NASA experiencing an acute shortage of plutonium-238 power supplies SC
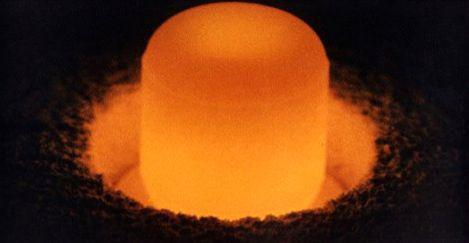
Isotope Pu-238 has an intensity of spontaneous fission of 1.1x106 divisions / s * kg (specific radioactivity of 17.5 Ci / g - that is 2.6 times more Pu-240) and very high thermal capacity: 567 W / kg. Strong neutron radiation and heating make it very inconvenient for handling and this limits its use mainly in the power supply. As weapons-grade plutonium is used Pu-239.
US used the РИТЭГи Plutonium-238 24 spacecraft. Among the machines, "eat" plutonium-238 are American "Voyager", launched in 1977 to Jupiter and Saturn, and has reached the edge of the solar system. Plutonium is used in near-Earth satellites and the Apollo program. Had to use a power source and « Mars 96 a >> (270 grams of plutonium for heating and power of the Russian rover).

Plutonium power sources used in other spacecraft for deep space exploration, where the use of solar panels is difficult or impossible:
SC "Galileo" orbiting Jupiter took 15, 6 kg of plutonium-238. spacecraft "Cassini" working on the orbit of Saturn is 32, 7 kg of plutonium-238. SC "New Horizons", flying up now to Pluto, has on board 10, 9 kg of plutonium-238. The rover «Curiosity» receives the necessary energy from the 4, 8 kg of plutonium-238 ul>.
In the US in 1988 was discontinued production of plutonium-238, and has since been used accumulated reserves. In 1992, the United States signed a five-year contract for the purchase of the isotope in Russia in the amount of 10 kg and the possibility of increasing the supply of not more than 40 kg. Contract extended several times until the middle of December 2009, Russia has notified the United States would not be able to deliver in the next two years and 10 kg of plutonium-238 for power supply spacecraft. Russia insisted to renew the contract of purchase for the new conditions.
In 2009, the National Research Council (NRC), a report recommending to resume production of plutonium-238 in order to avoid delay or complete abolition of future scientific missions.
Despite the relatively small amount of 75-150 million dollars needed to restore production, a difficult budget situation in the US and bureaucratic features of the American state mechanism buried for several years starting work to restore the production of isotopes. As usual in the United States in such situations, stakeholders and organizations have advocated "dirty linen in public" in public, calling for patriotism and involving lobbying politicians:
«I believe that the subcommittee, controls the budget of the Ministry of Energy, there are people who are opposed to the resumption of production of plutonium-238, - told Space.com Alan Stern. - They have the power to prevent it, they are already doing very effectively for a number of years. We need to turn to Russian, to get to the space station, we can not explore the moon as in the days when I was a boy, and now will lose the ability to explore the solar system to its very limits. This weakens the United States, and nothing but a deep sense of frustration can cause. Need to openly reveal the names of those people who are blocking the resumption of production of plutonium-238. This - antipatriots. " Blockquote>
In 2012, after several attempts, the Obama administration managed to push through the Congress to restore funding for the production of plutonium-238, provided that NASA will pay for repair aging infrastructure at the Los Alamos National Laboratory in New Mexico. After the repair the Department of Energy will start to produce 1, 5 kilograms of plutonium-238 in a year. This would bring the remaining 18 kg of plutonium to the required level of heat for use in MMRTG. Even if the production of plutonium not immediately released to the planned 1, 5 kg per year, enough plutonium stocks for the next decade. While NASA is planning only one mission using plutonium - , project identical rover «Curiosity». The plans for the remaining plutonium is not yet known. NASA is necessary to plan the expansion of production required isotope and also revive closed in 2013, the project , which produces 140 watts using 4 times less plutonium than it should be to get the same power with the help of MMRTG.
Sources i>:
li > - article found after publication, I recommend.
Source: