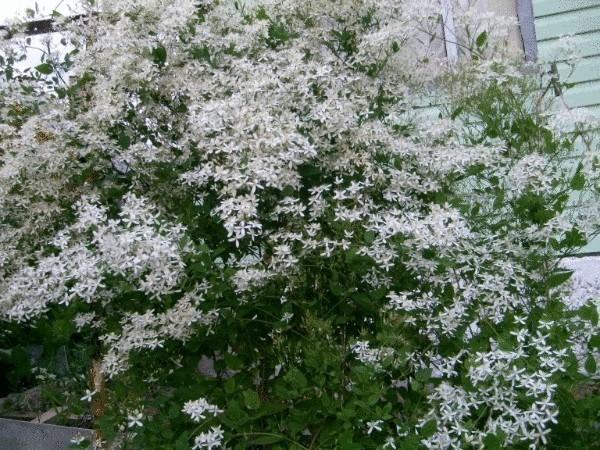

Clematis paniculata
Currently, landscaping is used more than 50 species of lianas belonging to different families. But the most common a relatively small number of types:
of the legume family — glycine;
family caprifoliaceae — honeysuckle perfoliate honeysuckle and Japanese;
family bereskleta — celastrus;
from the Magnolia family — lemongrass;
from the family of Ranunculaceae — clematis (clematis) Jackman, clematis paniculata;
family Araliaceae — ivy;
family kirksnove — kirkazon macrophylla; kirkazon Manchu;
of the family Vinogradov — Amur grape, grapes girl pyatilistochkovy;
family Actinidia — Actinidia arguta, Actinidia kolomikta;
the family bignonia — campsis rooting.
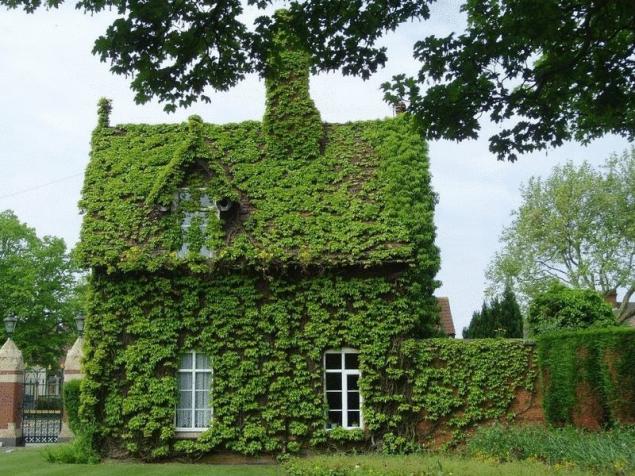

The ivy
In the preparation of seats for climbing plants it is necessary to ensure that the soil was nutritionally adequate. This is especially important in the landscaping of homes, as often the entire soil around the house during construction is removed. The seat is prepared in advance. If the soil is not fertile, in each of the seats should be 5 — 8 kg/ha organic fertilizer and complete fertilizer.
Make the holes with a diameter of 60 cm and a depth of 50 cm If the size of the holes can disrupt the architecture of structures, the diameter can be reduced, but it should not be less than 30 cm At the bottom of the pit lay crushed gravel or brick layer up to 10 cm, which is the drainage. The location of planting holes shall conform to the landscaping project. Typically plants are planted at some distance from the wall in ridges or holes.

Kirkazon macrophylla
When landscaping balconies and Windows you can use the plants planted in the soil near the house. To do this, whip vines down to the balcony or window in the cradle (cable). You can also grow climbing plants on balconies or at Windows in special boxes. Such boxes shall have a wall height of not less than 30 cm, width 20 cm length of the box set depending on the size of the balcony or window. In the bottom of the box every 10 — 15 cm drilled holes for water drainage.
When installed on the Windows or the balconies under the boxes enclose the strip to irrigation water could freely flow out the drainage holes. In addition, they should be placed metal or plastic sheets so that flowing water does not impinge on the wall of a building or located below the balcony. On the bottom of the drawer of the drainage stack layer 5 — 7 cm, and then poured the soil mixture in which the plants are planted.
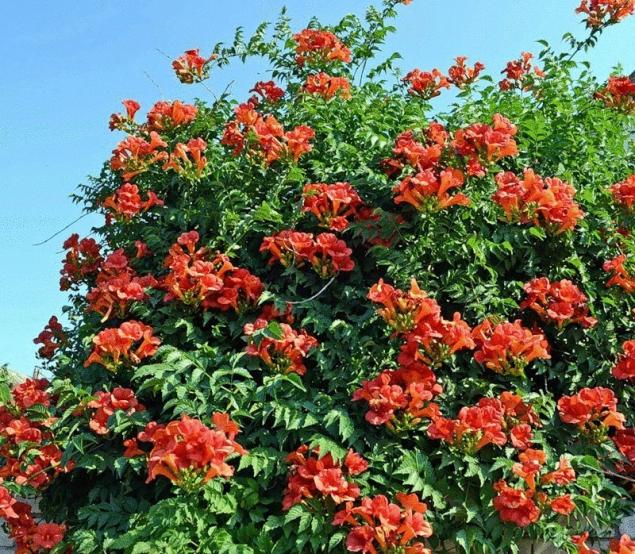

Campsis rooting
Plant climbing plants in the usual way, observing all the rules for the preservation of the root system. Care of established plants is regular weeding and loosening the soil, and timely watering. In the spring and during the summer it is necessary to conduct feeding. Single dose of fertilizers is: 100 g superphosphate and 50 g of ammonium nitrate to 1 m. the growth of shoots they were distributed on the supports in such a way that all of the decorated area was evenly covered with greenery. In addition, cut extra shoots for thinning highly dense places.
Sufficiently hardy species of vines in the winter be removed from the poles and covered fir branches, and they put a Mat of straw or other material. From Lomonosov and some other types of vines that are easy to regenerate shoots from underground parts, winter Spud lower part. published
Source: www.sadovoda.ru
Wisteria
The advantage of using climbing plants for landscaping is that with a relatively small depth of the green wall to green up significant space in height and width. Plants used in vertical gardening, grow quickly and therefore in a short time they can green up a variety of objects.
Use vertical gardening in the decoration of different buildings, stone walls and steep slopes, arbors, pergolas, etc. With landscaping of buildings climbing plants are placed along the walls, attaching directly to the wall or set on special supports. Greening the building also provides for the placing of plants on balconies and in window openings.

Perfoliate honeysuckle
You should consider the possibility of destruction of the powerful vines of the roof and other parts of buildings. Thus, a powerful Wisteria stems can sprawl to damage the roof. When landscaping balconies and Windows, you cannot create a solid green wall of climbing plants, as the room receives less light and air.
With vertical landscaping, retaining walls and steep slopes, you can use plants that rise up, attaching directly to plant surfaces or special devices, and also plants that hang down or fall down.

Japanese honeysuckle
Landscaping arbors, pergolas, trellis climbing plants, which twine around supports or attached to her antennae, hooks, etc., and are fixed on the support by tying stems, allows you to to create shade and coolness to plant the object, to close a variety of items and divide the territory into individual plots.
If vertical gardening use plants attached directly to the wall of buildings or to the supports using the "suckers" or adventitious roots, the walls should have a slightly rough surface. Such plants can include certain types and forms of girlish grapes, ivy, campsis and rooting.

Celastrus
When you use plants that do not have devices that allow them to attach to the bare walls, you must create a special support on which the plants climb upward, secured to her by tendrils (grape), petioles (clematis), or being twisted around (honeysuckle, kirkazon).
Some plants have to be tied up to supports. Support structures may be different, but they all must be durable and strong enough to withstand the weight of plants and, of course, not to reduce the ornamental plant facilities. Support made of wood or metal. In the first case, you need all parts in contact with the soil, treated with antiseptic (creosote).

Lemongrass
All supports are vertical posts or rails, which are connected by horizontal bars or bands. Design can be hard or soft. Most recent at the top attached to the walls of houses or other structures.
Types of plants for landscaping are selected depending on the climatic conditions of the area. On the North side planted shade-tolerant and moisture-loving species, and the southern light and is drought resistant. You must also consider the decorative quality of the vines and the intensity of their growth and capacity development.

Clematis paniculata
Currently, landscaping is used more than 50 species of lianas belonging to different families. But the most common a relatively small number of types:
of the legume family — glycine;
family caprifoliaceae — honeysuckle perfoliate honeysuckle and Japanese;
family bereskleta — celastrus;
from the Magnolia family — lemongrass;
from the family of Ranunculaceae — clematis (clematis) Jackman, clematis paniculata;
family Araliaceae — ivy;
family kirksnove — kirkazon macrophylla; kirkazon Manchu;
of the family Vinogradov — Amur grape, grapes girl pyatilistochkovy;
family Actinidia — Actinidia arguta, Actinidia kolomikta;
the family bignonia — campsis rooting.

The ivy
In the preparation of seats for climbing plants it is necessary to ensure that the soil was nutritionally adequate. This is especially important in the landscaping of homes, as often the entire soil around the house during construction is removed. The seat is prepared in advance. If the soil is not fertile, in each of the seats should be 5 — 8 kg/ha organic fertilizer and complete fertilizer.
Make the holes with a diameter of 60 cm and a depth of 50 cm If the size of the holes can disrupt the architecture of structures, the diameter can be reduced, but it should not be less than 30 cm At the bottom of the pit lay crushed gravel or brick layer up to 10 cm, which is the drainage. The location of planting holes shall conform to the landscaping project. Typically plants are planted at some distance from the wall in ridges or holes.

Kirkazon macrophylla
When landscaping balconies and Windows you can use the plants planted in the soil near the house. To do this, whip vines down to the balcony or window in the cradle (cable). You can also grow climbing plants on balconies or at Windows in special boxes. Such boxes shall have a wall height of not less than 30 cm, width 20 cm length of the box set depending on the size of the balcony or window. In the bottom of the box every 10 — 15 cm drilled holes for water drainage.
When installed on the Windows or the balconies under the boxes enclose the strip to irrigation water could freely flow out the drainage holes. In addition, they should be placed metal or plastic sheets so that flowing water does not impinge on the wall of a building or located below the balcony. On the bottom of the drawer of the drainage stack layer 5 — 7 cm, and then poured the soil mixture in which the plants are planted.

Campsis rooting
Plant climbing plants in the usual way, observing all the rules for the preservation of the root system. Care of established plants is regular weeding and loosening the soil, and timely watering. In the spring and during the summer it is necessary to conduct feeding. Single dose of fertilizers is: 100 g superphosphate and 50 g of ammonium nitrate to 1 m. the growth of shoots they were distributed on the supports in such a way that all of the decorated area was evenly covered with greenery. In addition, cut extra shoots for thinning highly dense places.
Sufficiently hardy species of vines in the winter be removed from the poles and covered fir branches, and they put a Mat of straw or other material. From Lomonosov and some other types of vines that are easy to regenerate shoots from underground parts, winter Spud lower part. published
Source: www.sadovoda.ru