1214
In NASA tested the prototype laser drilling of ice in Europe, Jupiter's moon

A few days ago, NASA is in the field to test it out laser drilling (melting) ice. Such a system is likely to be used by the research unit, drone, sent to Europe, a satellite of Jupiter.
The system is called VALKYRIE (link - technical description of the system, pdf). The tests were conducted in Alaska, Glacier Matanuska.
way, flight to Europe closer in time than many think. In the next year NASA receives 15 million on research and development program to create a robot podlednika for Europe. The mission itself can be carried out using a new ship-heavyweight Space Launch System , first run (test) which is scheduled for 2017.
This system is able to reduce the time required for the flight from Earth to Jupiter, with six years to two. Whatever it was, unmanned expedition to Europe, Jupiter's moon, can be carried out already in 2022. However, the first device running on Europe, descend to the surface of Jupiter's moon will not. Most likely, it will be an orbiter that will learn a lot about Europe itself, an endogenous and exogenous processes of the cosmic body.
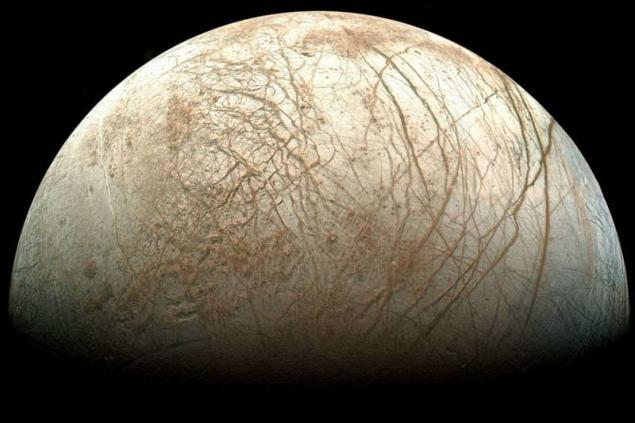
I think everybody has heard that scientists suggest the presence in the European ice-ocean that lies deep under the ice, and that may well be inhabited (at least inhabited by microorganisms, and it's good). In 1979, suspicions about the possible presence of water beneath the ice called "Voyager 2", which flew past, made high-quality images of Europa's surface. It turned out that the ice is very small impact craters, much less than it should be. Scientists have suggested that the reason for it - liquid water, which is pouring on the surface of Europa, and freezing again, closes holes in the ice armor.
Suspicions confirmed «Galileo», to get even more high-quality images of Europe in 1999. The picture shows that the ice on Europa's surface is covered with cracks, where, in fact, possible ingress of water on the surface.
In general, the idea of an expedition to Europe matures and develops slowly starting to be realized.
Back to our laser driller. This system is called Cryobot, and it should be noted that this is - is not the first Cryobot, designed by scientists. One of the most successful was Cryobot NASA designed in the laboratory in 2001. Then the machine drilled a hole in the glacier, Svalbard (Norway), depth of 23 meters.
Early projects Cryobot were not very realistic as a result of a "small" problem. Ice thickness in Europe may be about 30 kilometers, and the energy of any, even the most capacious battery is not enough to drill a little, at least part of this column. But there is a solution: a small supply of nuclear fuel. It was such a source will be installed at Cryobot VALKYRIE.
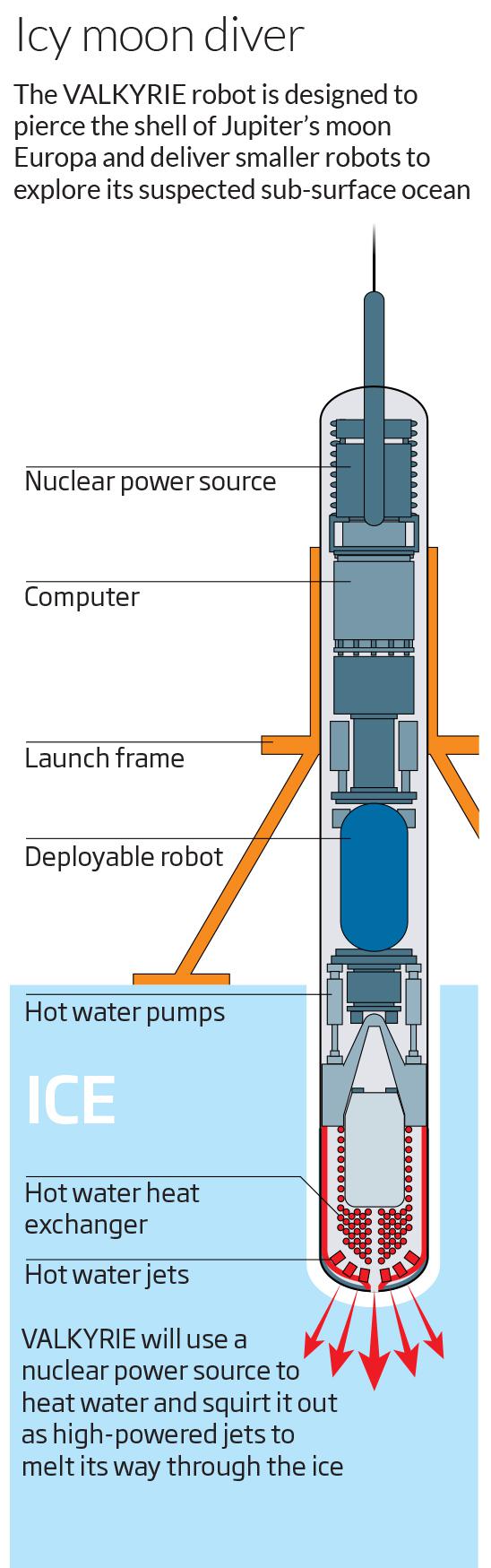
On Earth, the test device with the power supply is prohibited, so scientists have found another way out.
Apparatus equipped with a system based on optical fiber through which the laser power of 5000 watts. The size of the device: 1, 6 meters in length and 0 to 45 m - wide. ROP ice is about three feet per hour. Of course, Cryobot to be sent to Europe to be more powerful and more. The test model was able to drill the ice to a depth of 30 meters, which is the current record among Cryobot.
Model, which will be sent to Europe, will be equipped with more sensors and systems, allows you to "find" the obstacles in the ice, so that their rounded Cryobot (because the ice can be frozen boulders that the laser current power simply not control).
Development is conducted in such a way that the full model Cryobot could introduce another robot, and dive under the ice Europe after VALKYRIE drill thickness of the ice.
The following year, the system will be tested on said glacier, and it will be updated VALKYRIE, with 3D-radar and biochemical small "laboratory" on the board, which checks for life in the water under the ice.
The last test VALKYRIE in the world - an attempt to drill 3km thickness of ice on one of the lakes of the South Pole.
Via newscientist
Source: habrahabr.ru/post/231399/
At Stanford figured out how to increase the capacity of lithium-ion batteries in 3-4 times using carbon nanospheres
Smart home in the US Honda is ready for testing