638
Neuroscientists have learned to control neurons using ultrasound

Neuroscientists at the Institute of Biological Research im.Salka (California, USA) представили new technique selective stimulation of neurons called sonogenetika. In a работе they claim to have received the opportunity to activate the neurons noninvasively by ultrasound.
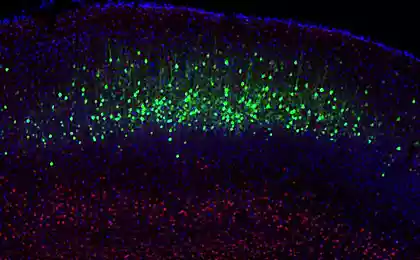
To study the biology of the brain several years ago developed a scheme incorporating relevant neurons with light. The cage came up to introduce the sodium channel gene responsive to photons. If you shine a cell in it are beginning to enter the sodium ions, which excites the neuron. However, with the reassurance of neurons has not yet learned how to cope - to calm the cells release potassium ions to the outside, but there are light-controlled channels in nature have not yet been found.
This invention immediately moved forward neurobiology. Scientists rushed to mice and hastily began to put one experiment after another, knowing the structure of the brain. They were able to track the process of memory formation, switch on and off pain receptors, simulate the effects of drugs and even turn on and off an erection. However, all these studies were carried out so far only in mice. After all, the main problem of this method - the need prodelyvat canal in the skull and the brain to supply optics.
The inventor of the technology sonogenetiki, Shrikant Chalasani , an assistant professor in the Laboratory of Molecular Neurobiology, says that his proposed ultrasonic method is able to activate dates neurons. Thus ultrasound penetrates through the skin and the skull bone without affecting any other cells in the body.
"We believe that the use of ultrasound for non-invasive activation of neurons can be widely used for decoding of neural pathways in the brain, enclosed in unbroken shell of the skull and the skin».
Another claimed advantage of technology is the ability of activation of different groups of neurons, since the possibility of changing the frequency of the sound exceeds the range of wavelengths of light to which neurons react in optogenetics.
To use this technology also requires the addition of an additional gene in a cell. The researchers found that the protein TRP-4, found in nature in invertebrates, sensitive to ultrasound. Adding this protein with the help of the virus in the organism popular with researchers worms-nematodes C. Elegans, the scientists were able to create some neurons are sensitive to ultrasound. For example, in one experiment, the worm was able to make the turn, giving certain ultrasonic pulses.
Although TRP-4 protein is not found in mice and humans, it does not mean that the new technology is useless for us - scientists claim that by adding the corresponding genes cause cells to produce this protein.
In this regard, while the use of technology on vertebrate animals and man only hypothetical. Furthermore, since the light travels faster than sound, and the processes in the human brain occur fast enough control neurons not be possible for all processes. Rather, it implies Chalasani technology sonogenetiki optogenetics and will complement each other.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/262618/