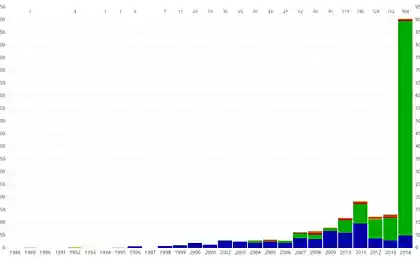
1086
Perhaps the opening of the first exo-uranium
Employees of the State of Ohio University утверждают, that they were the first to discover uranopodobnuyu planets orbiting a distant star.
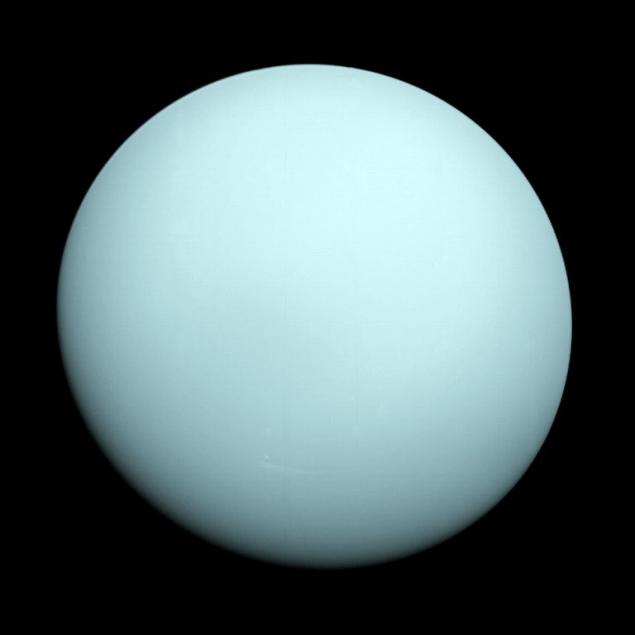

In our solar system, there are three main types of planets with a solid surface (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars), gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn), as well as the planet, except for gas containing methane and also ice (Uranus and Neptune). Previously discovered exoplanets belong to one of the first two types.
The newly discovered planet is massive enough, and while orbiting, the radius of which is close to the radius of the orbit of Uranus. Thus, astronomers have concluded that it should, and in its composition to be similar to Uranus.
The first exo-uranium was discovered by gravitational microlensing. This effect occurs at the moment of crossing the sky trajectories of the two stars. Then the closer one focuses the light from more distant because of the curvature of space caused by the gravitational influence, according to Einstein's relativity theory.
If the star is drawn around the focusing sufficiently massive planet, then because of its rotation apparent brightness of a distant star varies periodically. This change can be detected and calculate the mass of the planet for them, and the radius of its orbit. Interestingly, for the object OGLE-2008-BLG-092L, is a double star, the effect of gravitational microlensing observed twice - in 2008 and 2010. From these data and able to determine the presence in the system also massive and third companion - exo desired uranium. It should be noted that the exo-urany currently can only be opened by this method.
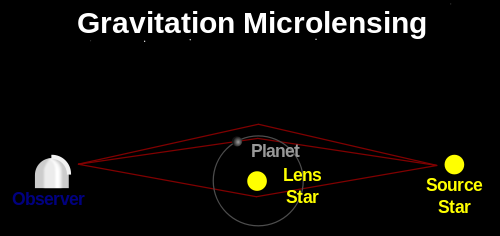
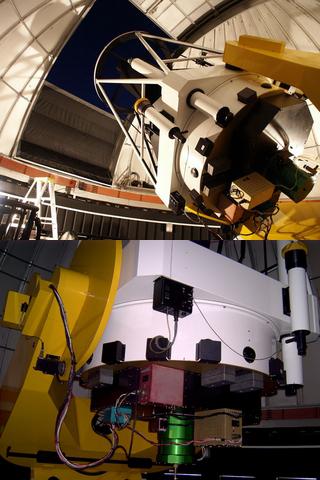
Observation was performed using 1, 3-meter Warsaw Telescope , set in the Chilean Las Campanas Observatory in the framework of Project Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment i> (OGLE) .
The results of the published in the journal The Astrophysical Journal i>.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/240350/

In our solar system, there are three main types of planets with a solid surface (Mercury, Venus, Earth and Mars), gas giants (Jupiter and Saturn), as well as the planet, except for gas containing methane and also ice (Uranus and Neptune). Previously discovered exoplanets belong to one of the first two types.
The newly discovered planet is massive enough, and while orbiting, the radius of which is close to the radius of the orbit of Uranus. Thus, astronomers have concluded that it should, and in its composition to be similar to Uranus.
The first exo-uranium was discovered by gravitational microlensing. This effect occurs at the moment of crossing the sky trajectories of the two stars. Then the closer one focuses the light from more distant because of the curvature of space caused by the gravitational influence, according to Einstein's relativity theory.
If the star is drawn around the focusing sufficiently massive planet, then because of its rotation apparent brightness of a distant star varies periodically. This change can be detected and calculate the mass of the planet for them, and the radius of its orbit. Interestingly, for the object OGLE-2008-BLG-092L, is a double star, the effect of gravitational microlensing observed twice - in 2008 and 2010. From these data and able to determine the presence in the system also massive and third companion - exo desired uranium. It should be noted that the exo-urany currently can only be opened by this method.

Observation was performed using 1, 3-meter Warsaw Telescope , set in the Chilean Las Campanas Observatory in the framework of Project Optical Gravitational Lensing Experiment i> (OGLE) .

The results of the published in the journal The Astrophysical Journal i>.
Source: geektimes.ru/post/240350/