567
Psychological muscle function
Title of the article, of course, a metaphor — more specifically, it is possible to speak about personality-psychological correspondences of the status of a number of muscle groups. Matching these, in spite of individual variability, is quite repeatable and associated with the patterns of age-related psychomotor and personal development, with their parallelism (see "Bodily psychocorrection" M. Sandomirsky).
Let's start with the fact that in classical psychoanalysis indicator of mental health is the power of Ego, and the goal of therapy is education of the Mature Ego.
Thirty six million two hundred forty four thousand eight
Similarly in bodynamics analysis introduces the concept of the bodily Ego, the functions of which are:
The term "biodynamically" (bodynamic) formed from the merger of two roots: body (body) + change (dynamics). Thus, we can decode it as "bodydynamics" analysis or the analysis of bodily development.
The method is based are representations of psychology of development of age, the anatomy and physiology of the neuromuscular system that describes the dynamics of the bodily development of the child its parallelism with the development of personality. The method developed by the Danish therapist L. Marcher (Lisbeth Marcher), a follower of V. Raich, relying on his idea of "muscular armour»
The representation of the corporeality of the Ego, assault and "binding" of certain personal qualities is derived and metaphorical representation of psychological functions of individual muscles or muscle groups that lie at the basis of corporal-psychic unity.
If this view is recognized correct, and that's just the opposite: through the normalization of the status of muscles can be carried out correction of psychological problems (principle of feedback.) Recognition of the status of individual muscles can be used to diagnose psychological problems.
L. Marcher approached the description of the formation of the structure of nature on the physical level as an integral part of psychomotor developmentI, but on a psychological level — as a naturally developing in time sequence alternative choices (see table. 2) that forms the structure of personality. Appropriate that most General elections are private personal properties as would get recorded in the muscles (see table. 1).
Table 1. Metaphorical psychological muscle function by L. Marcher Muscle groupPsychological muscle functionHead, neck
Facial muscles in General
The expression of feelings, social contacts
The muscles around the eyes the Focus of attention and short-term planning
The muscles of the mouth and tongue
Emotional acceptance of the Muscles in the front of the neck
Verbal expression the muscles of the back of the neck
Will power, pride, orientation in the circumstances
Shoulder girdle and arms
Extensors and flexors of the shoulder, and muscles, leading and outlet-shoulder
Personal space in relationships
The muscle lifting the shoulder
The ability to carry psychological "wear»
Rotator cuff self-Defense and the ability to accept support from others
Extensors of the forearm Repulsion, retention on the course
Flexors of the forearm the Attraction and retention of the Rotators of the forearm to Take and give the Flexors and extensors of the wrist
Positioning or social behavior monitoring
Muscle that opposes the thumb and little finger
The heightened awareness; writing
The extensors of the fingers a Thin device (change of borders); the ability "to let go of»
The flexors of the fingers Touch, learning and retention; the ability to take and give
Body Muscles of the anterior region of the thorax (large and small pectoral and serratus anterior muscles)
The feeling of self-worth and personal power (as in superficial and in deep contact)
Intercostals (primary muscles of respiration)
The feeling of fullness of being, "breathing space»
The diaphragm (secondary to respiratory muscle); the superficial muscles of the abdomen
Emotional self-control; hold and "digesting" emotions
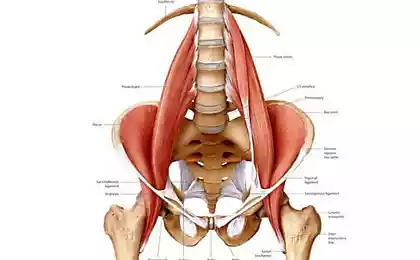
Large and small psoas muscles
Intimate attachment of the Extensors of the torso (spine)
The ability to withstand emotional and physical stressors
Square muscle of a loin
The balance between a focus on their own feelings or the emotions of others
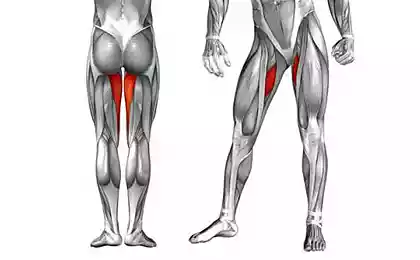
Pelvic floor muscles Sexual feelings Feet The hip flexors to Initiate the movement forward and psychological contact
Extensors of thigh-Assertion, the ability to "stand your ground»
Rotators of thigh Sexy-sensuous-perception
Muscles resulting a hip, Intimate and sensual contact
The extensor tibiae Personal boundaries in relationships
The flexors of the tibia select the direction and control of the movement forward
Peroneal muscle Personal balance in the group interaction
Extensors of foot and toes
Contact with reality Flexors of the foot self-Assertion, the ability "to stand on their own feet»
The flexors of the fingers a Sense of contact with the ground
Biodynamically analysis has made significant additions in raykovska ideas about the structure of nature and "muscular armor." In body psychotherapy the character structure was originally understood essentially as a set of unconscious, irrational behaviors in stressful situations — a set that is formed by each person from an early age (just playing childhood experiences and relate elements of irrationality).
Thus formed largely spontaneously, under the circumstances, (specify: perhaps, by imitating others). A set of typical psychological protection is, according to Reich, "character armor" and their reflection in the form of increased muscle tone "muscular armor."
Twenty million seven hundred forty nine thousand three hundred forty
Thus, according to L. Marcher, in the process of development of various muscle groups "ripen" at different times. Psychomotor development is a progressive "maturation" of certain muscles (and development of related movements).
Under the "maturation" refers to the achievement of such maturity of the neuromuscular apparatus, which makes the activity of this muscle was fully available to conscious control. The transition of the muscles in the "Mature" state is associated with a particular age period, and restricted to a fairly narrow time frame. This so-called critical or sensitive period of development, which is also associated with a lasting experience of the situation of primary teaching (imprint).
When the child faces stressful situations, there are two problems.
First, impaired psychomotor development, partial delay at this age stage (physical analogue of the Freudian fixation). At first, she has to play a protective role, but later became a brake on further development, the basis of an inferiority complex.
Second, emerging imprint usually contains biographical scenes, intense traumatic experiences. Although these memories and undergo displacement, but due to the fact that such protection is not absolute, they create a kind of "Achilles ' heel", the islets of increased psychological vulnerability in the personality structure. Associated with the "problem" muscles kinesthetic sensations partially are displaced, become unavailable to consciousness.
Table 2. The age periodization of psychological development of L. Marcher Stage of developmentAge limitPsychological content The existence of the Prenatal period and up to 3 months after birth
The relationship with the mother Demand From 1 month to 1.5 years is the Internalization of feelings of care from others to meet their needs
Autonomy From 8 months to 2.5 years of Independent movement and communication with others
Will From 2 to 4 years Ability to achieve goals and influence others
Love From 3 to 6 years the Ability to maintain cordial relations
Forming opinions From 5 to 8 years the Development of logical thinking, ability to make decisions based on the norms of culture
Collectivism From 7 to 12 years to be a member of a group/society
This implies two tasks physical therapy. Tactical task is the identification of muscular "blocks"; the problem is strategic, based on eliminating these "blocks" is development missing of bodily and psychological resources. The initial step in working with the patient is physical diagnostic procedure — preparation of individual muscle maps.
When such mapping is the study of about 200 muscles. Thus, unlike traditional physical therapy, we analyze not only static mechanical characteristics — muscle tone (i.e., state of muscles at rest), but also dynamic characteristics of the condition of the muscle. This so-called reactivity, that is, the reflex response of muscles to mechanical stimulation of the manual — palpation.
A similar response of muscle can be compared with the feedback channel, a signal of the subconscious about the acceptability/unacceptability of this bodily contact. If the tone of the muscle and its reactivity correspond to the median range of the conditional scale (range rules), it is considered that this muscle is in a resourceful state. Otherwise, its status is regarded as a deviation from the norm, respectively, Hypo - or Hyper-reactivity.
Comparison with the scheme of age psychomotor development suggests, at what age did the traumatic situation that affect the state of the muscles. Psychological trauma transferred during a critical period of development of age or even more at an early age, is manifest in hypotonia (giperaktivnosti) of the respective muscles. If the trauma occurred at an older age, the outcome is a hypertonia (Hyper-reactivity).
How your body tells you what you really want
Do not like the outcome — change their behavior
Unlike Rakovskovo approach biodynamically analysis refuses to forcible remove the "muscular armor" in order not to leave the patient defenseless. Instead, it is proposed to teach the patient awareness of the presence of their own "shell" in different situations, as a method of control of emotions and access to internal resources.
In the end, along with restoration resource status of the relevant muscles, this leads to a strengthening or "awakening" the bodily Ego, the harmonizing of the functions which is the main goal of the psycho-correction work.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: ishchenko.pro/mirra/psixologicheskie-funkcii-myshc/
Let's start with the fact that in classical psychoanalysis indicator of mental health is the power of Ego, and the goal of therapy is education of the Mature Ego.
Thirty six million two hundred forty four thousand eight
Similarly in bodynamics analysis introduces the concept of the bodily Ego, the functions of which are:
- thinking;
- emotional control;
- position in life (beliefs and patterns of behavior);
- the balance of "I" (inner psychological balance between "I" and "others" between the senses and the mind);
- zooming in/out (external balance in relations with people);
- relationships with other people;
- centering (self-esteem);
- grounding and reality testing;
- the formation boundaries (assertive);
- selfexpression.
The term "biodynamically" (bodynamic) formed from the merger of two roots: body (body) + change (dynamics). Thus, we can decode it as "bodydynamics" analysis or the analysis of bodily development.
The method is based are representations of psychology of development of age, the anatomy and physiology of the neuromuscular system that describes the dynamics of the bodily development of the child its parallelism with the development of personality. The method developed by the Danish therapist L. Marcher (Lisbeth Marcher), a follower of V. Raich, relying on his idea of "muscular armour»
The representation of the corporeality of the Ego, assault and "binding" of certain personal qualities is derived and metaphorical representation of psychological functions of individual muscles or muscle groups that lie at the basis of corporal-psychic unity.
If this view is recognized correct, and that's just the opposite: through the normalization of the status of muscles can be carried out correction of psychological problems (principle of feedback.) Recognition of the status of individual muscles can be used to diagnose psychological problems.
L. Marcher approached the description of the formation of the structure of nature on the physical level as an integral part of psychomotor developmentI, but on a psychological level — as a naturally developing in time sequence alternative choices (see table. 2) that forms the structure of personality. Appropriate that most General elections are private personal properties as would get recorded in the muscles (see table. 1).
Table 1. Metaphorical psychological muscle function by L. Marcher Muscle groupPsychological muscle functionHead, neck
Facial muscles in General
The expression of feelings, social contacts
The muscles around the eyes the Focus of attention and short-term planning
The muscles of the mouth and tongue
Emotional acceptance of the Muscles in the front of the neck
Verbal expression the muscles of the back of the neck
Will power, pride, orientation in the circumstances
Shoulder girdle and arms
Extensors and flexors of the shoulder, and muscles, leading and outlet-shoulder
Personal space in relationships
The muscle lifting the shoulder
The ability to carry psychological "wear»
Rotator cuff self-Defense and the ability to accept support from others
Extensors of the forearm Repulsion, retention on the course
Flexors of the forearm the Attraction and retention of the Rotators of the forearm to Take and give the Flexors and extensors of the wrist
Positioning or social behavior monitoring
Muscle that opposes the thumb and little finger
The heightened awareness; writing
The extensors of the fingers a Thin device (change of borders); the ability "to let go of»
The flexors of the fingers Touch, learning and retention; the ability to take and give
Body Muscles of the anterior region of the thorax (large and small pectoral and serratus anterior muscles)
The feeling of self-worth and personal power (as in superficial and in deep contact)
Intercostals (primary muscles of respiration)
The feeling of fullness of being, "breathing space»
The diaphragm (secondary to respiratory muscle); the superficial muscles of the abdomen
Emotional self-control; hold and "digesting" emotions
Large and small psoas muscles
Intimate attachment of the Extensors of the torso (spine)
The ability to withstand emotional and physical stressors
Square muscle of a loin
The balance between a focus on their own feelings or the emotions of others
Pelvic floor muscles Sexual feelings Feet The hip flexors to Initiate the movement forward and psychological contact
Extensors of thigh-Assertion, the ability to "stand your ground»
Rotators of thigh Sexy-sensuous-perception
Muscles resulting a hip, Intimate and sensual contact
The extensor tibiae Personal boundaries in relationships
The flexors of the tibia select the direction and control of the movement forward
Peroneal muscle Personal balance in the group interaction
Extensors of foot and toes
Contact with reality Flexors of the foot self-Assertion, the ability "to stand on their own feet»
The flexors of the fingers a Sense of contact with the ground
Biodynamically analysis has made significant additions in raykovska ideas about the structure of nature and "muscular armor." In body psychotherapy the character structure was originally understood essentially as a set of unconscious, irrational behaviors in stressful situations — a set that is formed by each person from an early age (just playing childhood experiences and relate elements of irrationality).
Thus formed largely spontaneously, under the circumstances, (specify: perhaps, by imitating others). A set of typical psychological protection is, according to Reich, "character armor" and their reflection in the form of increased muscle tone "muscular armor."
Twenty million seven hundred forty nine thousand three hundred forty
Thus, according to L. Marcher, in the process of development of various muscle groups "ripen" at different times. Psychomotor development is a progressive "maturation" of certain muscles (and development of related movements).
Under the "maturation" refers to the achievement of such maturity of the neuromuscular apparatus, which makes the activity of this muscle was fully available to conscious control. The transition of the muscles in the "Mature" state is associated with a particular age period, and restricted to a fairly narrow time frame. This so-called critical or sensitive period of development, which is also associated with a lasting experience of the situation of primary teaching (imprint).
When the child faces stressful situations, there are two problems.
First, impaired psychomotor development, partial delay at this age stage (physical analogue of the Freudian fixation). At first, she has to play a protective role, but later became a brake on further development, the basis of an inferiority complex.
Second, emerging imprint usually contains biographical scenes, intense traumatic experiences. Although these memories and undergo displacement, but due to the fact that such protection is not absolute, they create a kind of "Achilles ' heel", the islets of increased psychological vulnerability in the personality structure. Associated with the "problem" muscles kinesthetic sensations partially are displaced, become unavailable to consciousness.
Table 2. The age periodization of psychological development of L. Marcher Stage of developmentAge limitPsychological content The existence of the Prenatal period and up to 3 months after birth
The relationship with the mother Demand From 1 month to 1.5 years is the Internalization of feelings of care from others to meet their needs
Autonomy From 8 months to 2.5 years of Independent movement and communication with others
Will From 2 to 4 years Ability to achieve goals and influence others
Love From 3 to 6 years the Ability to maintain cordial relations
Forming opinions From 5 to 8 years the Development of logical thinking, ability to make decisions based on the norms of culture
Collectivism From 7 to 12 years to be a member of a group/society
This implies two tasks physical therapy. Tactical task is the identification of muscular "blocks"; the problem is strategic, based on eliminating these "blocks" is development missing of bodily and psychological resources. The initial step in working with the patient is physical diagnostic procedure — preparation of individual muscle maps.
When such mapping is the study of about 200 muscles. Thus, unlike traditional physical therapy, we analyze not only static mechanical characteristics — muscle tone (i.e., state of muscles at rest), but also dynamic characteristics of the condition of the muscle. This so-called reactivity, that is, the reflex response of muscles to mechanical stimulation of the manual — palpation.
A similar response of muscle can be compared with the feedback channel, a signal of the subconscious about the acceptability/unacceptability of this bodily contact. If the tone of the muscle and its reactivity correspond to the median range of the conditional scale (range rules), it is considered that this muscle is in a resourceful state. Otherwise, its status is regarded as a deviation from the norm, respectively, Hypo - or Hyper-reactivity.
Comparison with the scheme of age psychomotor development suggests, at what age did the traumatic situation that affect the state of the muscles. Psychological trauma transferred during a critical period of development of age or even more at an early age, is manifest in hypotonia (giperaktivnosti) of the respective muscles. If the trauma occurred at an older age, the outcome is a hypertonia (Hyper-reactivity).
How your body tells you what you really want
Do not like the outcome — change their behavior
Unlike Rakovskovo approach biodynamically analysis refuses to forcible remove the "muscular armor" in order not to leave the patient defenseless. Instead, it is proposed to teach the patient awareness of the presence of their own "shell" in different situations, as a method of control of emotions and access to internal resources.
In the end, along with restoration resource status of the relevant muscles, this leads to a strengthening or "awakening" the bodily Ego, the harmonizing of the functions which is the main goal of the psycho-correction work.
P. S. And remember, only by changing their consumption — together we change the world! ©
Source: ishchenko.pro/mirra/psixologicheskie-funkcii-myshc/