1075
Commonwealth of fauna and flora
Figs sweet, helpful, and yes bad chews contains recycled remains of dead wasps. As the wasp got there? And why, if it is known, all still continue to eat it? The strange truth is related to reproduction.
Continued under the cut ...
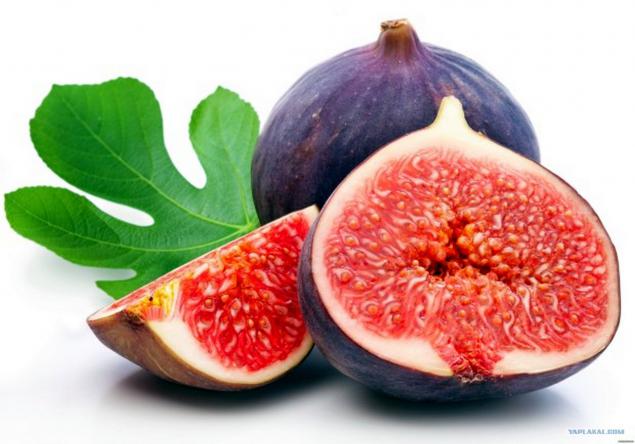

All relationships of fig wasps and reduced to the fact that neither the one nor the other, are not good replicators, and they just found an unusual way to help each other. Figs - it actually turned inside flower known as sikonium. But because of its structure, most pollinating insects just can not get to the pollen. Fortunately, there is one insect, fig wasp, which knows how to get to sikoniumu and pollinate the plant. Unfortunately for Microsoft, this one-way trip.
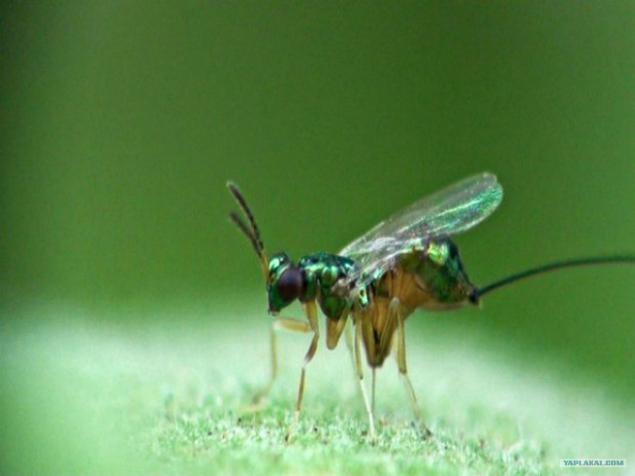
Wasps need the specific environment in which they grow and feed on the larvae. It just so happens that the inner part of figs - perfect for baby wasps. Therefore, the female wasp gets inside through a tiny passageway figs. The only problem is that this passage is so narrow that they are on the road to lose their wings and antennae, so then they can not get out. Nevertheless, this is a dangerous mission allows the wasps to reach the ideal place to lay eggs.
But as figs pollinated if the wasps can get only one flower and stay there? After the eggs hatch, there will be many males and females wasps. After mating, the males spend their brief existence, digging tunnels in figs, whereas the females have an escape route after their full development. When they fly, they remain a bit of pollen, which they transferred to another flower - and pollinated figs.
It turns out that, along with figs we eat the remains of the female wasps and their male offspring? Not quite: in figs have an enzyme called ficin, splitting the dead wasps on the protein, which becomes part of the mature fruit. In fact the whole body wasps in figs remains. And it crispy parts - the seeds, not the remains of wasps.
Source

Continued under the cut ...

All relationships of fig wasps and reduced to the fact that neither the one nor the other, are not good replicators, and they just found an unusual way to help each other. Figs - it actually turned inside flower known as sikonium. But because of its structure, most pollinating insects just can not get to the pollen. Fortunately, there is one insect, fig wasp, which knows how to get to sikoniumu and pollinate the plant. Unfortunately for Microsoft, this one-way trip.
Wasps need the specific environment in which they grow and feed on the larvae. It just so happens that the inner part of figs - perfect for baby wasps. Therefore, the female wasp gets inside through a tiny passageway figs. The only problem is that this passage is so narrow that they are on the road to lose their wings and antennae, so then they can not get out. Nevertheless, this is a dangerous mission allows the wasps to reach the ideal place to lay eggs.
But as figs pollinated if the wasps can get only one flower and stay there? After the eggs hatch, there will be many males and females wasps. After mating, the males spend their brief existence, digging tunnels in figs, whereas the females have an escape route after their full development. When they fly, they remain a bit of pollen, which they transferred to another flower - and pollinated figs.
It turns out that, along with figs we eat the remains of the female wasps and their male offspring? Not quite: in figs have an enzyme called ficin, splitting the dead wasps on the protein, which becomes part of the mature fruit. In fact the whole body wasps in figs remains. And it crispy parts - the seeds, not the remains of wasps.
Source